If you have no idea how Routing Information Protocol (RIP) works, I suggest reading this lesson first, where I explain how RIP works. In this lesson, I’ll show you how to configure the RIP on a Cisco router. This is the topology that I will use:
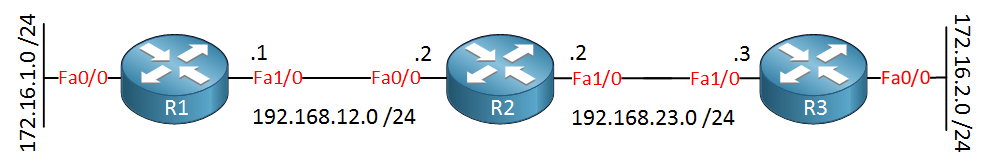
Above, we see three routers called R1, R2, and R3. There are a couple of networks, so we’ll have something to advertise in RIP. First, let’s configure all the interfaces:
R1>enable
R1#configure terminal
R1(config)#interface fastEthernet 0/0
R1(config-if)#no shutdown
R1(config-if)#ip address 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.0
R1(config-if)#exit
R1(config)#interface fastEthernet 1/0
R1(config-if)#ip address 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.0
R1(config-if)#no shutdownR2>enable
R2#configure terminal
R2(config)#interface fastEthernet 0/0
R2(config-if)#no shutdown
R2(config-if)#ip address 192.168.12.2 255.255.255.0
R2(config-if)#exit
R2(config)#interface FastEthernet 1/0
R2(config-if)#no shutdown
R2(config-if)#ip address 192.168.23.2 255.255.255.0
R2(config-if)#exit
R3>enable
R3#configure terminal
R3(config)#interface fastEthernet 0/0
R3(config-if)#no shutdown
R3(config-if)#ip address 172.16.2.3 255.255.255.0
R3(config-if)#exit
R3(config)#interface fastEthernet 1/0
R3(config-if)#no shutdown
R3(config-if)#ip address 192.168.23.3 255.255.255.0
R3(config-if)#exitBefore we continue RIP, we’ll check the routing tables:
R1#show ip route
Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - S-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default,
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
C 192.168.12.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet1/0
172.16.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
C 172.16.1.0 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0R2#show ip route
Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - S-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default,
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
C 192.168.12.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
C 192.168.23.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet1/0R3#show ip route
Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - S-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default,
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
172.16.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
C 172.16.2.0 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
C 192.168.23.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet1/0Our routers only know one thing…their directly connected interfaces. Let’s configure RIP and see what happens:
R1(config)#router rip
R1(config-router)#network 192.168.12.0
R1(config-router)#network 172.16.1.0R2(config)#router rip
R2(config-router)#network 192.168.12.0We use the router rip command to go to the RIP configuration. The next step is to use the network command, which does two things. Let’s zoom in on R1 and R2 so I can explain this a bit more:
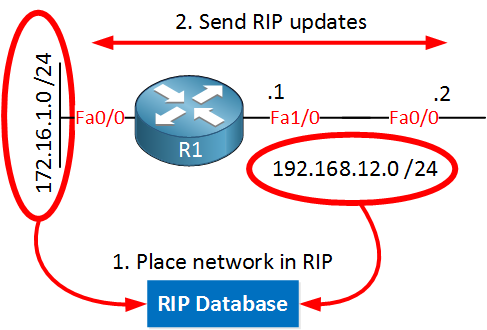
- All networks that fall within the range of the network command will be advertised in RIP to other routers.
- RIP updates will be sent on the interface that falls within the range of the network command.
R1(config-router)#network 192.168.12.0When I type “network 192.168.12.0” I will put all networks that fall within the 192.168.12.0 range in the RIP database. The FastEthernet1/0 interface has network 192.168.12.0 /24, so this will be placed in the RIP database. It will also send RIP updates on this interface.
R1(config-router)#network 172.16.1.0172.16.1.0 /24 that is configured on FastEthernet 0/0 falls within the 172.16.1.0 range so it will be placed in the RIP database.
We will also send RIP updates on the FastEthernet 0/0 interface. This might sound a bit silly since there is no other router connected to this interface, there’s no point in sending RIP updates in this direction. I’ll show you how to deal with this later.
Let’s take a look at R2:
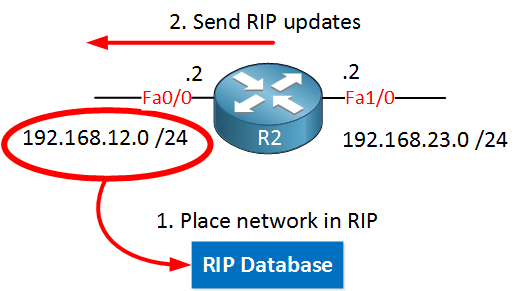
R2(config-router)#network 192.168.12.0On R2, I only used the network command above. This means that it will put 192.168.12.0 /24 in the RIP database and send RIP updates on its FastEthernet 0/0 interface. At this moment it won’t advertise network 192.168.23.0 /24 in RIP, and it won’t send RIP updates on the FastEthernet 1/0 interface.
Let’s check the routing tables of R1 and R2!
R1#show ip route rip R2#show ip route rip
R 172.16.0.0/16 [120/1] via 192.168.12.1, 00:00:21, FastEthernet0/0Instead of typing show ip route you can also use show ip route rip. This will show you only the RIP information in the routing table. As you can see, R1 didn’t learn anything from R2. This is because network 192.168.23.0 /24 isn’t advertised on R2.
R2 has learned network 172.16.0.0 /16. Why do we see 172.16.0.0 /16 and not 172.16.1.0 /24? Keep in mind that by default RIP is running version 1 which is classful. It does NOT send a subnet mask along with the routing updates. Since 172.16.1.0 /24 is in the class B range it will be advertised as 172.16.0.0 /16.
I’ll configure RIP version 2 later so you can see the difference between classless and classful.
Anyway, let’s see if we can make R1 learn about 192.168.23.0 /24:
R2(config)#router rip
R2(config-router)#network 192.168.23.0I’ll use this network command; let me show you another picture of R2:
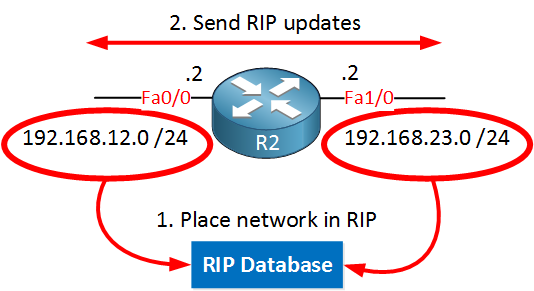
When I use the “network 192.168.23.0” command it will place 192.168.23.0 /24 in the RIP database, AND it will send RIP updates on the FastEthernet 1/0 interface. Let’s check R1:
R1#show ip route rip
R 192.168.23.0/24 [120/1] via 192.168.12.2, 00:00:16, FastEthernet1/0Now, R1 knows how to reach this network. Let’s take a closer look at this entry…
R 192.168.23.0/24The “R” means that this entry was learned through RIP, and 192.168.23.0 /24 is the network that we learned.
[120/1]The first number (120) is the administrative distance. The second number (1) is the metric. RIP uses “hop count” as the metric, so network 192.168.23.0/24 is one hop away.
via 192.168.12.2This is the next hop IP address. If we want to reach network 192.168.23.0 /24, we’ll send IP packets to 192.168.12.2.
00:00:16This is the time since the last update for this entry. RIP sends an update every 30 seconds, so this value will never be higher than 29 seconds.
FastEthernet1/0This is the outgoing interface. When we want to reach network 192.168.23.0 /24, we’ll use this interface for outgoing traffic.
There is one last thing I want to share with you about the network command. Let me show you R2 one more time:
R2 has these two interfaces, and I used these network commands:
R2(config-router)#network 192.168.12.0
R2(config-router)#network 192.168.23.0I also could use:
R2(config-router)#network 0.0.0.0All networks that fall under the 0.0.0.0 range are advertised in RIP. In other words, every interface that has an IP address that falls under this range will have RIP activated on it. Network 0.0.0.0 basically means “enable RIP on all interfaces and advertise everything.” This is what we call the “shotgun approach.” I sometimes like to use it in labs when I quickly want to advertise all networks on my router.
We still have one router to configure, so let’s enable RIP on R3, shall we?
R3(config)#router rip
R3(config-router)#network 172.16.2.0
R3(config-router)#network 192.168.23.0First, I’ll enable the network commands. Now let’s see what we find in our routing tables:
R1#show ip route rip
R 192.168.23.0/24 [120/1] via 192.168.12.2, 00:00:21, FastEthernet1/0R2#show ip route rip
R 172.16.0.0/16 [120/1] via 192.168.23.3, 00:00:15, FastEthernet1/0
[120/1] via 192.168.12.1, 00:00:11, FastEthernet0/0R3#show ip route rip
R 192.168.12.0/24 [120/1] via 192.168.23.2, 00:00:26, FastEthernet1/0Now, this is an interesting output. There are a couple of interesting things here:
- R1 didn’t learn about network 172.16.2.0 /24.
- R3 didn’t learn about network 172.16.1.0 /24.
- R2 has 172.16.0.0 /16 in its routing table with two next-hop IP addresses:
- 192.168.23.3.
- 192.168.12.1.
Currently, we are running RIP version 1, which is classful. This means that R1 advertises 172.16.1.0 /24 as 172.16.0.0 and R3 advertises 172.16.2.0 /24 as 172.16.0.0.
So what does R2 do with this information? Whenever you learn about a network from two different sources with the same metric, your router will do load-balancing. For example, when R2 receives an IP packet meant for 172.16.1.1, it might send it to R3, and the IP packet will be dropped.
R1 and R3 are not learning about network 172.16.1.0 /24 or 172.16.2.0 /24, but why is this happening? Let me show you a picture:
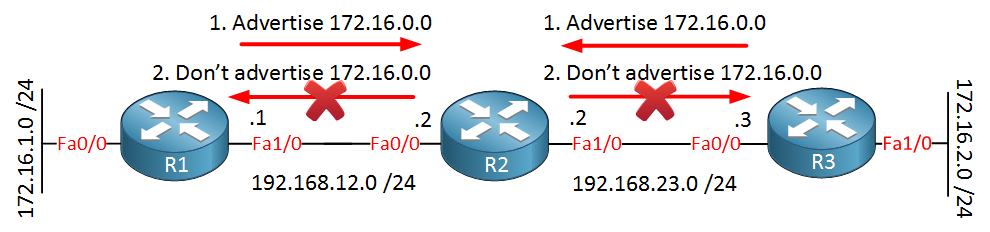
R1 and R3 both advertise 172.16.0.0 to R2. R2 stores this information in its routing table but doesn’t advertise 172.16.0.0 to R1 or R3 because of split horizon. You don’t advertise to your neighbor what you learned from them…
So how to fix this? We need to make sure that R1 and R3 send a subnet mask with their RIP updates….it’s time for RIP version 2 because it’s classless.
There is a very useful command to verify what routing protocols you are using. Let me show you:
R1#show ip protocols
Routing Protocol is "rip"
Outgoing update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Incoming update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Sending updates every 30 seconds, next due in 21 seconds
Invalid after 180 seconds, hold down 180, flushed after 240
Redistributing: rip
Default version control: send version 1, receive any version
Interface Send Recv Triggered RIP Key-chain
FastEthernet0/0 1 1 2
FastEthernet1/0 1 1 2
Automatic network summarization is in effect
Maximum path: 4
Routing for Networks:
172.16.0.0
192.168.12.0
Routing Information Sources:
Gateway Distance Last Update
192.168.12.2 120 00:00:03
Distance: (default is 120)Show ip protocols is a very useful command, so I recommend writing it down somewhere. This isn’t just for RIP; it shows you information for any other routing protocol. We can see that we are running RIP version 1 and that we are sending RIP updates on interface FastEthernet 0/0 and 1/0. You can also see the networks that we are advertising (172.16.0.0 and 192.168.12.0).
Let’s now switch our routers to RIP version 2:
R1(config)#router rip
R1(config-router)#version 2
R1(config-router)#no auto-summaryR2(config)#router rip
R2(config-router)#version 2
R2(config-router)#no auto-summaryR3(config)#router rip
R3(config-router)#version 2
R3(config-router)#no auto-summaryJust type version 2 to switch to this version. By default, RIP version 2 will behave classful and won’t send a subnet mask. I need to type no auto-summary to make it behave classless and send a subnet mask with its RIP updates.
R1#show ip protocols
Routing Protocol is "rip"
Outgoing update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Incoming update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Sending updates every 30 seconds, next due in 19 seconds
Invalid after 180 seconds, hold down 180, flushed after 240
Redistributing: rip
Default version control: send version 2, receive version 2
Interface Send Recv Triggered RIP Key-chain
FastEthernet0/0 2 2
FastEthernet1/0 2 2
Automatic network summarization is not in effect
Maximum path: 4
Routing for Networks:
172.16.0.0
192.168.12.0
Routing Information Sources:
Gateway Distance Last Update
192.168.12.2 120 00:00:23
Distance: (default is 120)You can see that we are now using RIP version 2. Let’s see if there’s a difference in our routing tables:
R1#show ip route rip
172.16.0.0/24 is subnetted, 2 subnets
R 172.16.2.0 [120/2] via 192.168.12.2, 00:00:24, FastEthernet1/0
R 192.168.23.0/24 [120/1] via 192.168.12.2, 00:00:24, FastEthernet1/0R2#show ip route rip
172.16.0.0/24 is subnetted, 2 subnets
R 172.16.1.0 [120/1] via 192.168.12.1, 00:00:08, FastEthernet0/0
R 172.16.2.0 [120/1] via 192.168.23.3, 00:00:26, FastEthernet1/0R3#show ip route rip
R 192.168.12.0/24 [120/1] via 192.168.23.2, 00:00:16, FastEthernet1/0
172.16.0.0/24 is subnetted, 2 subnets
R 172.16.1.0 [120/2] via 192.168.23.2, 00:00:16, FastEthernet1/0This is looking better. You can see that R2 has learned about networks 172.16.1.0 /24 and 172.16.2.0 /24. This is because R1 and R3 are advertising 172.16.1.0 /24 and 172.16.2.0 /24, not 172.16.0.0 anymore. R1 and R3 also have learned about each other’s networks.
You now know how to configure RIP, and you have seen some show commands to look up information. We can also use a debug command to see in real-time what our router is doing. Let’s look at a RIP example!
R2#debug ip rip
RIP protocol debugging is onDebug IP rip is how we enable it. You will see messages like these:
R2#
RIP: received v2 update from 192.168.12.1 on FastEthernet0/0
172.16.1.0/24 via 0.0.0.0 in 1 hopsHere’s what you see when R2 receives a RIP update from R1. We learn about network 172.16.1.0 /24.
RIP: sending v2 update to 224.0.0.9 via FastEthernet0/0 (192.168.12.2)
RIP: build update entries
172.16.2.0/24 via 0.0.0.0, metric 2, tag 0
192.168.23.0/24 via 0.0.0.0, metric 1, tag 0This is the RIP update that R2 will send to R1. It carries network 172.16.2.0 /24 and 192.168.23.0 /24. In case you are wondering what 224.0.0.9 means…RIP version 2 doesn’t use broadcast but multicast for delivery. 224.0.0.9 is the multicast address for RIP version 2.
Last but not least, I want to show you how to create summaries when using RIP. Here’s the topology we will use:


Hi !!!
Plesea, you can check pictrue 7, i can’t see Fa0/2 on router Spade. It’s two port Fa0/0 ???
Thanks for pointing that out, I just fixed it!
Hi Rene
Very simple yet brilliant exaple of LIVE lab. I am very happy to find this post and recommand to anyone who wants to be CCNA, cheers Ajay NZ
Thanks Ajay!
Awesome job in explaining clearly.