Lesson Contents
When you use the BGP aggregate-address command on Cisco IOS without any parameters, then all information of individual route attributes such as AS_PATH is lost.
This can cause issues since the AS_PATH is used for loop prevention. For example, it’s possible that an AS installs a summary that it shouldn’t. With the AS-SET parameter, you can optionally include AS information in the summary. In this lesson, I’ll show you how to do this.
Configuration
Here is the topology we’ll use:
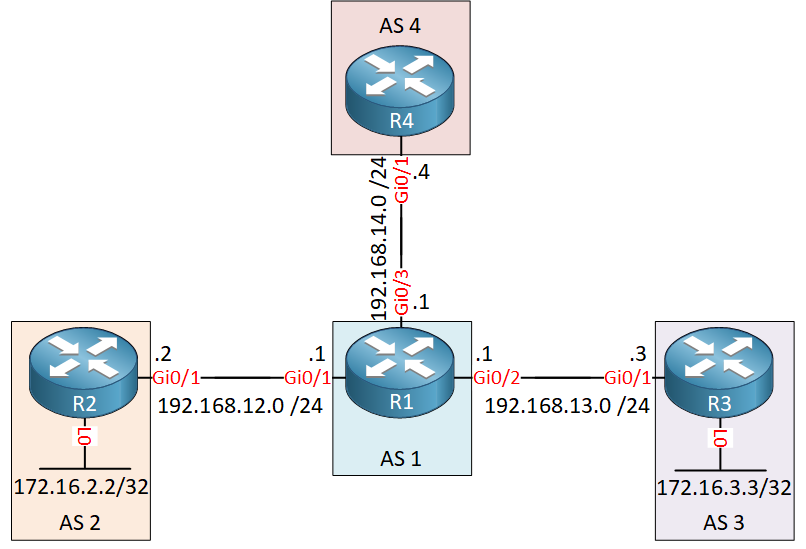
We have four routers, all in a different AS. R2 and R3 have a loopback with an IP address that are advertised in BGP. R1 will send an aggregate to R4.
Configurations
Want to take a look for yourself? Here you will find the startup configuration of each device.
R1
hostname R1
!
ip cef
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
ip address 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.0
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/2
ip address 192.168.13.1 255.255.255.0
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/3
ip address 192.168.14.1 255.255.255.0
!
router bgp 1
neighbor 192.168.12.2 remote-as 2
neighbor 192.168.13.3 remote-as 3
neighbor 192.168.14.4 remote-as 4
!
endR2
hostname R2
!
ip cef
!
interface Loopback0
ip address 172.16.2.2 255.255.255.255
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
ip address 192.168.12.2 255.255.255.0
!
router bgp 2
network 172.16.2.2 mask 255.255.255.255
neighbor 192.168.12.1 remote-as 1
!
endR3
hostname R3
!
ip cef
!
interface Loopback0
ip address 172.16.3.3 255.255.255.255
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
ip address 192.168.13.3 255.255.255.0
!
router bgp 3
network 172.16.3.3 mask 255.255.255.255
neighbor 192.168.13.1 remote-as 1
!
endR4
hostname R4
!
ip cef
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
ip address 192.168.14.4 255.255.255.0
!
router bgp 4
neighbor 192.168.14.1 remote-as 1
!
endRight now, there is no aggregate so R4 sees two separate prefixes with the correct AS path information:
R4#show ip bgp
BGP table version is 3, local router ID is 192.168.14.4
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, f RT-Filter,
x best-external, a additional-path, c RIB-compressed,
t secondary path,
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 172.16.2.2/32 192.168.14.1 0 1 2 i
*> 172.16.3.3/32 192.168.14.1 0 1 3 iEach prefix has the correct AS path.
Without AS-SET
Let’s create a summary/aggregate. We’ll start without the AS-SET parameter so that we have a before and after example:
R1(config)#router bgp 1
R1(config-router)#aggregate-address 172.16.0.0 255.255.0.0 summary-onlyHere’s what we get on R4:
R4#show ip bgp
BGP table version is 10, local router ID is 192.168.14.4
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, f RT-Filter,
x best-external, a additional-path, c RIB-compressed,
t secondary path,
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 172.16.0.0 192.168.14.1 0 0 1 iWe see the 172.16.0.0/16 prefix but all AS path information is lost. This prefix seems to come from AS 1 only.
If R4 was connected to R2 or R3 then those routers would install this prefix without hesitation since they don’t see their own AS number in the summary route. This could cause routing loops.
With AS-SET
Let’s add the as-set parameter on R1 now:
R1(config)#router bgp 1
R1(config-router)#aggregate-address 172.16.0.0 255.255.0.0 summary-only as-setHere’s what we get on R4:



Hi Rene,
Just to be confirm , If we put the command
aggregate-address 172.16.0.0 255.255.0.0 summary-only as-seton R1 then R2/R3 also get the prefix & discard based on as path , right ?Thanksbr//zaman
Hi Zaman,
If you add
as-setthen the AS numbers of the prefixes are included so if there is a link between R2/R4 and R3/R4 and they receive this aggregate, they will drop it because they see their own AS number yes.Rene
Dear Rene,
If we set community for the aggregate-address and send this to eBGP speaker, on eBGP speaker can we see community for this aggregate-address.
//BR
Waqar
Hi Rene
is there a incorrect that is the As name.
where is the AS 3 ,in my opinion R3 will be in the AS 3
Hello Bahri
Thanks for catching that! I’ve informed Rene and he will fix it.
Thanks again!
Laz