When you are configuring QoS on your Cisco switches, you are probably familiar with the concept of “trust boundaries”. If not, take a look at this lesson that I wrote earlier that explains the concept and teaches you how to trust markings or (re)mark packets or Ethernet frames.
Using the mls qos trust command, we can trust the Cos or DSCP value or an IP phone. We can set a new CoS value with the mls qos cos command if we like. The downside of these two commands is that it applies to all packets or Ethernet frames that arrive on the FastEthernet 0/1 interface. What if we wanted to be a bit more specific? Let me show you an example:
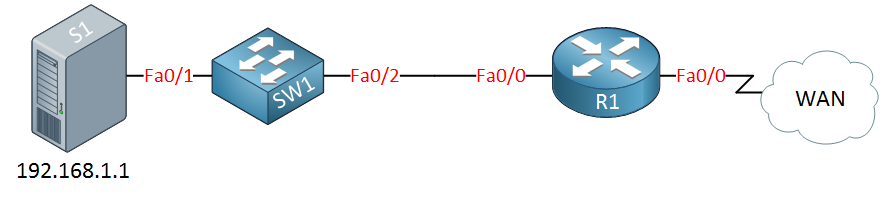
Above, you see a small network with a server, switch, and a router connected to a WAN. Let’s imagine the server is running a couple of applications:
- SSH server.
- Mail server.
- MySQL server.
What if the server cannot mark its IP packets with a DSCP value, but we want to prioritize SSH traffic on the router when it leaves the serial 0/0 interface? In that case, we’ll have to do classification and marking ourselves. I will show you how to do this on a Cisco catalyst switch. You can use a standard, extended, or MAC access-list in combination with MQC (Modular QoS Configuration) to get the job done.
Let’s start with the standard access-list to classify traffic from the server. Since a standard access-list can only match on source IP addresses, I will be unable to differentiate between different applications…
SW1(config)#class-map match-all SERVER SW1(config-cmap)#match access-group 1
We’ll use a class-map to select our traffic. I will refer to access-list 1 with the match command.
SW1(config)#access-list 1 permit 192.168.1.1
Access-list 1 will match IP address 192.168.1.1. This is the classification part, but we still have to mark our traffic. This is done with a policy-map:
SW1(config)#policy-map SET-DSCP-SERVER SW1(config-pmap)#class SERVER SW1(config-pmap-c)#set ip dscp 40
Above, I created a policy map called “SET-DSCP-SERVER” and I’m referring to the class-map “SERVER” that I created before. Using the set command, I will set the DSCP value to 40. Now I am almost done, I still need to activate this policy map on the interface:
SW1(config)#interface FastEthernet 0/1 SW1(config-if)#service-policy input SET-DSCP-SERVER
This is how you activate it on the interface. Use the service-policy command, and you can use the input or output keyword to apply it to inbound or outbound traffic. If you want to verify your configuration and see if traffic is being marked, you can use the following command:
SW1#show policy-map interface FastEthernet 0/1 FastEthernet0/1 Service-policy input: SET-DSCP-SERVER Class-map: SERVER (match-all) 0 packets, 0 bytes 5 minute offered rate 0 bps, drop rate 0 bps Match: access-group 1 Class-map: class-default (match-any) 0 packets, 0 bytes 5 minute offered rate 0 bps, drop rate 0 bps Match: any 0 packets, 0 bytes 5 minute rate 0 bps
Above, you can see that the policy-map has been applied to the FastEthernet0/1 interface, and even better, you can see the number of packets that have matched this policy-map and class-map. At the moment, there are 0 packets (nothing is connected to my switch at the moment). You can also see the class-default class. All traffic that doesn’t belong to a class-map will belong to the class-default class.
The example above is nice to demonstrate the class-map and policy-map, but I was only able to match the source IP address because of the standard access-list. Let me show you another example that will only match SSH traffic using an extended access-list:
SW1(config)#class-map SSH SW1(config-cmap)#match access-group 100
First, i’ll create a class-map called SSH that matches access-list 100. Don’t forget to create the access-list:
SW1(config)#access-list 100 permit tcp host 192.168.1.1 eq 22 any
Access-list 100 will match source IP address 192.168.1.1 and source port 22 (SSH). Now we’ll pull it all together with the policy-map:



Hi Rene, i like your blog and web gns3vault
I’ve a question because i’m doing troubleshooting with qos in switches and when i look at the policy i don’t see what i expect to see.
i have applied a policy fa0/1 input. i inject traffic but i don’t see ever increasing packet. Could it be because it is a switch ? when is a router i see increases
C3560-24TS_1#sh policy-map interface
FastEthernet0/1
Service-policy input: QoS_In
... Continue reading in our forumHi Cat,
This is really confusing but the output on the 3560 will never show any hits. I’m not sure if it is IOS-specific but I’ve seen it on multiple switches.
Rene
Hello Rene,
thanks a lot for your efforts . I am on of your fans
regarding it is always shows 0 packets . a limitation of the platform (same for almost all the fixed configuration Catalysts). the counters don’t work and there is no tweak you can perform to make them work. The only command that shows you any half-useful statistics is ‘show mls qos interface statistics’. This will show you counters for the incoming & outgoing DSCP & CoS values, plus two counters for ‘Inprofile’ and ‘Outprofile’. These last two counters show you what traffic has adhered to its con
... Continue reading in our forumHi Rene,
I have a question and may not be related to this section but it is to switches. I have been having latency issues with all my users in one location. We install a new 3560x switch with Access to shares, printing and voip and they are very very slow. I called cisco in regards to checking QOS on my switch, spoke to 2 different Engineers and I got different opinions, I have mls qos statements but QOS never enable so one opinion recommended these settings on the interface:
... Continue reading in our forumHi Alfredo,
QoS on switches can be a pain…first of all, if you don’t have “mls qos” enabled then it won’t do any packet rewriting but it will still be queuing.
Take a look at this post, there I explain how queuing works and there’s a great video that explains QoS on the switches:
https://networklessons.com/quality-of-service/how-to-configure-queuing-on-cisco-catalyst-3560-and-3750-switch
Here’s an example of a production 3560 switch here without “mls qos” enabled, you can see it’s queuing:
... Continue reading in our forum