Lesson Contents
All routers in the path of the LSP keep track of the state of the tunnel. When there is a failure somewhere in the LSP, depending on your interfaces and protocols, it can take up to two minutes before this is detected. This can be an issue.
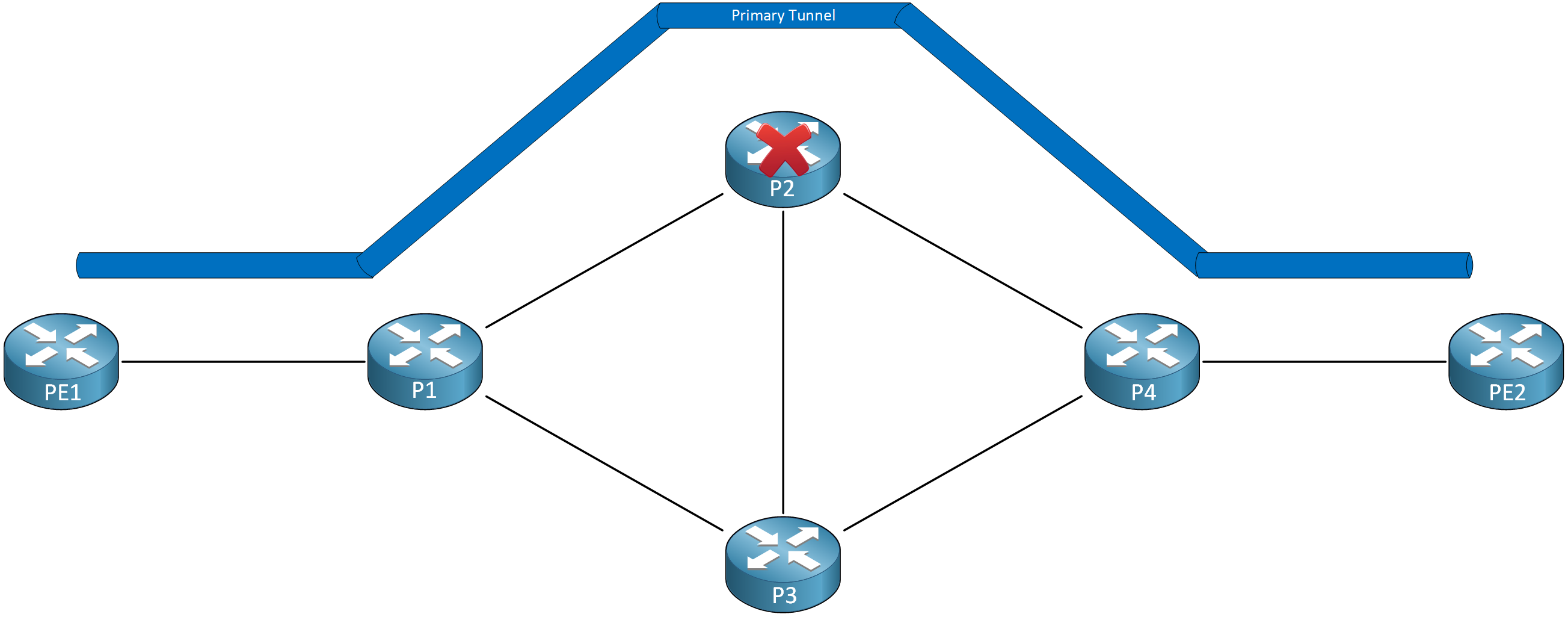
Take a look at the following topology:
We have a Traffic Engineering (TE) tunnel from PE1 to PE2. When something happens with P2, routers behind P2 should know about the failure immediately. If not, they will keep track of the state of the LSP even though the path is unavailable. P4 and PE2 might reserve bandwidth, preventing other tunnels from being built.
Three mechanisms cause a router to activate MPLS TE fast reroute and send traffic down a backup tunnel:
- Interface-down notification
- Loss of signal
- RSVP hello neighbor down notification
Point-to-point links like PPP or HDLC use keepalives. When you don’t receive keepalives, the interface goes down, and the router triggers an interface-down notification.
An example of a loss of signal is when you cut the cable or do a shutdown on a remote interface. This is not very reliable, though. Here is an example:
Above, we have a switch in between P1 and P2. When something happens with P2, SW1 will detect this, and the interface goes down. The connection from P1 to SW1 is fine, so there is no way for P1 to figure out that P2 is gone.
This is a scenario where the third mechanism can help.
RSVP hellos work similarly to hello messages that routing protocols like OSPF, IS-IS, or EIGRP use. It’s also similar to BFD.
An RSVP hello contains a hello message, and in it, we have a request or an acknowledgment.
We send hello request messages, and when we don’t receive acknowledgments, we declare the neighbor down. When this happens, it triggers a fast reroute (FRR) immediately and switches to a backup tunnel. This makes RSVP hellos a good companion for MPLS TE FRR node protection.
There are two types of hello instances:
- Active: the router that actively sends hello messages to the neighbor.
- Passive: the router responds to hello messages but does not send hello messages.
Configuration
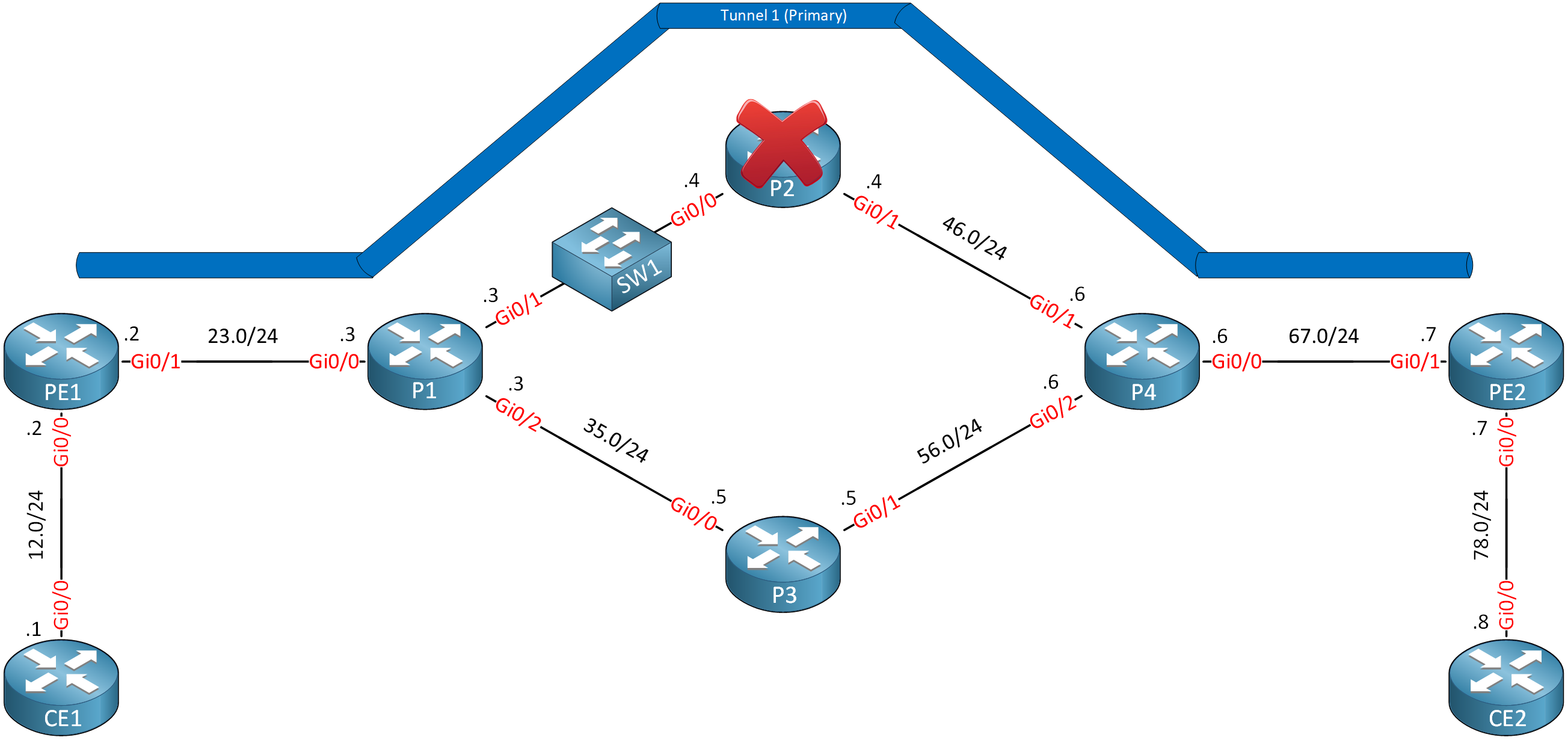
Let’s look at RSVP hello’s in action. This is the topology:
This is the topology and configuration we used in MPLS TE FRR node protection. We have a tunnel from PE1 to PE2 through P2. We’ll configure RSVP hellos between P1 and P2. We’ll simulate a node failure of P2 by blocking these RSVP hello messages, causing a fast reroute.
I use IOSv Software (VIOS-ADVENTERPRISEK9-M), Version 15.9(3)M4
Configurations
Want to take a look for yourself? Here you will find the startup configuration of each device.
CE1
hostname CE1
!
ip cef
!
interface Loopback0
ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255
ip router isis
isis circuit-type level-2-only
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0
ip address 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.0
ip router isis
isis circuit-type level-2-only
!
router isis
net 49.0001.0001.0001.0001.0001.00
is-type level-2-only
metric-style wide
!
endCE2
hostname CE2
!
ip cef
!
interface Loopback0
ip address 8.8.8.8 255.255.255.255
ip router isis
isis circuit-type level-2-only
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0
ip address 192.168.78.8 255.255.255.0
ip router isis
!
router isis
net 49.0001.0008.0008.0008.0008.00
is-type level-2-only
metric-style wide
!
endP1
hostname P1
!
ip cef
!
mpls traffic-eng tunnels
!
interface Loopback0
ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255
ip router isis
isis circuit-type level-2-only
!
interface Tunnel2
ip unnumbered Loopback0
tunnel mode mpls traffic-eng
tunnel destination 6.6.6.6
tunnel mpls traffic-eng priority 7 7
tunnel mpls traffic-eng bandwidth 750
tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option 1 explicit name INCLUDE_P3_P2
no routing dynamic
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0
ip address 192.168.23.3 255.255.255.0
ip router isis
mpls traffic-eng tunnels
mpls ip
isis circuit-type level-2-only
ip rsvp bandwidth 1000000
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
ip address 192.168.34.3 255.255.255.0
ip router isis
mpls traffic-eng tunnels
mpls traffic-eng backup-path Tunnel2
mpls ip
isis circuit-type level-2-only
ip rsvp bandwidth 1000000
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/2
ip address 192.168.35.3 255.255.255.0
ip router isis
mpls traffic-eng tunnels
mpls ip
isis circuit-type level-2-only
ip rsvp bandwidth 1000000
!
router isis
mpls traffic-eng router-id Loopback0
mpls traffic-eng level-2
net 49.0001.0003.0003.0003.0003.00
is-type level-2-only
metric-style wide
!
ip explicit-path name INCLUDE_P3_P2 enable
next-address 192.168.35.5
next-address loose 4.4.4.4
!
mpls ldp router-id Loopback0 force
!
endP2
hostname P2
!
ip cef
!
mpls traffic-eng tunnels
!
interface Loopback0
ip address 4.4.4.4 255.255.255.255
ip router isis
isis circuit-type level-2-only
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0
ip address 192.168.34.4 255.255.255.0
ip access-group NO_DSCP_CS5 in
ip router isis
mpls traffic-eng tunnels
mpls ip
isis circuit-type level-2-only
ip rsvp bandwidth 1000000
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
ip address 192.168.46.4 255.255.255.0
ip router isis
mpls traffic-eng tunnels
mpls ip
isis circuit-type level-2-only
ip rsvp bandwidth 1000000
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/2
ip address 192.168.45.4 255.255.255.0
ip router isis
mpls traffic-eng tunnels
mpls ip
isis circuit-type level-2-only
ip rsvp bandwidth 1000000
!
router isis
mpls traffic-eng router-id Loopback0
mpls traffic-eng level-2
net 49.0001.0004.0004.0004.0004.00
is-type level-2-only
metric-style wide
!
ip access-list extended NO_DSCP_CS5
deny ip any any dscp cs5
permit ip any any
!
mpls ldp router-id Loopback0 force
!
endP3
hostname P3
!
no logging console
!
ip cef
!
mpls traffic-eng tunnels
!
interface Loopback0
ip address 5.5.5.5 255.255.255.255
ip router isis
isis circuit-type level-2-only
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0
ip address 192.168.35.5 255.255.255.0
ip router isis
mpls traffic-eng tunnels
mpls ip
isis circuit-type level-2-only
ip rsvp bandwidth 1000000
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
ip address 192.168.56.5 255.255.255.0
ip router isis
mpls traffic-eng tunnels
mpls ip
isis circuit-type level-2-only
ip rsvp bandwidth 1000000
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/2
ip address 192.168.45.5 255.255.255.0
ip router isis
mpls traffic-eng tunnels
mpls ip
isis circuit-type level-2-only
ip rsvp bandwidth 1000000
!
router isis
mpls traffic-eng router-id Loopback0
mpls traffic-eng level-2
net 49.0001.0005.0005.0005.0005.00
is-type level-2-only
metric-style wide
!
mpls ldp router-id Loopback0 force
!
endP4
hostname P4
!
ip cef
!
mpls traffic-eng tunnels
!
interface Loopback0
ip address 6.6.6.6 255.255.255.255
ip router isis
isis circuit-type level-2-only
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0
ip address 192.168.67.6 255.255.255.0
ip router isis
mpls traffic-eng tunnels
mpls ip
isis circuit-type level-2-only
ip rsvp bandwidth 1000000
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
ip address 192.168.46.6 255.255.255.0
ip router isis
mpls traffic-eng tunnels
mpls ip
isis circuit-type level-2-only
ip rsvp bandwidth 1000000
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/2
ip address 192.168.56.6 255.255.255.0
ip router isis
mpls traffic-eng tunnels
mpls ip
isis circuit-type level-2-only
ip rsvp bandwidth 1000000
!
router isis
mpls traffic-eng router-id Loopback0
mpls traffic-eng level-2
net 49.0001.0006.0006.0006.0006.00
is-type level-2-only
metric-style wide
!
mpls ldp router-id Loopback0 force
!
endPE1
hostname PE1
!
ip cef
!
mpls traffic-eng tunnels
!
interface Loopback0
ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255
ip router isis
isis circuit-type level-2-only
!
interface Tunnel1
ip unnumbered Loopback0
tunnel mode mpls traffic-eng
tunnel destination 7.7.7.7
tunnel mpls traffic-eng autoroute announce
tunnel mpls traffic-eng priority 7 7
tunnel mpls traffic-eng bandwidth 750
tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option 1 explicit name EXCLUDE_P3
tunnel mpls traffic-eng fast-reroute
no routing dynamic
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0
ip address 192.168.12.2 255.255.255.0
ip router isis
isis circuit-type level-2-only
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
ip address 192.168.23.2 255.255.255.0
ip router isis
mpls traffic-eng tunnels
mpls ip
isis circuit-type level-2-only
ip rsvp bandwidth 1000000
!
router isis
mpls traffic-eng router-id Loopback0
mpls traffic-eng level-2
net 49.0001.0002.0002.0002.0002.00
is-type level-2-only
metric-style wide
!
ip explicit-path name EXCLUDE_P3 enable
exclude-address 5.5.5.5
!
mpls ldp router-id Loopback0 force
!
endPE2
hostname PE2
!
ip cef
!
mpls traffic-eng tunnels
!
interface Loopback0
ip address 7.7.7.7 255.255.255.255
ip router isis
isis circuit-type level-2-only
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0
ip address 192.168.78.7 255.255.255.0
ip router isis
isis circuit-type level-2-only
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
ip address 192.168.67.7 255.255.255.0
ip router isis
mpls traffic-eng tunnels
mpls ip
isis circuit-type level-2-only
ip rsvp bandwidth 1000000
!
router isis
mpls traffic-eng router-id Loopback0
mpls traffic-eng level-2
net 49.0001.0007.0007.0007.0007.00
is-type level-2-only
metric-style wide
!
mpls ldp router-id Loopback0 force
!
endFirst, we need to enable RSVP hello messages globally on both routers:
P1 & P2
(config)#ip rsvp signalling helloAnd we enable it on the interfaces:
P1(config)#interface GigabitEthernet 0/1
P1(config-if)#ip rsvp signalling hello P2(config)#interface GigabitEthernet 0/0
P2(config-if)#ip rsvp signalling helloThese are the only required commands to make this work.
ip rsvp signalling hello fast-reroute command. When you use these, commands are saved as ip rsvp signalling hello without fast-reroute.I will configure three additional commands:
P1(config)#interface GigabitEthernet 0/1
P1(config-if)#ip rsvp signalling hello refresh interval 400
P1(config-if)#ip rsvp signalling hello refresh misses 6
P1(config-if)#ip rsvp signalling hello dscp 40Here’s what it does:
- We send a hello message every 400 ms.
- We can miss six acknowledgments from our neighbor before we declare it down.
- We change the DSCP value to 40 (CS5).
Verification
Let’s verify our work. The show ip rsvp hello instance command tells us everything we need:
P1#show ip rsvp hello instance summary
Active Instances:
Client Neighbor I/F State LostCnt LSPs Interval
FRR 192.168.34.4 Gi0/1 Up 10 1 400
Passive Instances:
- None -
Active = Actively tracking neighbor state on behalf of clients:
RR = ReRoute, FRR = Fast ReRoute, or GR = Graceful Restart
Passive = Responding to hello requests from neighborAbove, we see that P1 uses the active instance. We use RSVP hellos for fast reroute. Here is P2:
P2#show ip rsvp hello instance summary
Active Instances:
- None -
Passive Instances:
Neighbor I/F
192.168.34.3 Gi0/0
Active = Actively tracking neighbor state on behalf of clients:
RR = ReRoute, FRR = Fast ReRoute, or GR = Graceful Restart
Passive = Responding to hello requests from neighborP2 uses the passive instance. You can see some more details when you swap summary for detail:
P1#show ip rsvp hello instance detail
Neighbor 192.168.34.4 (router ID: 4.4.4.4) Source 192.168.34.3
Type: Active (sending requests)
I/F: GigabitEthernet0/1
State: Up (Since: 2022 December Wednesday 21 15:33:34 )
Clients: Fast Reroute
LSPs protecting: 1
Missed acks: 6, IP DSCP: 0x28
Refresh Interval (msec)
Configured: 400
Statistics: (from 106 samples)
Min: 400
Max: 400
Average: 400
Waverage: 400 (Weight = 0.8)
Current: 400
Last sent Src_instance: 0x74F2DEC1
Last recv nbr's Src_instance: 0xB4B9D9DB
Counters:
Communication with neighbor lost:
Num times: 10 (last time at 1d01h)
Reasons:
Missed acks: 9
Bad Src_Inst received: 0
Bad Dst_Inst received: 0
I/F went down: 0
Neighbor disabled Hello: 1
Msgs Received: 193458
Sent: 193987
Suppressed: 0Above, you see the optional values that we configured. The output on P2 is simpler because it’s a passive instance:
P2#show ip rsvp hello instance detail
Neighbor 192.168.34.3 (router ID: 3.3.3.3) Source 192.168.34.4
Type: Passive (responding to requests)
I/F: GigabitEthernet0/0
Last sent Src_instance: 0xB4B9D9DB
Last recv nbr's Src_instance: 0x74F2DEC1
Counters:
Msgs Received: 262
Sent: 262If you want to see what RSVP hello packets look like, take a look at this capture:
Packet Capture: MPLS TE FRR RSVP Hello Message
Fast Reroute
Now let’s figure out whether RSVP can trigger fast reroute. As you can see, I have a backup tunnel:


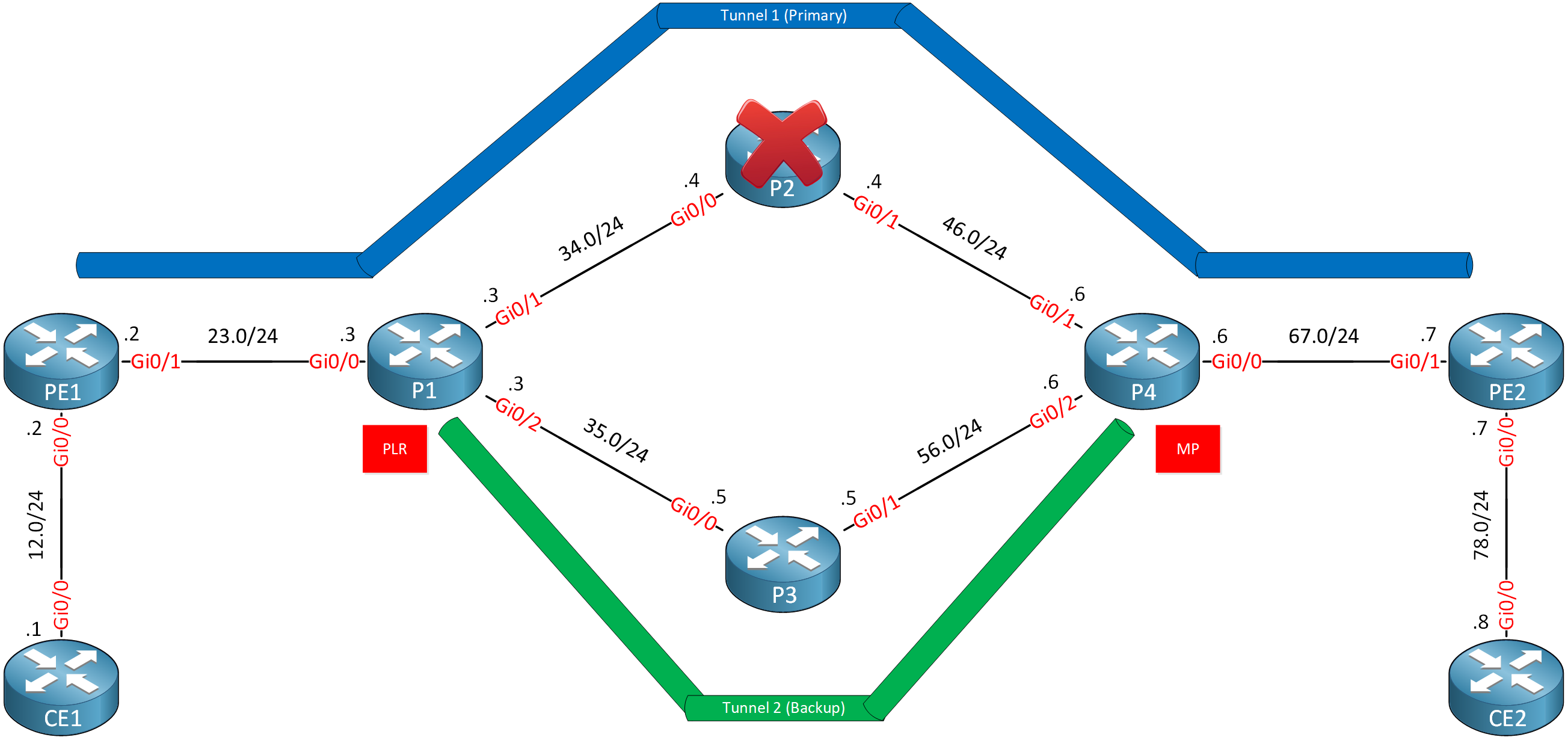

Hello Prisyla
Indeed, in the configuration of P1, we do see Tunnel2 configured with a tunnel destination of 4.4.4.4 which is P2, and it should be 6.6.6.6 which is P4. Thanks for pointing that out, I will let Rene know to take a look and consider making the necessary modifications.
Thanksa again!
Laz