Lesson Contents
Changes in an MPLS TE network are possible. Metrics can change, interfaces can go down or up, etc. It’s possible that an already established tunnel doesn’t use the most optimal path anymore. MPLS TE uses reoptimization to calculate the best path for a tunnel. There are two options:
- Periodic reoptimization.
- Manual reoptimization.
We’ll discuss both options in this lesson. To demonstrate reoptimization, I’ll use this topology:
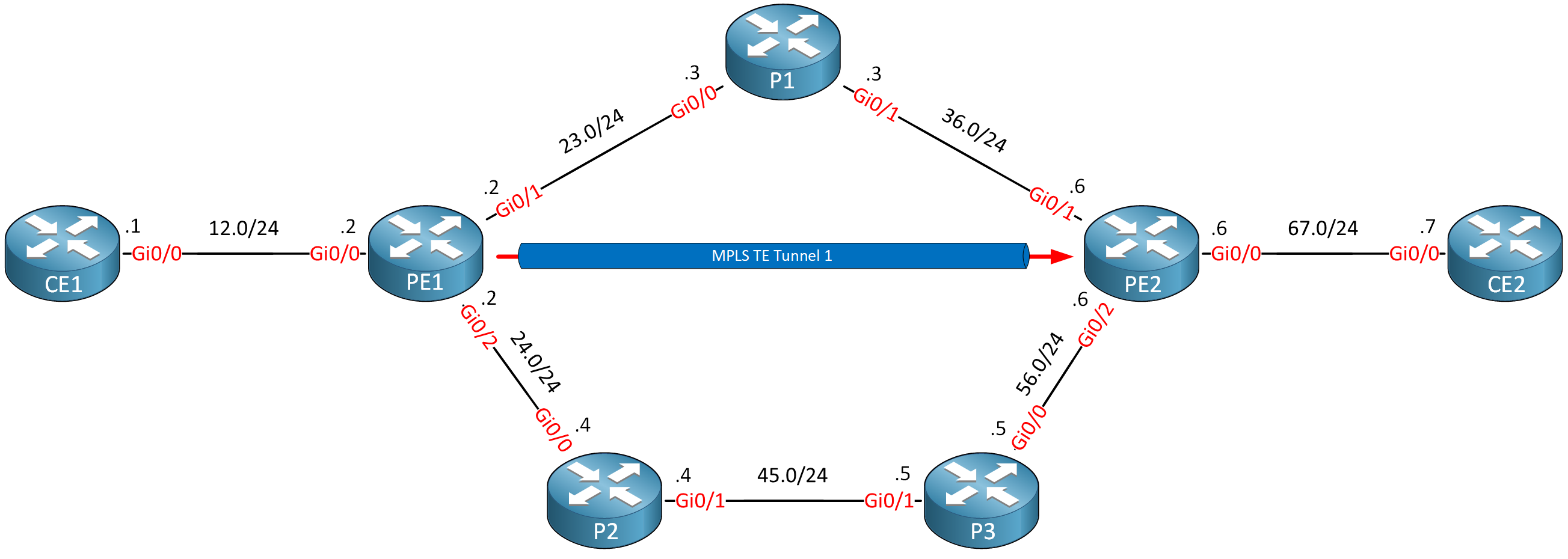
Routers PE1, P1, P2, P3, and PE2 are configured to use MPLS TE. There is a tunnel from PE1 to PE2. I use Cisco IOS Software, IOSv Software (VIOS-ADVENTERPRISEK9-M), Version 15.9(3)M4.
Configurations
Want to take a look for yourself? Here you will find the startup configuration of each device.
CE1
hostname CE1
!
ip cef
!
interface Loopback0
ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255
ip router isis
isis circuit-type level-2-only
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0
ip address 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.0
ip router isis
isis circuit-type level-2-only
!
router isis
net 49.0001.0001.0001.0001.0001.00
is-type level-2-only
metric-style wide
!
endCE2
hostname CE2
!
ip cef
!
interface Loopback0
ip address 7.7.7.7 255.255.255.255
ip router isis
isis circuit-type level-2-only
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0
ip address 192.168.67.7 255.255.255.0
ip router isis
isis circuit-type level-2-only
!
router isis
net 49.0001.0007.0007.0007.0007.00
is-type level-2-only
metric-style wide
!
endP1
hostname P1
!
ip cef
!
mpls traffic-eng tunnels
!
interface Loopback0
ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255
ip router isis
isis circuit-type level-2-only
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0
ip address 192.168.23.3 255.255.255.0
ip router isis
mpls traffic-eng tunnels
mpls ip
isis circuit-type level-2-only
ip rsvp bandwidth 1000000
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
ip address 192.168.36.3 255.255.255.0
ip router isis
mpls traffic-eng tunnels
mpls ip
isis circuit-type level-2-only
ip rsvp bandwidth 1000000
!
router isis
mpls traffic-eng router-id Loopback0
mpls traffic-eng level-2
net 49.0001.0003.0003.0003.0003.00
is-type level-2-only
metric-style wide
!
mpls ldp router-id Loopback0 force
!
endP2
hostname P2
!
ip cef
!
mpls traffic-eng tunnels
!
interface Loopback0
ip address 4.4.4.4 255.255.255.255
ip router isis
isis circuit-type level-2-only
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0
ip address 192.168.24.4 255.255.255.0
ip router isis
mpls traffic-eng tunnels
mpls ip
isis circuit-type level-2-only
ip rsvp bandwidth 1000000
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
ip address 192.168.45.4 255.255.255.0
ip router isis
mpls traffic-eng tunnels
mpls ip
isis circuit-type level-2-only
ip rsvp bandwidth 1000000
!
router isis
mpls traffic-eng router-id Loopback0
mpls traffic-eng level-2
net 49.0001.0004.0004.0004.0004.00
is-type level-2-only
metric-style wide
!
mpls ldp router-id Loopback0 force
!
endP3
hostname P3
!
ip cef
!
mpls traffic-eng tunnels
!
interface Loopback0
ip address 5.5.5.5 255.255.255.255
ip router isis
isis circuit-type level-2-only
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0
ip address 192.168.56.5 255.255.255.0
ip router isis
mpls traffic-eng tunnels
mpls ip
isis circuit-type level-2-only
ip rsvp bandwidth 1000000
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
ip address 192.168.45.5 255.255.255.0
ip router isis
mpls traffic-eng tunnels
mpls ip
isis circuit-type level-2-only
ip rsvp bandwidth 1000000
!
router isis
mpls traffic-eng router-id Loopback0
mpls traffic-eng level-2
net 49.0001.0005.0005.0005.0005.00
is-type level-2-only
metric-style wide
!
mpls ldp router-id Loopback0 force
!
endPE1
hostname PE1
!
ip cef
!
mpls traffic-eng tunnels
mpls traffic-eng logging lsp setups
mpls traffic-eng logging lsp teardowns
mpls traffic-eng reoptimize events link-up
!
interface Loopback0
ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255
ip router isis
isis circuit-type level-2-only
!
interface Tunnel1
ip unnumbered Loopback0
tunnel mode mpls traffic-eng
tunnel destination 6.6.6.6
tunnel mpls traffic-eng priority 7 7
tunnel mpls traffic-eng bandwidth 750
tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option 1 dynamic
no routing dynamic
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0
ip address 192.168.12.2 255.255.255.0
ip router isis
isis circuit-type level-2-only
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
ip address 192.168.23.2 255.255.255.0
ip router isis
mpls traffic-eng tunnels
mpls ip
isis circuit-type level-2-only
ip rsvp bandwidth 1000000
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/2
ip address 192.168.24.2 255.255.255.0
ip router isis
mpls traffic-eng tunnels
mpls ip
isis circuit-type level-2-only
ip rsvp bandwidth 1000000
!
router isis
mpls traffic-eng router-id Loopback0
mpls traffic-eng level-2
net 49.0001.0002.0002.0002.0002.00
is-type level-2-only
metric-style wide
!
mpls ldp router-id Loopback0 force
!
endPE2
hostname PE2
!
ip cef
!
mpls traffic-eng tunnels
!
interface Loopback0
ip address 6.6.6.6 255.255.255.255
ip router isis
isis circuit-type level-2-only
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0
ip address 192.168.67.6 255.255.255.0
ip router isis
isis circuit-type level-2-only
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
ip address 192.168.36.6 255.255.255.0
ip router isis
mpls traffic-eng tunnels
mpls ip
isis circuit-type level-2-only
ip rsvp bandwidth 1000000
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/2
ip address 192.168.56.6 255.255.255.0
ip router isis
mpls traffic-eng tunnels
mpls ip
isis circuit-type level-2-only
ip rsvp bandwidth 1000000
!
router isis
mpls traffic-eng router-id Loopback0
mpls traffic-eng level-2
net 49.0001.0006.0006.0006.0006.00
is-type level-2-only
metric-style wide
!
mpls ldp router-id Loopback0 force
!
endPeriodic Reoptimization
Let’s take a look at our tunnel:
PE1#show mpls traffic-eng tunnels Tunnel 1
Name: PE1_t1 (Tunnel1) Destination: 6.6.6.6
Status:
Admin: up Oper: up Path: valid Signalling: connected
path option 1, type dynamic (Basis for Setup, path weight 20)
Config Parameters:
Bandwidth: 750 kbps (Global) Priority: 7 7 Affinity: 0x0/0xFFFF
Metric Type: TE (default)
AutoRoute: disabled LockDown: disabled Loadshare: 750 bw-based
auto-bw: disabled
Active Path Option Parameters:
State: dynamic path option 1 is active
BandwidthOverride: disabled LockDown: disabled Verbatim: disabled
InLabel : -
OutLabel : GigabitEthernet0/1, 26
RSVP Signalling Info:
Src 2.2.2.2, Dst 6.6.6.6, Tun_Id 1, Tun_Instance 22
RSVP Path Info:
My Address: 192.168.23.2
Explicit Route: 192.168.23.3 192.168.36.3 192.168.36.6 6.6.6.6
Record Route: NONE
Tspec: ave rate=750 kbits, burst=1000 bytes, peak rate=750 kbits
RSVP Resv Info:
Record Route: NONE
Fspec: ave rate=750 kbits, burst=1000 bytes, peak rate=750 kbits
Shortest Unconstrained Path Info:
Path Weight: 20 (TE)
Explicit Route: 192.168.23.2 192.168.23.3 192.168.36.3 192.168.36.6
6.6.6.6
History:
Tunnel:
Time since created: 6 minutes, 57 seconds
Time since path change: 5 minutes, 36 seconds
Number of LSP IDs (Tun_Instances) used: 22
Current LSP:
Uptime: 5 minutes, 36 secondsThe output above tells us that PE1 goes through P1 to get to PE2. It uses the shortest path. Let’s see what happens when we shut an interface on P1:
P1(config)#interface GigabitEthernet 0/1
P1(config-if)#shutdownPE1 has to look for another path:
PE1#show mpls traffic-eng tunnels Tunnel 1
Name: PE1_t1 (Tunnel1) Destination: 6.6.6.6
Status:
Admin: up Oper: up Path: valid Signalling: connected
path option 1, type dynamic (Basis for Setup, path weight 30)
Config Parameters:
Bandwidth: 750 kbps (Global) Priority: 7 7 Affinity: 0x0/0xFFFF
Metric Type: TE (default)
AutoRoute: disabled LockDown: disabled Loadshare: 750 bw-based
auto-bw: disabled
Active Path Option Parameters:
State: dynamic path option 1 is active
BandwidthOverride: disabled LockDown: disabled Verbatim: disabled
InLabel : -
OutLabel : GigabitEthernet0/2, 16
RSVP Signalling Info:
Src 2.2.2.2, Dst 6.6.6.6, Tun_Id 1, Tun_Instance 23
RSVP Path Info:
My Address: 192.168.24.2
Explicit Route: 192.168.24.4 192.168.45.4 192.168.45.5 192.168.56.5
192.168.56.6 6.6.6.6
Record Route: NONE
Tspec: ave rate=750 kbits, burst=1000 bytes, peak rate=750 kbits
RSVP Resv Info:
Record Route: NONE
Fspec: ave rate=750 kbits, burst=1000 bytes, peak rate=750 kbits
Shortest Unconstrained Path Info:
Path Weight: 30 (TE)
Explicit Route: 192.168.24.2 192.168.24.4 192.168.45.4 192.168.45.5
192.168.56.5 192.168.56.6 6.6.6.6
History:
Tunnel:
Time since created: 7 minutes, 54 seconds
Time since path change: 12 seconds
Number of LSP IDs (Tun_Instances) used: 23
Current LSP:
Uptime: 12 seconds
Selection: reoptimization
Prior LSP:
ID: path option 1 [22]
Removal Trigger: path errorSo far, so good. PE1 now goes through P2 and P3 to get to PE2. Let’s enable the interface on P1 again:
P1(config)#interface GigabitEthernet 0/1
P1(config-if)#no shutdownLet’s check the tunnel path:
PE1#show mpls traffic-eng tunnels Tunnel 1
Name: PE1_t1 (Tunnel1) Destination: 6.6.6.6
Status:
Admin: up Oper: up Path: valid Signalling: connected
path option 1, type dynamic (Basis for Setup, path weight 30)
Config Parameters:
Bandwidth: 750 kbps (Global) Priority: 7 7 Affinity: 0x0/0xFFFF
Metric Type: TE (default)
AutoRoute: disabled LockDown: disabled Loadshare: 750 bw-based
auto-bw: disabled
Active Path Option Parameters:
State: dynamic path option 1 is active
BandwidthOverride: disabled LockDown: disabled Verbatim: disabled
InLabel : -
OutLabel : GigabitEthernet0/2, 16
RSVP Signalling Info:
Src 2.2.2.2, Dst 6.6.6.6, Tun_Id 1, Tun_Instance 23
RSVP Path Info:
My Address: 192.168.24.2
Explicit Route: 192.168.24.4 192.168.45.4 192.168.45.5 192.168.56.5
192.168.56.6 6.6.6.6
Record Route: NONE
Tspec: ave rate=750 kbits, burst=1000 bytes, peak rate=750 kbits
RSVP Resv Info:
Record Route: NONE
Fspec: ave rate=750 kbits, burst=1000 bytes, peak rate=750 kbits
Shortest Unconstrained Path Info:
Path Weight: 20 (TE)
Explicit Route: 192.168.23.2 192.168.23.3 192.168.36.3 192.168.36.6
6.6.6.6
History:
Tunnel:
Time since created: 8 minutes, 42 seconds
Time since path change: 1 minutes
Number of LSP IDs (Tun_Instances) used: 23
Current LSP:
Uptime: 1 minutes
Selection: reoptimization
Prior LSP:
ID: path option 1 [22]
Removal Trigger: path errorEven though the shortest unconstrained path is through P1, the tunnel doesn’t use this path yet. It remains on the path through P2 and P3. This happens because of the reoptimization timer. Take a look at the output below:

