Lesson Contents
When you reset the OSPF process, it drops all neighbor adjacencies. Other OSPF routers will have to rerun the SPF algorithm and figure out a new path in the network. With OSPF graceful restart, it allows you to restart the OSPF process on your router without dropping neighbor adjacencies. Your router will keep forwarding traffic while OSPF restarts and the network will not be interrupted.
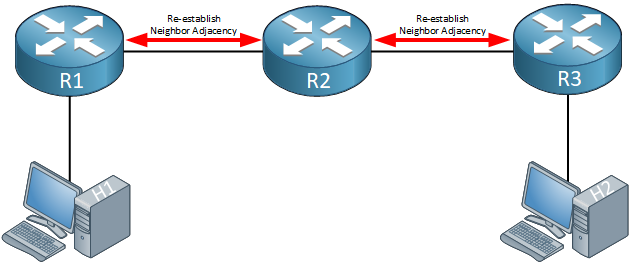
Here’s an example topology:
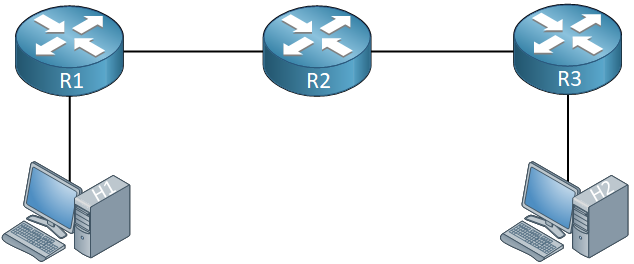
Above we have three routers and two hosts. If the OSPF process on R2 is reset, there is no way for R1 and R3 to reach each other anymore. H1 and H2 will be unable to exchange any data. If we use graceful restart on R2, forwarding will not be interrupted while R2 restarts its OSPF process.
How does it work?
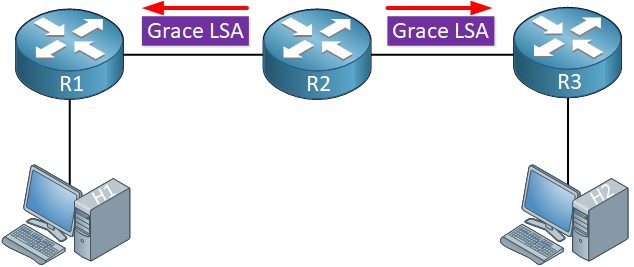
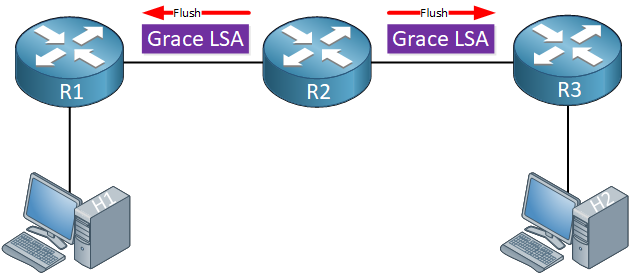
Graceful restart works by informing OSPF neighbors that it is going to restart. The router that is going to restart is called the restarting router, the restarting process is called the graceful restart mode. It starts by sending a link-local type 9 LSA called the grace LSA with a specified time called the grace period:
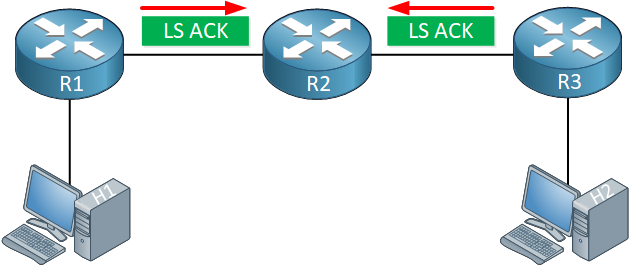
When the neighbors of R2 receive the grace LSA, they will respond with an acknowledgment:
R1 and R3, the neighbors of R2, are going to help with the graceful restart. These two routers will enter helper mode and are called the helper neighbors. During the grace period, R1 and R3 will act as if R2 is still out there even though they don’t receive any hello packets but will only do so if the topology doesn’t change during the graceful restart.
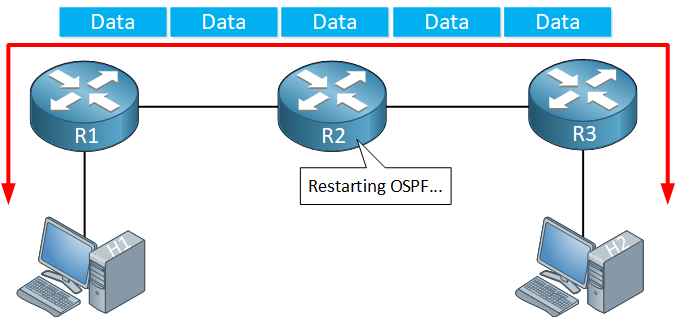
During the time that the router is restarting, there are no changes to the routing table and forwarding tables, so traffic will be forwarded as usual:
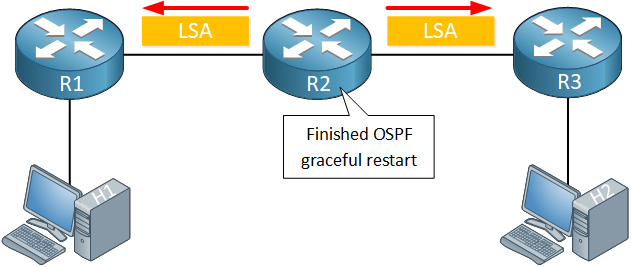
Once OSPF has restarted, it will re-establish neighbor adjacencies with the helper routers:
When the graceful restart has completed, the restarting router flushes the grace LSA. The restarting router continues with its regular OSPF tasks. It will re-originate its LSAs to its neighbors:
The restarting router continues with its regular OSPF tasks. It will re-originate its LSAs to its neighbors:
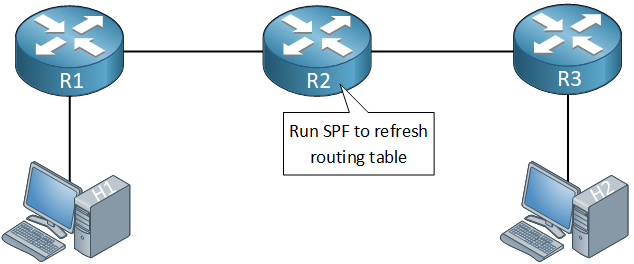
And it will rerun SPF to refresh the routing table:
R2 has now successfully restarted while there was no network downtime.
Most routers support helper mode but only routers with specific hardware support graceful restart. This is because routers require autonomous hardware for forwarding that is separated from the CPU. Cisco calls devices that support helper mode NSF-aware and devices that support graceful restart are called NSF-capable.
Now you have an idea of how OSPF graceful restart works, let’s add some more detail to this story.
Restarting Router
Entering graceful restart
Performing the graceful restart occurs when you use the appropriate command on a router that has OSPF graceful restart enabled. The grace period should not exceed the LSRefreshTime (1800 seconds) to avoid LSAs from aging out on the restarting router.
The restarting router enters the graceful restart by flooding the grace LSA. This is a type 9 LSA with a link-local scope. The grace LSA will be retransmitted until all adjacent neighbors have responded with an acknowledgment. If you don’t receive an acknowledgment from all neighbors, graceful restart will exit.
During graceful restart
During the graceful restart the restarting router will:
- Not originate any LSA types 1-5 and 7. The idea behind graceful restart is that other routers in the network will use the LSAs of the restarting router that were originated before the graceful restart.
- Not modify or flush any self-originated LSAs that it receives from neighbors.
- Run some calculations to restore virtual links if required but does not install new OSPF routes in the routing table. It will use the entries in the routing table from before the graceful restart.
- Elect itself as the DR (Designated Router) if it was the DR before the graceful restart. It knows that it was the DR by looking at the hello packet of a neighbor, which lists the restarting router as the DR on the segment.
Exiting graceful restart
The restarting router will exit the graceful restart if any of the following events occurs:



Hi Rene,
Thanks for your nice stuff .
So , how can we configure the Graceful restart and First we have to check the device is supported or not ?? Thx
br//zaman
Hello Zaman
You can find out about how to configure OSPF graceful restart at this Cisco Documentation. Note that OSPF graceful restart comes in two flavours: one which was implemented by Cisco, and one which is the IETF equivilent. Both can be implemented on Cisco devices. Because cisco Calls it Non Stop Forwarding, the command in both cases is
nsf.nsf ciscois used to implement the Cisco version whilensf ietfis use for the IETF version.Both commands are available in IOS version 12.2(33)SXH and later.
I hope this has been helpful!
Laz
Dear Agapides,
kindly,
- i have confuse about sentecnce “Once OSPF has restarted, it will re-establish neighbor adjacencies with the helper routers” it contradict ( sorry if wrong with using word I am not native), with concept of gracefull restart that neighbor adjacency is not down during ospf process restart..
... Continue reading in our forum2.usually i clear ospf process when i make change in LSDB using filtering or summerization or any thing else change LSDB ,so you mentioned if thers is changed in LSDB before & after gracefull restart , it terminate gracefull restart ( mean neighb
Dear Agapides,
from cisco documents,
During the NSF restart process, if neighbors that are not NSF-aware are detected on a network interface,NSF restart is aborted on the interface; however, NSF restart will continue on other interfaces.
is it mean if router 2 detect router 3 is non helpler capable " support or configure ",it will reset adj with r3 during restart ospf process ,keep traffic not interrup with R1 need your clearfication
Dear sir
kindlty, related with nsf ietf helper strict-lsa-checking, if defalut behavior when there have been changes in LSA type 1-5 and 7. helper mode will be exit ..why i need this command..