In this lesson, we’ll take a look at static routes and in particular, how to configure them.
Let me show you the following topology:
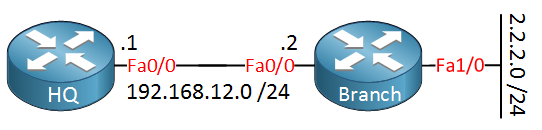
Look at the network in the picture above. We have a network with two sites, headquarters, and a branch office.
The headquarters is connected to the Branch office. Behind the branch office is a network with the 2.2.2.0 /24 network. We want to ensure that the headquarters can reach the 2.2.2.0 /24 network.
Let me show you how we configure this network using a static route:
HQ>enable
HQ#configure terminalFirst, I’ll go to enable mode and enter configuration mode.
HQ(config)#interface FastEthernet 0/0
HQ(config-if)#no shutdown
HQ(config-if)#ip address 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.0Branch>enable
Branch#configure terminal
Branch(config)#interface fastEthernet0/0
Branch(config-if)#no shutdown
Branch(config-if)#ip address 192.168.12.2 255.255.255.0
Branch(config-if)#exit
Branch(config)#interface fastEthernet 1/0
Branch(config-if)#no shutdown
Branch(config-if)#ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.0Then I’ll configure the IP addresses on the interfaces; don’t forget to do a no shutdown on the interfaces.
Let’s take a look at the routing tables of both routers:
HQ#show ip route
Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1,
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default,
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
C 192.168.12.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0Branch#show ip route
Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1,
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
C 192.168.12.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
2.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
C 2.2.2.0 is directly connected, FastEthernet1/0Use the show ip route command to view the routing table. This is what a router uses to make decisions about where to forward IP packets to. By default, a router only knows its directly connected networks. We configured an IP address with a subnet mask on the interface, so the router also knows the network address.
- Router HQ knows about network 192.168.12.0/24.
- Router Branch knows about network 192.168.12.0/24 and 2.2.2.0/24.
At this moment our HQ router has no idea how to reach network 2.2.2.0/24 because there is no entry in the routing table. What will happen when we try to reach it? Let’s check:



Hello Renne,
What does " 2.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets" mean in below output?
... Continue reading in our forum
Hi Rajagopal,
2.0.0.0 /8 is a class A network and 2.2.2.0 /24 is a “subnet” of this class A network.
The routing table will always show the class A network address (2.0.0.0 /8) and the subnets below it (2.2.2.0 /24).
Hope that helps!
Rene
How could you find the current non-used IP addresses in your LAN?. Is it safe to take any of them?
When you assign static IP addresses to devices then you should always keep track which devices are using which IP addresses. Otherwise you might find yourself one day assigning duplicate IP addresses to your devices.
If you want to find all devices in your LAN then you could try a tool like “nmap” (network scanner).
Hi Rene
I set up a simple network PC1 <-> R1 <-> R2 <-> PC2
All the static routes are implemented, pings work from PC1 to PC2. However when i do a trace from PC2 to PC1 or vice versa, I always get the (ICMP type:3, code:3, Destination port unreachable) at the end of the route hop.
I know that the t
... Continue reading in our forum