Lesson Contents
IPv6 ND Inspection is one of the IPv6 first-hop security features. It creates a binding table that is based on NS (Neighbor Solicitation) and NA (Neighbor Advertisement) messages. The switch then uses this table to check any future NS/NA messages. When the IPv6-LLA combination does not match, it drops the message. This only applies to NS/NA messages, it doesn’t drop any actual data packets that have a spoofed IPv6 or MAC address.
Configuration
To demonstrate ND inspection, we’ll use the following topology:
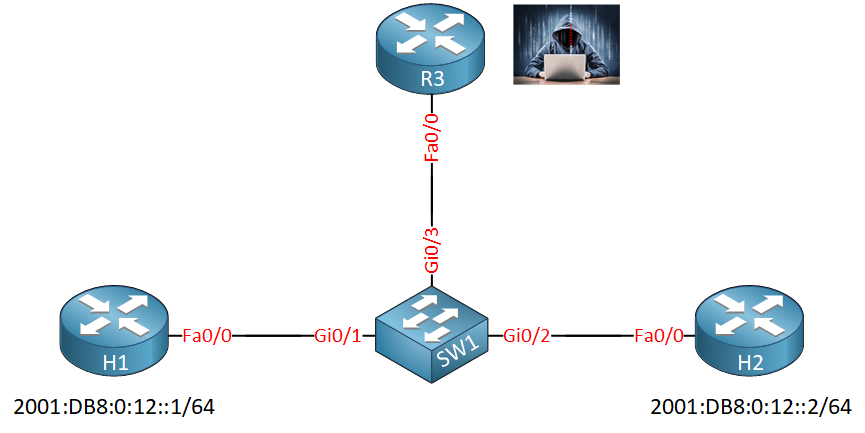
H1 and H2 are two legitimate devices with IPv6 addresses. I will use R3 to spoof an IPv6 address. SW1 is where we configure ND inspection.
Enabling this is very simple if you want to get started. You can do it with a single command:
SW1(config)#interface range gi0/1 - 2
SW1(config-if-range)#ipv6 nd inspectionLet’s send a ping from R1 to R2 to generate some ND/NA messages:
R1#ping 2001:DB8:0:12::2
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 2001:DB8:0:12::2, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 0/0/4 msNow let’s take a look at SW1:
SW1#show ipv6 neighbors binding
Binding Table has 4 entries, 4 dynamic
Codes: L - Local, S - Static, ND - Neighbor Discovery, DH - DHCP, PKT - Other Packet, API - API created
Preflevel flags (prlvl):
0001:MAC and LLA match 0002:Orig trunk 0004:Orig access
0008:Orig trusted trunk 0010:Orig trusted access 0020:DHCP assigned
0040:Cga authenticated 0080:Cert authenticated 0100:Statically assigned
IPv6 address Link-Layer addr Interface vlan prlvl age state Time left
ND FE80::21D:A1FF:FE8B:36D0 001D.A18B.36D0 Gi0/1 1 0005 4s REACHABLE 301 s
ND FE80::217:5AFF:FEED:7AF0 0017.5AED.7AF0 Gi0/2 1 0005 4s REACHABLE 305 s
ND 2001:DB8:0:12::2 0017.5AED.7AF0 Gi0/2 1 0005 15s REACHABLE 288 s
ND 2001:DB8:0:12::1 001D.A18B.36D0 Gi0/1 1 0005 10s REACHABLE 301 sAbove, we see four entries in the binding table. Two for R1 and two for R2. The binding table got populated by ND. You can see that the binding table can also be populated by other options like DHCP.
Let’s see what happens when we try to spoof an IPv6 address of R2 on R3. I’ll disable DAD (Duplicate Address Detection) first:
R3(config-if)#ipv6 nd dad attempts 0Now we’ll copy the IPv6 link-local address of R2 to R3:
R3(config)#interface FastEthernet 0/0
R3(config-if)#ipv6 address FE80::217:5AFF:FEED:7AF0 link-localLet’s do a ping from the spoofed link-local address of R3 to the link-local address of R1 to trigger some ND/NA messages:
R3#ping FE80::21D:A1FF:FE8B:36D0 source FE80::217:5AFF:FEED:7AF0 repeat 1This is what we get on SW1:
SW1#
%SISF-4-PAK_DROP: Message dropped A=FE80::217:5AFF:FEED:7AF0 G=- V=123 I=Gi0/3 P=NDP::RA Reason=More trusted entry existsThe switch drops the ND from R3 since we already have an entry from R2 in our binding table. The binding table works with a “first come, first served” logic. Since we already have an entry from R2, we don’t accept the ND from R3 for the spoofed address.
Static Binding
If you want, you could make the spoofed address of R3 work. Let’s take another look at the binding table:
SW1#show ipv6 neighbors binding | begin Pref
Preflevel flags (prlvl):
0001:MAC and LLA match 0002:Orig trunk 0004:Orig access
0008:Orig trusted trunk 0010:Orig trusted access 0020:DHCP assigned
0040:Cga authenticated 0080:Cert authenticated 0100:Statically assignedThe binding table has different preference levels. The lowest preference level is a MAC and LLA match. The highest preference level is a static binding. Since the binding table is used for some other features, understanding it is important. Let me show you how to create a static binding for R3. Here’s the MAC address of R3:
R3#show interfaces FastEthernet 0/0 | include bia
Hardware is MV96340 Ethernet, address is 0016.c7be.0ec8 (bia 0016.c7be.0ec8)Let’s create a static binding:
SW1(config)#ipv6 neighbor binding vlan 1 FE80::217:5AFF:FEED:7AF0 interface GigabitEthernet 0/3 0016.c7be.0ec8This shows up in our binding table:
SW1#show ipv6 neighbors binding
Binding Table has 4 entries, 3 dynamic
Codes: L - Local, S - Static, ND - Neighbor Discovery, DH - DHCP, PKT - Other Packet, API - API created
Preflevel flags (prlvl):
0001:MAC and LLA match 0002:Orig trunk 0004:Orig access
0008:Orig trusted trunk 0010:Orig trusted access 0020:DHCP assigned
0040:Cga authenticated 0080:Cert authenticated 0100:Statically assigned
IPv6 address Link-Layer addr Interface vlan prlvl age state Time left
ND FE80::21D:A1FF:FE8B:36D0 001D.A18B.36D0 Gi0/1 1 0005 6mn STALE 87780 s
S FE80::217:5AFF:FEED:7AF0 0016.C7BE.0EC8 Gi0/3 1 0100 2s REACHABLE 310 s
ND 2001:DB8:0:12::2 0017.5AED.7AF0 Gi0/2 1 0005 10mn STALE 88122 s
ND 2001:DB8:0:12::1 001D.A18B.36D0 Gi0/1 1 0005 10mn STALE 89190 sAbove, you can see the static binding. ND/NA messages from R3 are now accepted:
R3#ping FE80::21D:A1FF:FE8B:36D0 source FE80::217:5AFF:FEED:7AF0 repeat 1
Output Interface: FastEthernet0/0
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 1, 100-byte ICMP Echos to FE80::21D:A1FF:FE8B:36D0, timeout is 2 seconds:
Packet sent with a source address of FE80::217:5AFF:FEED:7AF0%FastEthernet0/0
!
Success rate is 100 percent (1/1), round-trip min/avg/max = 0/0/0 msLet’s get rid of R3 and clean up the policy before we continue:
R3(config)#interface FastEthernet 0/0
R3(config-if)#shutdownSW1(config)#ipv6 neighbor binding vlan 1 FE80::217:5AFF:FEED:7AF0 interface GigabitEthernet 0/3 0016.c7be.0ec8Policies
So far, we activated ND inspection with a single command and it worked out of the box. You can also customize it with policies. Let’s create a policy and look at the different options:
SW1(config)#ipv6 nd inspection policy MY_POLICY
SW1(config-nd-inspection)#?
IPv6 NDP inspection policy configuration mode:
default Set a command to its defaults
device-role Sets the role of the device attached to the port
drop-unsecure drop unsecure (3971) messages
exit Exit from NDP inspection policy configuration mode
limit Specifies a limit
no Negate a command or set its defaults
sec-level Specifies a minimum sec-level
tracking Override default tracking behavior
trusted-port setup trusted port
validate specific validationThere are quite some options, let’s walk through them. We’ll start with device-role:



Seems to be a typo:
“R1 and R2 are two legitimate devices with IPv6 addresses. I will use R3 to spoof an IPv6 address, SW1 is where we configure ND inspection.”
In the network diagram you have H1 and H2 instead of R1 and R2
Hello Elias
Thanks for pointing that out. I’ll let Rene know…
Laz
Hi Community !
I am finding most of the IPV6 first hop security topics (RAGUARD,DHCPGUARD,ND INSPECTION etc) NOT working with Cisco VIRL switch version as below.
Cisco IOS Software, vios_l2 Software (vios_l2-ADVENTERPRISEK9-M), Version 15.2(CML_NIGHTLY_20180619)FLO_DSGS7
This is a very important MUST PRACTICE topic on the ENARSI exam. please suggest suitable VIRL Cisco image.
Hello Raghu
You are correct. It seems that this particular switch version is behaving strangely. It has the ipv6 nd command available, but if you add anything after that, it says “unrecognized command.”
Based on this Cisco learning network thread, others have faced similar situations. Still, others are able to implement RA Guard on this image. According to this documentation, it seems that IPv6 is not supported by t
... Continue reading in our forumHi Lazaros,
Could you please share the procedure to downgrade cisco Virl Cisco IOS Software, vios_l2 Software (vios_l2-ADVENTERPRISEK9-M), Version 15.2(CML_NIGHTLY_20180619)
Raghunath