Lesson Contents
In this lesson we’ll take a look how we can configure a default route in EIGRP. Basically there are two methods how you can do this:
- Create a static route and advertise it into EIGRP.
- Flag an EIGRP route as the default network.
We will take a look at both methods. This is the topology we will use:
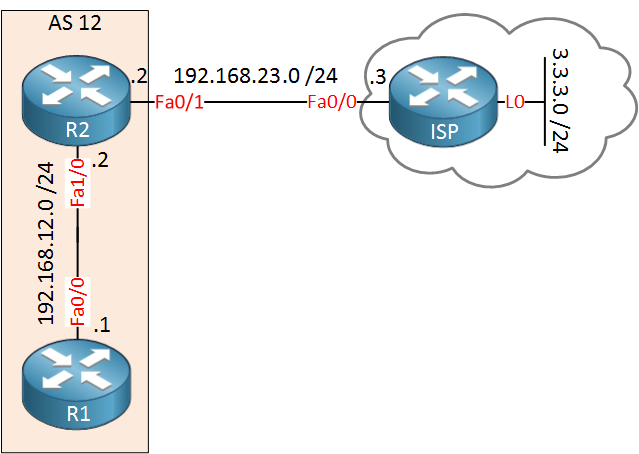
R1 and R2 are configured for EIGRP, R2 is connected to an ISP router. Behind the ISP is network 3.3.3.0 /24 that we can use to test our default route.
Configuration
Here’s the configuration of R1 and R2:
R1#show run | section eigrp
router eigrp 12
network 192.168.12.0
no auto-summaryR2#show run | section eigrp
router eigrp 12
network 192.168.12.0
no auto-summaryNothing special, R1 and R2 are neighbors but that’s it.
Static Default Route
Let’s start with the first option, the static default route:
R2(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 FastEthernet 0/1
R2(config)#router eigrp 12
R2(config-router)#network 0.0.0.0We configure the default route on R2 with FastEthernet 0/1 as the exit interface. In EIGRP we can use the network 0.0.0.0 command to advertise this. This might sound strange but it works, normally you can only use the network command to advertise networks on interfaces but EIGRP wil make an exception for this default route.
Let’s see what R1 thinks of this:
R1#show ip route eigrp | begin 0.0.0.0
Gateway of last resort is 192.168.12.2 to network 0.0.0.0
D* 0.0.0.0/0 [90/30720] via 192.168.12.2, 00:01:11, FastEthernet0/0R1 has learned the default route.
Configurations
Want to take a look for yourself? Here you will find the final configuration of each device.
ISP
hostname ISP
!
interface FastEthernet0/0
ip address 192.168.23.3 255.255.255.0
!
interface Loopback0
ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.0
!
ip route 192.168.12.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.23.2
!
endR1
hostname R1
!
interface FastEthernet0/0
ip address 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.0
!
router eigrp 12
no auto-summary
network 192.168.12.0
!
endR2
hostname R2
!
interface FastEthernet0/1
ip address 192.168.23.2 255.255.255.0
!
interface FastEthernet1/0
ip address 192.168.12.2 255.255.255.0
!
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 FastEthernet0/1
!
router eigrp 12
no auto-summary
network 192.168.12.0
network 0.0.0.0
!
endLet’s look at the other method. Let’s get rid of the default route now so we can try the other method:
R2(config)#router eigrp 12
R2(config-router)#no network 0.0.0.0
R2(config)#no ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 FastEthernet 0/1There we go…let’s continue!
IP Default Network
This one is a bit tricky, we can use the ip default-network command to tell other EIGRP routers that this is a network of “last resort”. This means that they can use it as a default route. We will advertise the network between R2 and ISP in EIGRP and configure it as the “default network”:



thanks for this lesson rene. yeah i tried the ip default network command on ios 15 and it didnt work.
the one that work is creating a default route and advertise it with 0.0.0.0. but the problem is, it acts like advertise all the directly connected networks i have, R1 learn the network between R2 and ISP. i also try to add a loopback interface on R2 and suddenly R1 learns it.
is this the normal behavior of network 0.0.0.0? eventhough i have static route?
Hi John,
That’s the normal behavior of the network command yes, I’ve explained it here:
https://networklessons.com/rip/how-to-configure-rip-on-a-cisco-router
Probably the best way to advertise a default route is to redistribute it into EIGRP:
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 null0 (if you don’t have a static route)
router eigrp 1
redistribute static metric 1 1 1 1 1
This will always work.
Rene
Hi Rene,
Is there a tutorial on EIGRP default routes using redistribution?
Cheers
Rob
Hi Rob,
I don’t have a separate tutorial for it but I can explain how to do it here:
The default route to the null0 interface is only needed if you don’t have a default route in your routing table. The route-map with prefix-list is used to make sure th
... Continue reading in our forumhi Rene,
In the case of ip default network as u explained above, I don’t understand why we need to configure a default route on R2 for the network 192.168.23.3 as in R1 it already shows * next to the “D” for this EIGRP entry.
Shashank