Lesson Contents
In the first lesson about DMVPN we discussed the basics of multipoint GRE and NHRP. The second lesson was a basic configuration of DMVPN phase 1. This time i’ll explain how you can configure DMVPN phase 2. Once we have a basic configuration then we can try to run RIP, EIGRP, OSPF and BGP on top of it.
The configuration of DMVPN phase 1 and 2 is similar except for two key items:
- The spoke routers will now use multipoint GRE interfaces instead of point-to-point GRE interfaces.
- We don’t configure a manual destination anymore on the spoke routers.
That’s it, those two changes make the difference between running DMVPN phase 1 or 2. Let’s take a look at the configuration. Here’s the topology we will use:
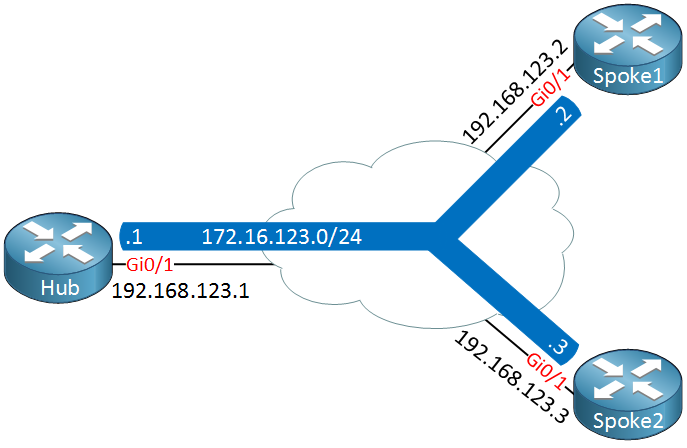
Above we have one hub router and two spoke routers. We use 192.168.123.0/24 as the underlay network and 172.16.123.0/24 as the overlay network.
Configuration
Let’s start with the hub configuration:
Hub(config)#interface Tunnel0
Hub(config-if)#ip address 172.16.123.1 255.255.255.0
Hub(config-if)#ip nhrp authentication DMVPN
Hub(config-if)#ip nhrp map multicast dynamic
Hub(config-if)#ip nhrp network-id 1
Hub(config-if)#tunnel source GigabitEthernet0/1
Hub(config-if)#tunnel mode gre multipoint
Hub(config-if)#endThe configuration of the hub above is exactly the same as in DMVPN phase 1, no changes here. Let’s look at the spoke routers:
Spoke1(config)#interface Tunnel0
Spoke1(config-if)#ip address 172.16.123.2 255.255.255.0
Spoke1(config-if)#ip nhrp authentication DMVPN
Spoke1(config-if)#ip nhrp map 172.16.123.1 192.168.123.1
Spoke1(config-if)#ip nhrp map multicast 192.168.123.1
Spoke1(config-if)#ip nhrp network-id 1
Spoke1(config-if)#ip nhrp nhs 172.16.123.1
Spoke1(config-if)#tunnel source GigabitEthernet0/1
Spoke1(config-if)#tunnel mode gre multipointSpoke2(config)#interface Tunnel0
Spoke2(config-if)#ip address 172.16.123.3 255.255.255.0
Spoke2(config-if)#ip nhrp authentication DMVPN
Spoke2(config-if)#ip nhrp map 172.16.123.1 192.168.123.1
Spoke2(config-if)#ip nhrp map multicast 192.168.123.1
Spoke2(config-if)#ip nhrp network-id 1
Spoke2(config-if)#ip nhrp nhs 172.16.123.1
Spoke2(config-if)#tunnel source GigabitEthernet0/1
Spoke2(config-if)#tunnel mode gre multipointThe configuration above is exactly the same as in DMVPN phase 1 except for two commands:
- We removed the tunnel destination command.
- We added the tunnel mode command to use GRE multipoint.
That’s it! We now have a DMVPN phase 2 network. Let’s verify our work…
Verification
First we should check if the hub has received some NHRP registrations from the spoke routers:
Hub#show dmvpn
Legend: Attrb --> S - Static, D - Dynamic, I - Incomplete
N - NATed, L - Local, X - No Socket
T1 - Route Installed, T2 - Nexthop-override
C - CTS Capable
# Ent --> Number of NHRP entries with same NBMA peer
NHS Status: E --> Expecting Replies, R --> Responding, W --> Waiting
UpDn Time --> Up or Down Time for a Tunnel
==========================================================================
Interface: Tunnel0, IPv4 NHRP Details
Type:Hub, NHRP Peers:2,
# Ent Peer NBMA Addr Peer Tunnel Add State UpDn Tm Attrb
----- --------------- --------------- ----- -------- -----
1 192.168.123.2 172.16.123.2 UP 00:09:48 D
1 192.168.123.3 172.16.123.3 UP 00:09:56 DAbove we see two registrations with the NBMA and tunnel addresses of our spoke routers. Let’s use the same command on the spoke routers:



Thanks for the good explanation Rene. I am using Cisco 7200 with IOS version 12.4(24g) but
show dmvpncommand is not working. Other configuration commands to setup DMVPN worked.Hello Abhishek
It seems that this command is not available in your IOS version. You can see from the following Cisco CLI reference, that the command was introduced in the T train of code and not in the mainline which is your IOS version.
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/ios-xml/ios/security/s1/sec-s1-cr-book/sec-cr-s4.html#wp2815505246
Even so, this is simply a show command that conveniently displays the components of the topology. You can still obtain the same information with a variety of other show commands such as those indicated in the following Cis
... Continue reading in our forumHello Rene
Hope you doing great.
On
show dmvpnoutput I see Attrb → S for Spokes routers meaning that the NBMA peer Address is learned Statically.Shouldn’t be Attrb → S like the Hub router?
Thank you in advance!
Regards,
Victor
Hello Victor
When you use DMVPN with NHRP in the configuration found in the lesson, on each spoke you use the following command:
ip nhrp map <tunnel address> <hub NBMA address>This creates a static peer address, and that’s why you see the “S” indicator on the spoke router. This is considered a statically configured NBMA peer address.
On the hub, however, you have no such configuration. The hub is configured to accept NHRP requests to dynamically add the addresses of the spokes. For this reason, on the Hub, you will see the “D” designation that these are dyn
... Continue reading in our forumHi Laz,
Please explain the commands by taking example of IPs we used in n/w topology for DMVPN.
- ip nhrp map 172.16.123.1 192.168.123.1
- ip nhrp map multicast 192.168.123.1
- diff b/w ip nhrp map multicast dynamic and ip nhrp map multicast
- ip nhrp mode multipoint command instead of tunnel destination address.
... Continue reading in our forum3)ip nhrp nhs 172.16.123.1 ( why are we using tunnel address here, it should be
public ip)
192.168.123.1
we know tunnel destination command is being used to specify destination
address but multipoint mean it can be both source and destination ip. so how
can w