Lesson Contents
OSPF uses LSA type 3 for inter-area prefixes. If you want, you can filter these between OSPF areas. Since you can only filter between areas, you’ll have to configure this on the ABR. Filtering is possible inbound or outbound an area using the area filter-list command.
In this lesson, I will demonstrate how to use this command to filter LSA type 3 between different areas. This is the topology that I will be using:
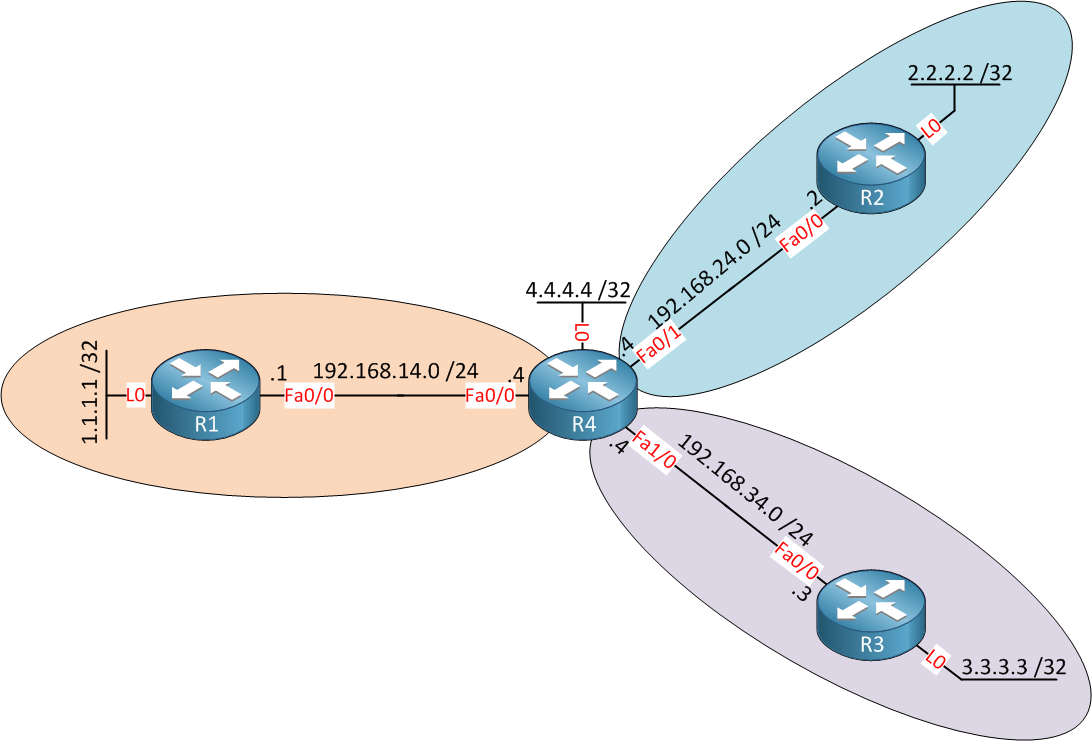
R1, R2, and R3 are located in their corresponding area number and have a loopback 0 interface. The prefix on this loopback will be advertised in OSPF. In the middle, you can see R4, the ABR for areas 1,2 and 3. We’ll create some filters on R4 to demonstrate the area filter-list command. Let me show you the OSPF configuration first:
OSPF Area Configuration
I will show you all the network commands I used so you can replicate this. R1,R2 and R3 will be in their own area and R4 is the ABR:
R1(config)#router ospf 1
R1(config-router)#network 1.1.1.1 0.0.0.0 area 1
R1(config-router)#network 192.168.14.0 0.0.0.255 area 1R2(config)#router ospf 1
R2(config-router)#network 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0 area 2
R2(config-router)#network 192.168.24.0 0.0.0.255 area 2R3(config)#router ospf 1
R3(config-router)#network 3.3.3.3 0.0.0.0 area 3
R3(config-router)#network 192.168.34.0 0.0.0.255 area 3R4(config)#router ospf 1
R4(config-router)#network 4.4.4.4 0.0.0.0 area 0
R4(config-router)#network 192.168.14.0 0.0.0.255 area 1
R4(config-router)#network 192.168.24.0 0.0.0.255 area 2
R4(config-router)#network 192.168.34.0 0.0.0.255 area 3Before we continue, it’s best to verify that we have working OSPF neighbor adjacencies:
R4#show ip ospf neighbor
Neighbor ID Pri State Dead Time Address Interface
1.1.1.1 1 FULL/BDR 00:00:33 192.168.14.1 FastEthernet0/0
2.2.2.2 1 FULL/BDR 00:00:39 192.168.24.2 FastEthernet0/1
3.3.3.3 1 FULL/BDR 00:00:39 192.168.34.3 FastEthernet1/0The ABR has three working OSPF neighbor adjacencies. Now it’s time to create some filters. We’ll start with inbound filtering.
Inbound Area LSA Type 3 filtering
I will start by filtering some prefixes that are headed toward area 3. The inbound filter will filter prefixes from all areas sent to 1 area. First, we’ll take a look at the routing table of R3 in area 3:
R3#show ip route ospf
1.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
O IA 1.1.1.1 [110/3] via 192.168.34.4, 00:03:50, FastEthernet0/0
2.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
O IA 2.2.2.2 [110/3] via 192.168.34.4, 00:03:50, FastEthernet0/0
O IA 192.168.14.0/24 [110/2] via 192.168.34.4, 00:03:50, FastEthernet0/0
4.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
O IA 4.4.4.4 [110/2] via 192.168.34.4, 00:03:50, FastEthernet0/0
O IA 192.168.24.0/24 [110/2] via 192.168.34.4, 00:03:50, FastEthernet0/0All prefixes that R3 has learned are inter-area prefixes (LSA Type 3). Let’s filter 2.2.2.2 /32 from entering area 3. First, we’ll create a prefix-list:
R4(config)#ip prefix-list INTO-AREA3 deny 2.2.2.2/32
R4(config)#ip prefix-list INTO-AREA3 permit 0.0.0.0/0 le 32This prefix-list will deny 2.2.2.2 /32 and allow all other prefixes. Now we have to apply it to the area:
R4(config)#router ospf 1
R4(config-router)#area 3 filter-list prefix INTO-AREA3 inIf you want, you can verify that the area filter is active with the show ip ospf command:
R4#show ip ospf 1 | begin Area 3
Area 3
Number of interfaces in this area is 1
Area has no authentication
SPF algorithm last executed 00:01:50.060 ago
SPF algorithm executed 3 times
Area ranges are
Area-filter INTO-AREA3 in
Number of LSA 5. Checksum Sum 0x03C737
Number of opaque link LSA 0. Checksum Sum 0x000000
Number of DCbitless LSA 0
Number of indication LSA 0
Number of DoNotAge LSA 0
Flood list length 0Now take a look at the routing table of R3 again:
R3#show ip route ospf
1.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
O IA 1.1.1.1 [110/3] via 192.168.34.4, 00:07:19, FastEthernet0/0
4.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
O IA 4.4.4.4 [110/3] via 192.168.34.4, 00:07:19, FastEthernet0/0
O IA 192.168.14.0/24 [110/2] via 192.168.34.4, 00:07:19, FastEthernet0/0
O IA 192.168.24.0/24 [110/2] via 192.168.34.4, 00:07:19, FastEthernet0/0Prefix 2.2.2.2 /32 is gone from the routing table as it has been filtered by the ABR (R4). The nice thing about inbound filtering is that it doesn’t matter from which area the prefix came. Everything that goes into area 3 will hit the prefix-list and will be filtered. I can demonstrate this to you by filtering something else, for example, the two prefixes 192.168.14.0 /24 (area 1) and 192.168.24.0 /24 (area 2). Let’s change our prefix-list:
R4(config)#ip prefix-list INTO-AREA3 seq 6 deny 192.168.14.0/24
R4(config)#ip prefix-list INTO-AREA3 seq 7 deny 192.168.24.0/24Now take a look again at the routing table of R3:
R3#show ip route ospf
1.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
O IA 1.1.1.1 [110/3] via 192.168.34.4, 00:01:22, FastEthernet0/0
4.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
O IA 4.4.4.4 [110/3] via 192.168.34.4, 00:01:22, FastEthernet0/0The 192.168.14.0 /24 and 192.168.24.0 /24 prefixes are now gone from the routing table. It doesn’t matter which area they come from…
Configurations
Want to take a look for yourself? Here you will find the final configuration of each device.
R1
hostname R1
!
interface Loopback0
ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255
!
interface FastEthernet0/0
ip address 192.168.14.1 255.255.255.0
!
router ospf 1
network 1.1.1.1 0.0.0.0 area 1
network 192.168.14.0 0.0.0.255 area 1
!
endR2
hostname R2
!
interface Loopback0
ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255
!
interface FastEthernet0/0
ip address 192.168.24.2 255.255.255.0
!
router ospf 1
network 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0 area 2
network 192.168.24.0 0.0.0.255 area 2
!
endR3
hostname R3
!
interface Loopback0
ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255
!
interface FastEthernet0/0
ip address 192.168.34.3 255.255.255.0
!
router ospf 1
network 3.3.3.3 0.0.0.0 area 3
network 192.168.34.0 0.0.0.255 area 3
!
endR4
hostname R4
!
interface Loopback0
ip address 4.4.4.4 255.255.255.255
!
interface FastEthernet0/0
ip address 192.168.14.4 255.255.255.0
!
interface FastEthernet0/1
ip address 192.168.24.4 255.255.255.0
!
interface FastEthernet1/0
ip address 192.168.34.4 255.255.255.0
!
router ospf 1
area 3 filter-list prefix INTO-AREA3 in
network 4.4.4.4 0.0.0.0 area 0
network 192.168.14.0 0.0.0.255 area 1
network 192.168.24.0 0.0.0.255 area 2
network 192.168.34.0 0.0.0.255 area 3
!
ip prefix-list INTO-AREA3 seq 5 deny 2.2.2.2/32
ip prefix-list INTO-AREA3 seq 6 deny 192.168.14.0/24
ip prefix-list INTO-AREA3 seq 7 deny 192.168.24.0/24
ip prefix-list INTO-AREA3 seq 10 permit 0.0.0.0/0 le 32
!
endNow you know how inbound filtering works, let’s take a look at outbound filtering.
Outbound Area LSA Type 3 filtering
The outbound filter lets us filter a prefix from 1 area to all other areas. Let’s see if we can filter 3.3.3.3 /32 so that R1 and R2 won’t have it in their routing table anymore. First, we’ll verify if they have learned about this prefix:



Thank you Rene.
thank you Rene.
Hi Rene,
Is the prefix-list is included in the Routing manipulation or possible security such as access-list?
Is this material for CCNP or CCNA?
Thanks
Ael Irsal
Hi Ael,
Prefix-lists are CCNP material, you won’t find them in the CCNA exam(s).
Rene
Hi Rene,
It would be very useful if you can include with simulation labs using packet tracer .
btw, thanks for your demonstration..
thanks
ruby