Without network address translation (NAT) or port address translation (PAT), you probably wouldn’t be able to access the internet from your computer, or at least you’ll be the only one in the house having internet access…in this lesson, I want to give you an explanation of why and how we use NAT/PAT for Internet access.
Let’s start with a topology:
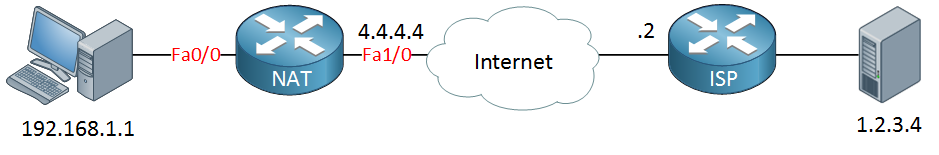
On the left side, we have a computer on our LAN with the IP address 192.168.1.1 connected to a router. From our ISP, we got the IP address 4.4.4.4, and there’s a server on the Internet using IP address 1.2.3.4. If our computer sends something to the server what would be the source and destination IP address of the IP packet, it will send?
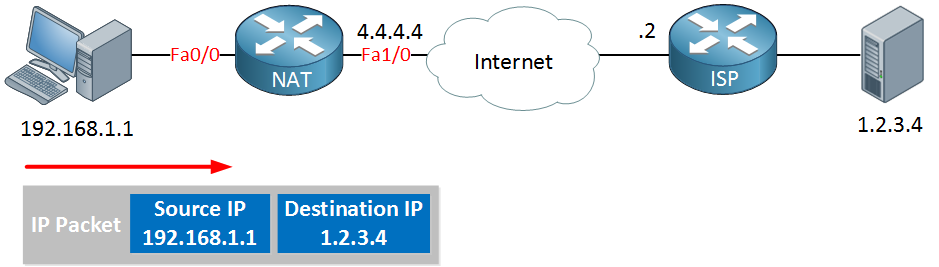
The source IP address will be our computer, and the destination IP address will be the server as you can see in the IP packet in the picture above.
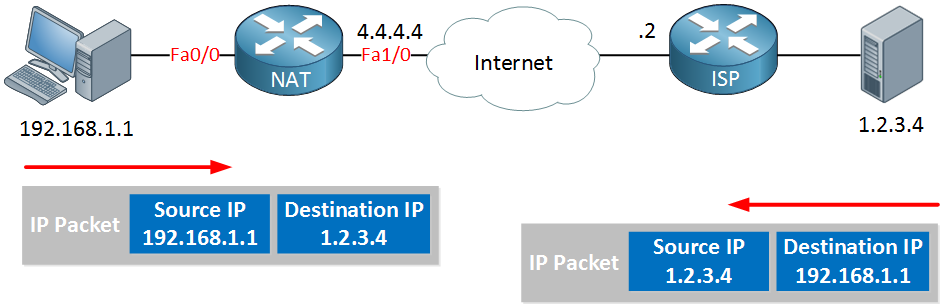
Once our server responds, it will create an IP packet specifying the computer’s IP address as the destination, and the source IP address will be its own IP address.
Is there anything wrong with this example? No, it’s perfectly fine except for one detail…the IP address of the computer and the IP address on the router are private IP addresses. Private IP addresses are meant for our LANs and public IP addresses are for the Internet.
This time we will configure NAT (Network Address Translation) and see what the difference is…



Hello Rene,
Great video. I have a suggestion please. Can you start doing like a CCIE video series, many people understand better with videos and the way you explain topics is very great and straight forward, i hope you can implement this idea which will be so great. thanks
Ammar,
Hi Ammar,
Glad to hear you like it. About the videos, I will. My goal is to have a video for each of the tutorials I have.
Rene
Hello Rene,
That would be perfect. People like videos and prefer them more that going through books haha , i am looking forward for the videos. Thanks
If we already have dynamic NAT then why there is a need for PAT?
When you use dynamic NAT, you require a pool with public IP addresses. Each host that gets translated requires a public IP address from the pool.
PAT allows us to translate multiple private IP addresses to a single public IP address.