Lesson Contents
IS-IS supports summarization but since it is a link-state routing protocol, you can’t do this within an area as the link-state database have to be the same on all routers within the area. You can only configure summarization on a “border”. That would be an area border router or a router that is doing redistribution..
In this lesson, I’ll walk you through both options.
Configuration
This is the topology we will use:
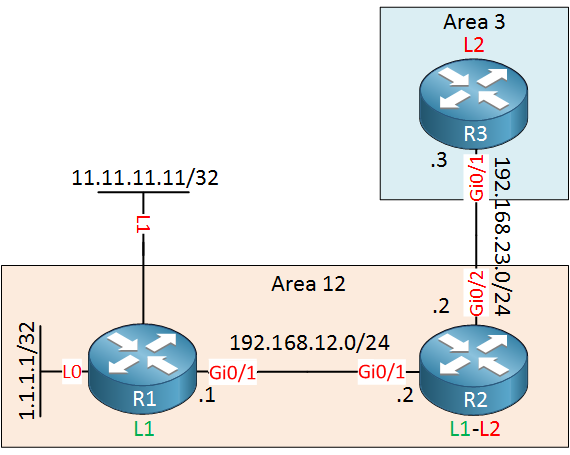
Above we have R1 and R2 in area 12. R3 is in area 3. On R1 we have two loopback interfaces. Loopback 0 will be advertised in IS-IS, loopback 1 will be redistributed. I will show you how to summarize both routes.
Configurations
Want to take a look for yourself? Here you will find the startup configuration of each device.
R1
hostname R1
!
ip cef
!
interface Loopback0
ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255
!
interface Loopback1
ip address 11.11.11.11 255.255.255.255
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
ip address 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.0
ip router isis
!
router isis
net 49.0012.0000.0000.0001.00
is-type level-1
log-adjacency-changes
!
endR2
hostname R2
!
ip cef
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
ip address 192.168.12.2 255.255.255.0
ip router isis
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/2
ip address 192.168.23.2 255.255.255.0
ip router isis
!
router isis
net 49.0012.0000.0000.0002.00
log-adjacency-changes
!
endR3
hostname R3
!
ip cef
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
ip address 192.168.23.3 255.255.255.0
ip router isis
!
router isis
net 49.0003.0000.0000.0003.00
log-adjacency-changes
!
endSummarization
Let’s get started. First, we enable IS-IS on the loopback 0 interface:
R1(config)#interface Loopback 0
R1(config-if)#ip router isisThis loopback has the 1.1.1.1/32 prefix which will show up on R2’s level 1 database:
R2#show isis database level-1 verbose R1.00-00
IS-IS Level-1 Link State Database:
LSPID LSP Seq Num LSP Checksum LSP Holdtime ATT/P/OL
R1.00-00 0x00000007 0x1252 1164 0/0/0
Area Address: 49.0012
NLPID: 0xCC
Hostname: R1
Metric: 10 IS R2.01
IP Address: 1.1.1.1
Metric: 10 IP 192.168.12.0 255.255.255.0
Metric: 10 IP 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255And it will be copied to R2’s level 2 database:
R2#show isis database level-2 verbose R2.00-00
IS-IS Level-2 Link State Database:
LSPID LSP Seq Num LSP Checksum LSP Holdtime ATT/P/OL
R2.00-00 * 0x00000007 0x5965 1146 0/0/0
Area Address: 49.0012
NLPID: 0xCC
Hostname: R2
Metric: 10 IS R2.02
IP Address: 192.168.23.2
Metric: 10 IP 192.168.12.0 255.255.255.0
Metric: 10 IP 192.168.23.0 255.255.255.0
Metric: 20 IP 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255This route will show up in the routing table of R2:
R2#show ip route isis
1.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
i L1 1.1.1.1 [115/20] via 192.168.12.1, 00:01:10, GigabitEthernet0/1Let’s see if we can summarize this route so that R3 receives a summary:
R2(config)#router isis
R2(config-router)#summary-address 1.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 ?
level-1 Summarize into level-1 area
level-1-2 Summarize into both area and sub-domain
level-2 Summarize into level-2 sub-domain
metric Set metric for summay route
tag Set tag
<cr>Let’s create a basic summary without specifying anything:
R2(config-router)#summary-address 1.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 Now let’s take a look how this influences R2’s database. Nothing will change in its level 1 database but the LSP in the level 2 database will change:
R2#show isis database level-2 verbose R2.00-00
IS-IS Level-2 LSP R2.00-00
LSPID LSP Seq Num LSP Checksum LSP Holdtime ATT/P/OL
R2.00-00 * 0x00000008 0x8D33 1135 0/0/0
Area Address: 49.0012
NLPID: 0xCC
Hostname: R2
Metric: 10 IS R2.02
IP Address: 192.168.23.2
Metric: 10 IP 192.168.12.0 255.255.255.0
Metric: 10 IP 192.168.23.0 255.255.255.0
Metric: 20 IP 1.0.0.0 255.0.0.0Above we see that R2 now shows 1.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 in its database. Let’s check its routing table:
R2#show ip route isis
Gateway of last resort is not set
1.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
i su 1.0.0.0/8 [115/20], 00:02:22, Null0
i L1 1.1.1.1/32 [115/20] via 192.168.12.1, 00:05:11, GigabitEthernet0/1R2 has created a discard route to null 0 for the 1.0.0.0/8 summary. Let’s take a look at R3 now:
R3#show isis database level-2 verbose R2.00-00
IS-IS Level-2 LSP R2.00-00
LSPID LSP Seq Num LSP Checksum LSP Holdtime ATT/P/OL
R2.00-00 0x00000008 0x8D33 1002 0/0/0
Area Address: 49.0012
NLPID: 0xCC
Hostname: R2
Metric: 10 IS R2.02
IP Address: 192.168.23.2
Metric: 10 IP 192.168.12.0 255.255.255.0
Metric: 10 IP 192.168.23.0 255.255.255.0
Metric: 20 IP 1.0.0.0 255.0.0.0R3 receives R2’s LSP with the summary route so that’s what it will install in its routing table:
R3#show ip route isis
i L2 1.0.0.0/8 [115/30] via 192.168.23.2, 00:03:29, GigabitEthernet0/1
i L2 192.168.12.0/24 [115/20] via 192.168.23.2, 00:36:20, GigabitEthernet0/1That’s all there is to it.
Redistribution Summarization
Now let’s see how we can summarize redistributed routes. I will redistribute the second loopback interface of R1 into IS-IS with a simple route-map:
R1(config)#route-map L1_ONLY
R1(config-route-map)#match interface Loopback 1
R1(config)#router isis
R1(config-router)#redistribute connected route-map L1_ONLY level-1Without summarization, here’s what the level 1 database looks like:
R2#show isis database level-1 verbose R1.00-00
IS-IS Level-1 LSP R1.00-00
LSPID LSP Seq Num LSP Checksum LSP Holdtime ATT/P/OL
R1.00-00 0x00000008 0xC75F 1180 0/0/0
Area Address: 49.0012
NLPID: 0xCC
Hostname: R1
Metric: 10 IS R2.01
IP Address: 1.1.1.1
Metric: 10 IP 192.168.12.0 255.255.255.0
Metric: 10 IP 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255
Metric: 0 IP-External 11.11.11.11 255.255.255.255R2 has installed this entry in its routing table:
R2#show ip route isis
1.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
i su 1.0.0.0/8 [115/20], 00:08:37, Null0
i L1 1.1.1.1/32 [115/20] via 192.168.12.1, 00:11:26, GigabitEthernet0/1
11.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
i L1 11.11.11.11 [115/10] via 192.168.12.1, 00:00:31, GigabitEthernet0/1Let’s summarize this redistribute route on R1. You can do this with the same summary-address command:
R1(config)#router isis
R1(config-router)#summary-address 11.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 level-1If you summarize into level 1, make sure you add the level-1 parameter or nothing will happen. Let’s check the routing table of R1:
R1#show ip route isis
i*L1 0.0.0.0/0 [115/10] via 192.168.12.2, 00:43:46, GigabitEthernet0/1
11.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
i su 11.0.0.0/8 [115/0], 00:00:39, Null0
i L1 192.168.23.0/24 [115/20] via 192.168.12.2, 00:44:13, GigabitEthernet0/1We can see that R1 has installed a discard route for this summary. Let’s check the level 1 database:
R2#show isis database level-1 verbose R1.00-00
IS-IS Level-1 LSP R1.00-00
LSPID LSP Seq Num LSP Checksum LSP Holdtime ATT/P/OL
R1.00-00 0x00000009 0xD76F 1139 0/0/0
Area Address: 49.0012
NLPID: 0xCC
Hostname: R1
Metric: 10 IS R2.01
IP Address: 1.1.1.1
Metric: 10 IP 192.168.12.0 255.255.255.0
Metric: 10 IP 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255
Metric: 0 IP-External 11.0.0.0 255.0.0.0Above we can see that the route was summarized directly in the level 1 database. We can find the summarized route in the routing table of R2:
R2#show ip route isis
1.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
i su 1.0.0.0/8 [115/20], 00:11:37, Null0
i L1 1.1.1.1/32 [115/20] via 192.168.12.1, 00:14:26, GigabitEthernet0/1
i L1 11.0.0.0/8 [115/10] via 192.168.12.1, 00:01:10, GigabitEthernet0/1That’s it.
Configurations
Want to take a look for yourself? Here you will find the final configuration of each device.


Hi Rene,
Is there any rule where we can do summarize like OSPF ABR/ASBR ?? Thanks
br//zaman
Hi Zaman,
Like OSPF, you can’t do summarization within an area. You can do it between level 1/2 or areas.
Rene
Just a small typo: on R1 IS-IS is configured for gigabit 0/1 but the picture shows gigabit 0/2.
Thank you,
Stefanita
Thank you Stefanita, just fixed this.
Rene
Above we have R1 and R3 in area 12.<<<Typo(R1 and R2 are in area 12) R3 is in area 3. On R1 we have two loopback interfaces. Loopback 0 will be advertised in IS-IS, loopback 1 will be redistributed. I will show you how to summarize both routes.
Thanks