Stateless autoconfiguration for IPv6 is like a “mini-DHCP” server for IPv6. Routers running IPv6 can give the prefix of the network and a gateway address to clients looking for an IPv6 address. IPv6 uses the NDP (Neighbor Discovery Protocol), and one of the things this protocol offers is RS (Route Solicitation and (RA) Router Advertisement messages that help an IPv6 device configure an IPv6 address automatically. Let’s take a look at a configuration example:
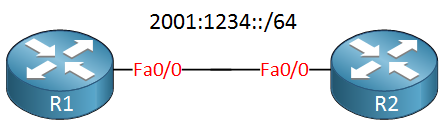
I will use two routers to show you how stateless autoconfiguration works. R2 will have an IPv6 address and is going to send router advertisements. R1 will use this to configure its own IPv6 address.
R2(config)#ipv6 unicast-routing
R2(config)#interface fastEthernet 0/0
R2(config-if)#ipv6 address 2001:1234::/64 eui-64Besides configuring an IPv6 address, we must use the ipv6 unicast-routing command to make R2 act like a router. Remember this command since you need it for routing protocols as well.
R1(config)#interface fastEthernet 0/0
R1(config-if)#ipv6 address autoconfigWe need to enable ipv6 address autoconfig on R1 to make sure it generates its own IPv6 address.
R1#debug ipv6 nd
ICMP Neighbor Discovery events debugging is onR2#debug ipv6 nd
ICMP Neighbor Discovery events debugging is onWe can use debug ipv6 nd to watch the whole process.



Good article…
Making it a little more comprehensive will make it a lot better and one of the best learning source especially for starters.
Thanks. I’ll add some more IPv6 stuff in the feature, especially since the new CCNA exams cover much more IPv6 then the previous version.
good article. But I could not get ipv6 address from my neighbor router in gns3 ((
Did you enable the interfaces? It worked fine on a couple of 3600 routers in GNS3.
it works for me. using 7200