Lesson Contents
Large enterprise networks might have many access points (AP), and not all APs require the same settings.
With the previous generation of WLCs running AireOS, many settings were global settings that applied to all access points (AP). Whether they needed it or not.
The Cisco Wireless LAN controllers (WLC) based on IOS-XE, such as the Catalyst 9800, allow granular control of all settings without configuring every AP individually. They accomplish this by using a combination of tags and profiles.
In a nutshell, here is how it works:
- We configure settings and parameters in profiles.
- We link these profiles to tags.
- We add tags to one or more APs.
Here’s how to visualize this:
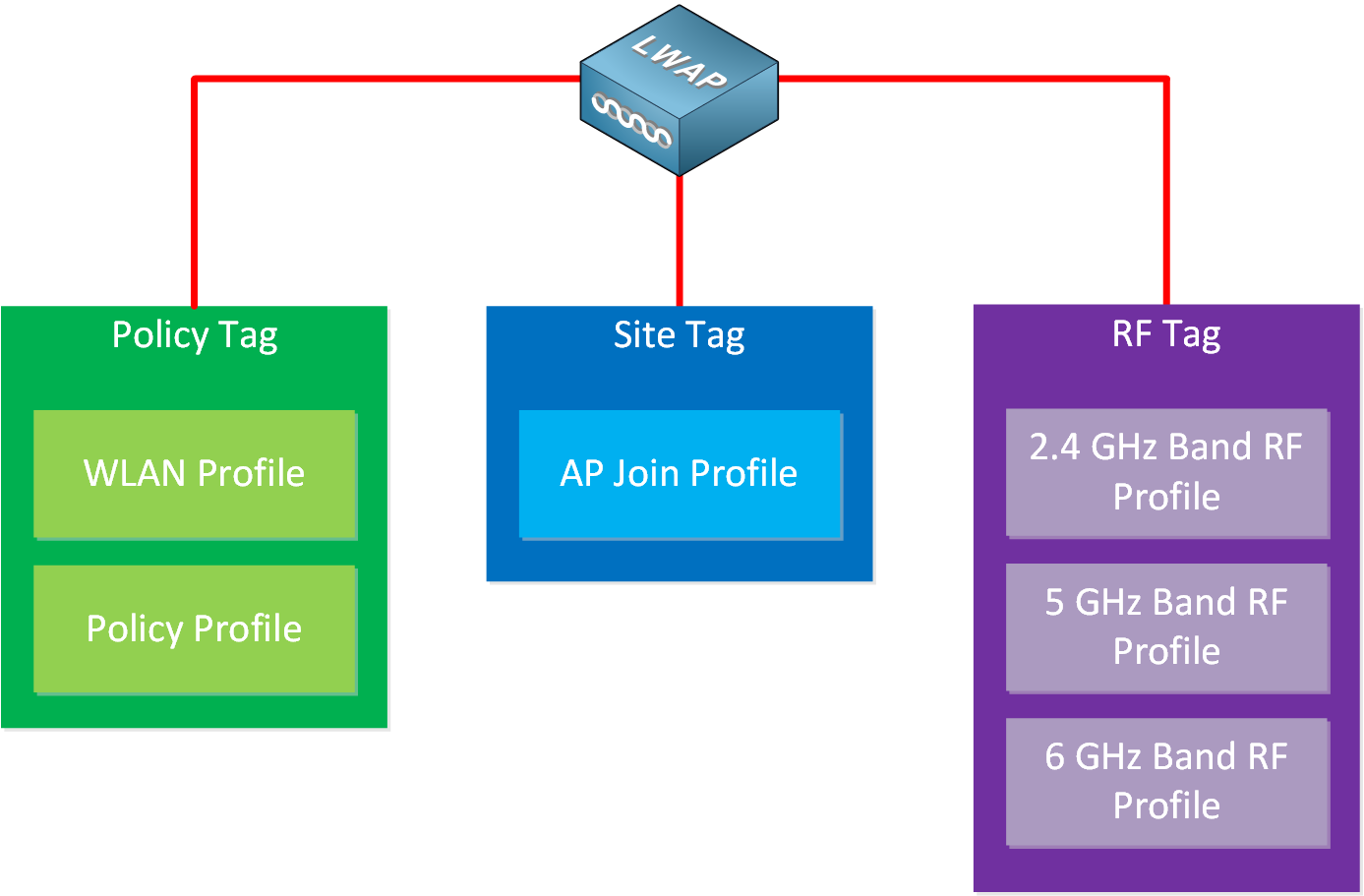
This is a scalable method to configure many APs based on the requirements of the wireless LAN. Here is an example:
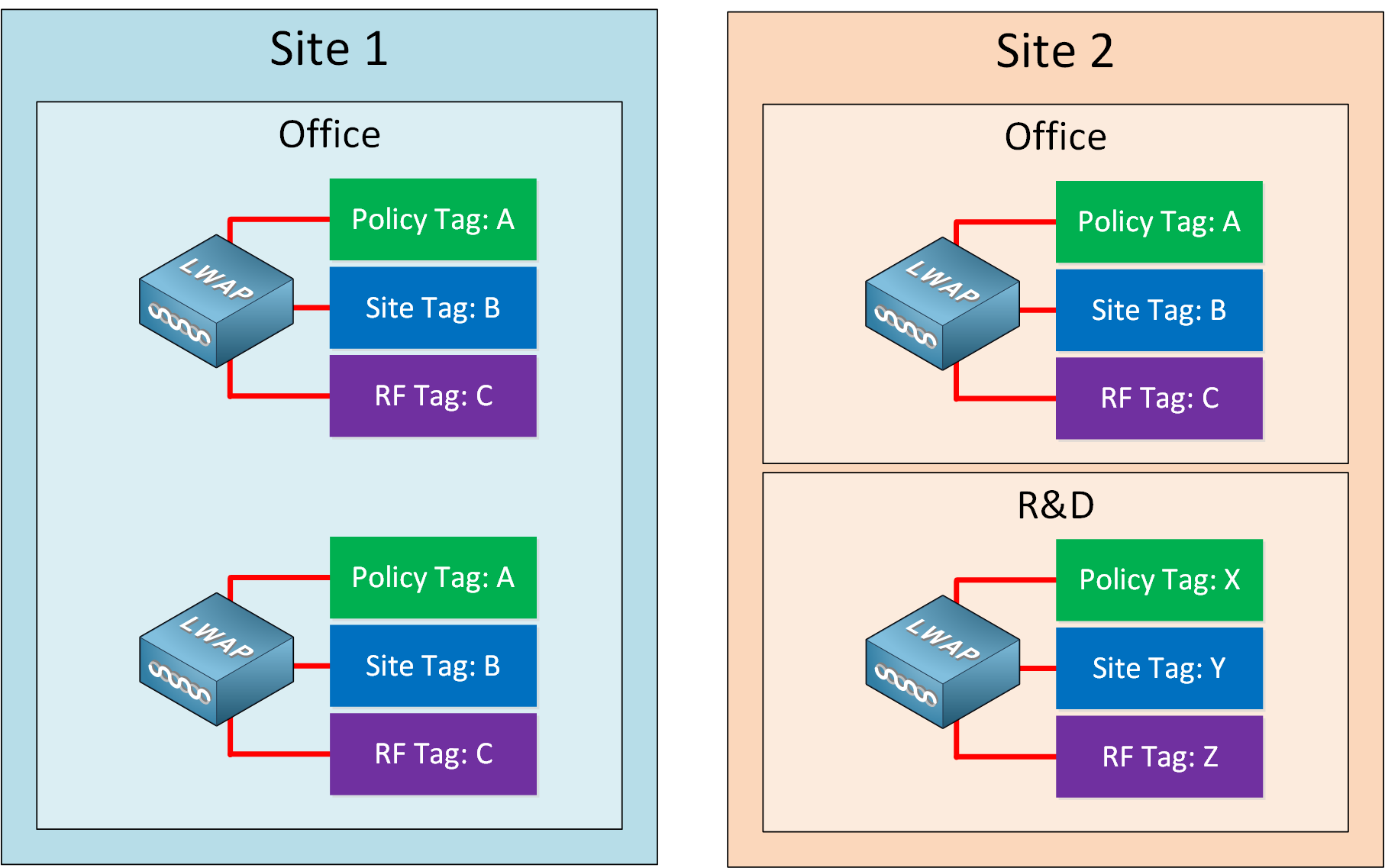
Imagine we have a network with multiple sites. Site one only has an office. Site two has an office and an R&D department. The wireless LAN in the office might use a different SSID and different security settings than the wireless LAN for the R&D department. By using different tags that use other profiles, we can quickly apply different settings to groups of APs.
Tags
There are three tags:
- Policy tag
- Site tag
- RF tag
We’ll examine each in detail.
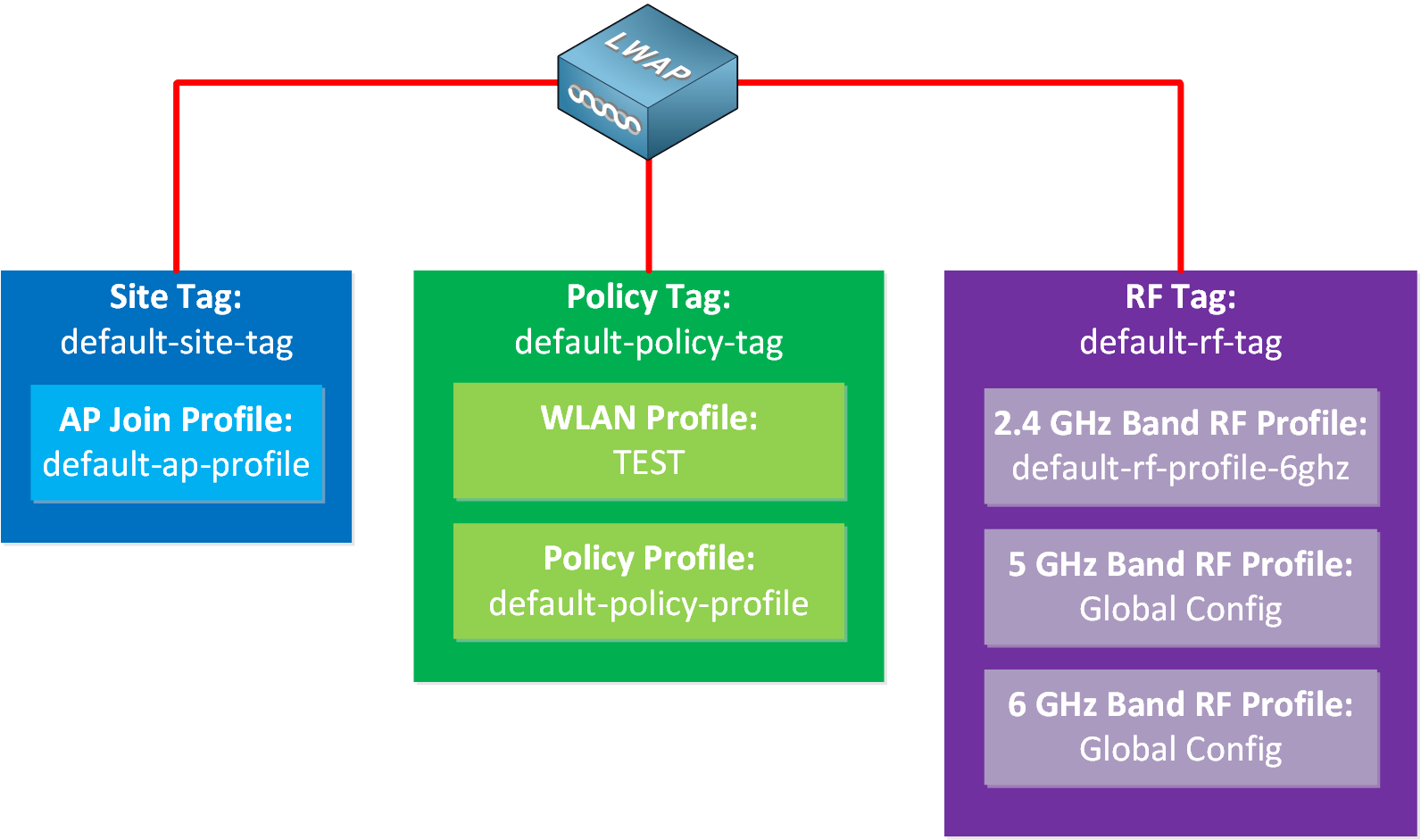
Default Tags
By default, APs get assigned the following default tags:
- Policy: default-policy-tag
- Site: default-site-tag
- RF: default-rf-tag
I’m using Cisco IOS Software [Dublin], C9800-CL Software (C9800-CL-K9_IOSXE), Version 17.11.1, RELEASE SOFTWARE (fc2) for the upcoming examples.
Here’s a screenshot where you can see the default tags:
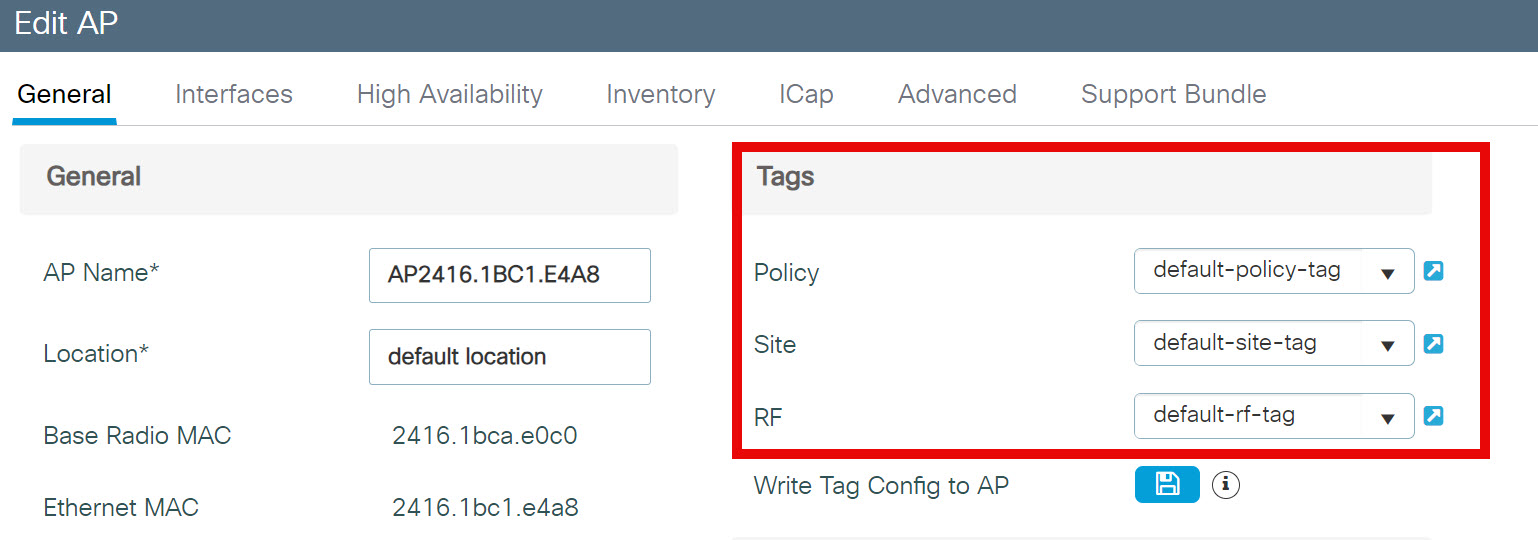
You can edit these default tags, or you can create new ones. Let’s take a closer look at these tags.
Policy Tag
The policy tag is where we link a WLAN profile and policy profile. Take a look at the screenshot below:
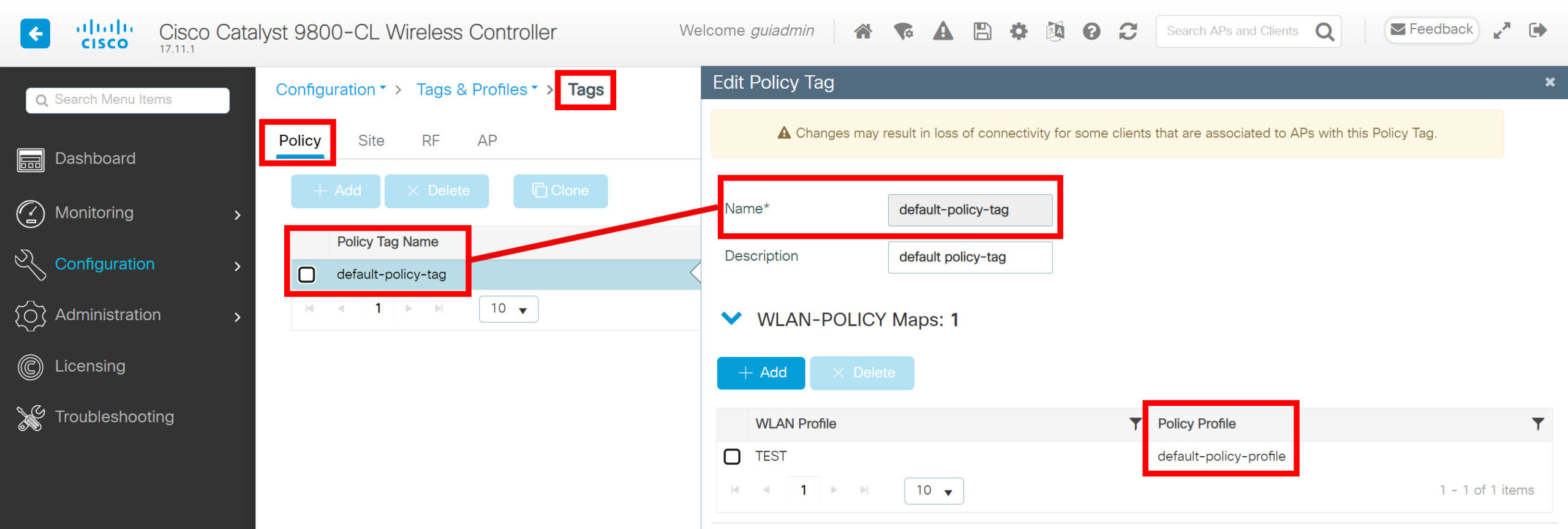
In the policy tag settings, we can see two things:
- This tag uses the “default-policy-profile” profile.
- This tag uses the “TEST” WLAN profile.
Here’s how to visualize this tag:

Site Tag
The site tag is where we link the AP join profile (and Fabric Control Plane Name). Here is a screenshot of the site tag settings:
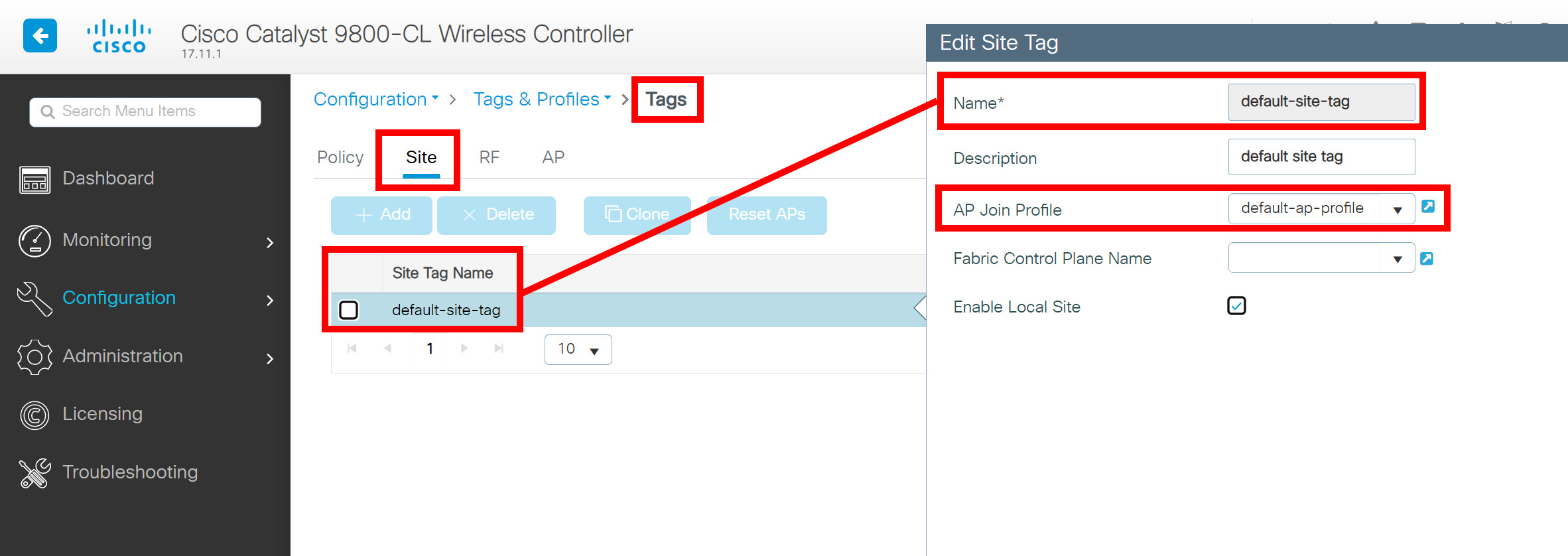
The “default-site-tag” tag uses the profile “default-ap-profile”. Here’s a visualization:

RF Tag
The RF tag links the RF profiles for the different frequencies. Here is a screenshot of the “default-rf-tag” tag:
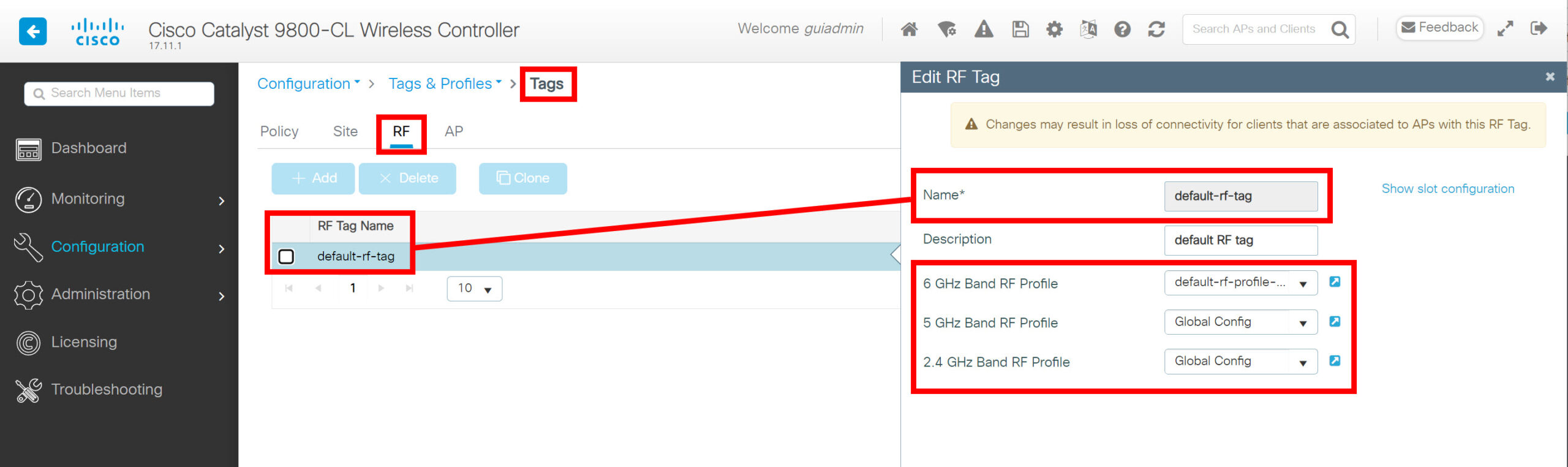
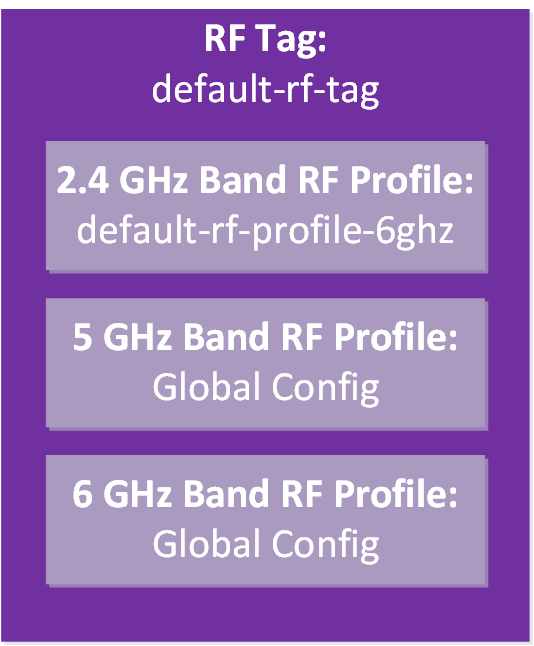
This output is interesting. By default, it has a “default-rf-profile-6ghz” for the 6 GHz band, but for the 2.4 and 5 GHz bands, it refers to the global config instead of a profile. I’m surprised they didn’t use a profile by default for the 2.4 and 5 GHz bands as well. Here’s how to visualize this:
Let me show you the “global config” items. Here’s what these global configuration settings look like:
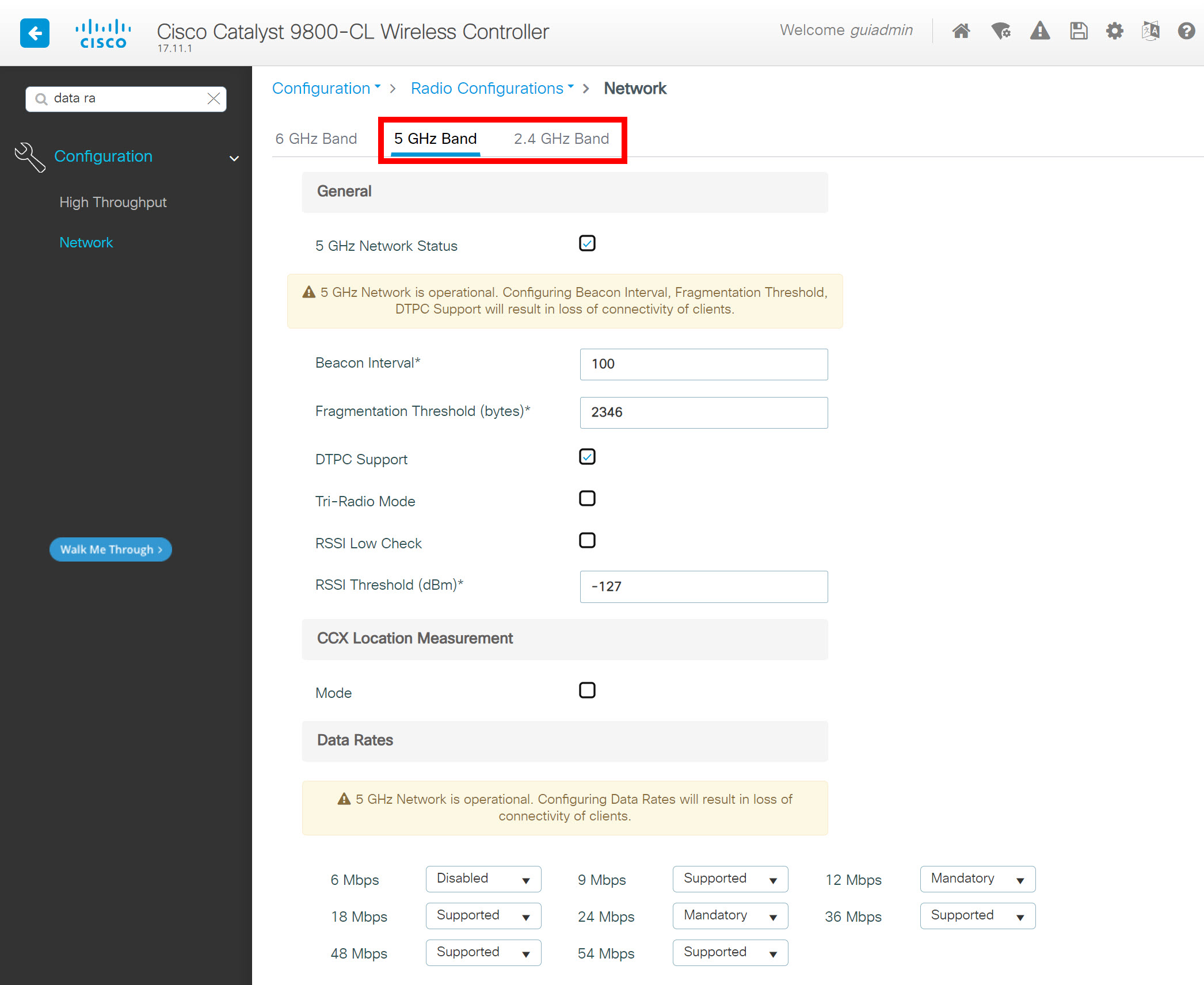
Below are the default RRM settings per band:
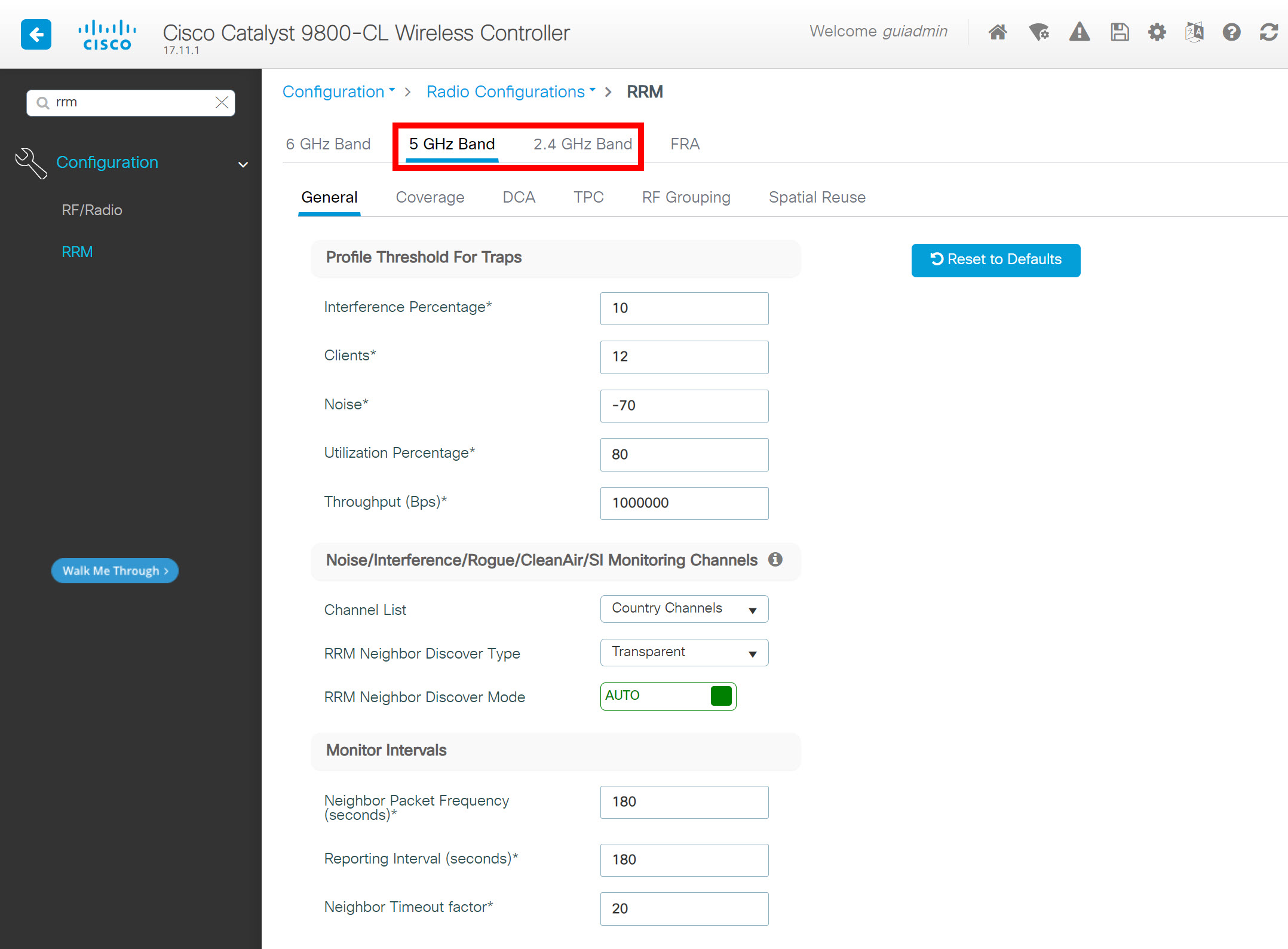
There are global configuration items, not a profile. However, these settings can also be configured in a profile. I’m unsure why they used global settings for these two bands. Here is a visualization of all default AP tags and profiles:
Profiles
A profile is a collection of settings and parameters. There are many different profiles we can use, such as:
- AP Join Profile
- Calendar Profile
- Flex Profile
- Multi BSSID Profile
- Policy Profile
- Power Profile
- Remote LAN Profile
- RF/Radio Profile
- WLAN Profile
The WLC has some default profiles which you can edit, or you can create new profiles. We’ll take a look at the most common profiles.
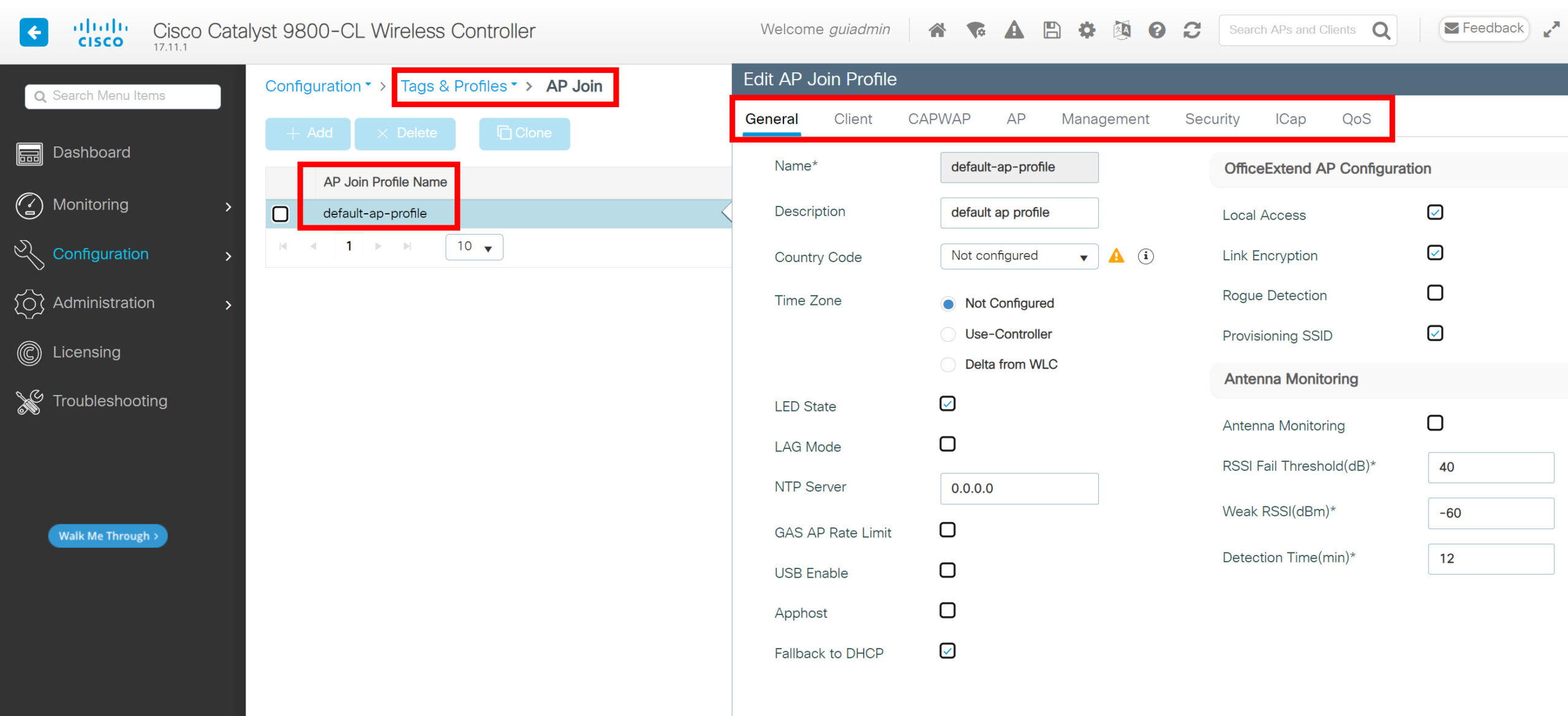
AP Join Profile
The AP join profile has all settings related to the AP. For example:
- General
- Country code
- LED state
- NTP Server
- OfficeExtend
- Client
- TCP MSS
- CAPWAP
- Heartbeat and discovery timers
- Backup and secondary WLC
- AP
- Management
- TFTP
- System Log
- Telnet
- SSH
- CDP
- Security
- Rogue Detection
- ICap
- Client Telemetry
- AP Telemetry
- QoS
- DSCP settings
Here is what it looks like:
WLAN Profile
This profile is where we configure the SSID and security settings for the wireless LAN. For example:
- General
- SSID
- Status (enabled or disabled)
- Broadcast SSID
- Radio Policy
- 6 GHz
- 5 GHz
- 2.4 GHz
- Security
- Layer two
- WPA, WPA2, WPA3, WEP.
- WPA parameters
- WPA2/WPA3 encryption
- Protected management frame
- Fast transition
- Authentication key management
- MPSK
- Layer three
- Web policy
- AAA
- Authentication list
- Local EAP Authentication
- Layer two
- Advanced
- P2P Blocking Action
- MIMO settings
- Client Steering
- Max Client Connections
- Load balance
- Band select
- WMM Policy
- mDNS
- Assisted Roaming
- DTIM Period
- Add To Policy Tags
- This is where you link the WLAN profile to a policy tag.
Here is what it looks like:


