Multicast for IPv6 can be configured using static RPs, BSR or embedded RP. In this example I want to show you how to configure IPv6 multicast using BSR. This is the topology that I will use:
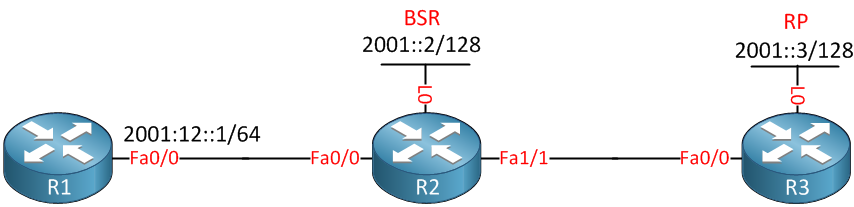
Above we have 3 routers. R1 will be the receiver of the multicast stream, R2 will be the BSR and R3 will be the RP. First we’ll have to do our homework and configure all IPv6 addresses on the interfaces:
R1(config)#ipv6 unicast-routing
R1(config)#interface fastEthernet 0/0
R1(config-if)#ipv6 address 2001:12::1/64R2(config)#ipv6 unicast-routing
R2(config)#interface fastEthernet 0/0
R2(config-if)#ipv6 enable
R2(config-if)#exit
R2(config)#interface fastEthernet 1/1
R2(config-if)#ipv6 enable
R2(config-if)#exit R2(config)#interface loopback 0 R2(config-if)#ipv6 address 2001::2/128R3(config)#ipv6 unicast-routing
R3(config)#interface fastEthernet 0/0
R3(config-if)#ipv6 enable
R3(config-if)#exit
R3(config)#interface loopback 0
R3(config-if)#ipv6 address 2001::3/128With the IPv6 addresses up and running we can configure EIGRP to advertise the loopback interfaces of R2/R3 and the 2001:12::/64 network between R1/R2:
R1(config)#ipv6 router eigrp 1
R1(config-rtr)#router-id 1.1.1.1
R1(config-rtr)#no shutdown
R1(config)#interface fastEthernet 0/0
R1(config-if)#ipv6 eigrp 1R2(config)#ipv6 router eigrp 1
R2(config-rtr)#router-id 2.2.2.2
R2(config-rtr)#no shutdownR2(config)#interface loopback 0
R2(config-if)#ipv6 eigrp 1
R2(config-if)#exit
R2(config)#interface fastEthernet 0/0
R2(config-if)#ipv6 eigrp 1
R2(config-if)#exit
R2(config)#interface fastEthernet 1/1
R2(config-if)#ipv6 eigrp 1R3(config)#ipv6 unicast-routing
R3(config)#ipv6 router eigrp 1
R3(config-rtr)#router-id 3.3.3.3
R3(config-rtr)#no shutdownR3(config)#interface loopback 0
R3(config-if)#ipv6 eigrp 1
R3(config-if)#exit
R3(config)#interface fastEthernet 0/0
R3(config-if)#ipv6 eigrp 1Because I don’t have any IPv4 addresses, I have to configure an EIGRP router ID myself. With the configuration above the 2001:12::/64, 2001::2/128, and 2001::3/128 networks should be reachable from any router. Now we can continue with our multicast setup:
R1,R2 & R3:
(config)#ipv6 multicast-routingFirst, enable multicast routing for IPv6, or we are going nowhere. The next step is to configure the RP and BSR:



ping only works if source interface lo0 supplied
Hi
Is ipv6 multicast required on CCIE V5 lab ??
Yup it’s on the blueprint so you can encounter it.
best CCIE R/S explanation …thanks
Hi,
we did not use a command like
ipv6 pim sparse-modebut the pim neighborship is established. How can ipv6 establish this?regards.