RIPNG is the exact same protocol as RIP for IPv4 but it has been upgraded to support IPv6. In this lesson i’ll demonstrate to you how to configure it on Cisco routers. Here’s the topology that we’ll use:
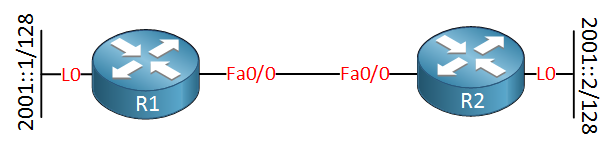
Let’s use this topology to configure RIPNG. I’m going to create a loopback interface on each router to advertise in RIPNG. Note that I don’t have any global unicast IPv6 addresses on the FastEthernet interface because the RIPNG updates will be sent using the link-local addresses.
R1(config)#ipv6 unicast-routing
R1(config)#interface loopback 0
R1(config-if)#ipv6 address 2001::1/128R2(config)#ipv6 unicast-routing
R2(config)#interface loopback 0
R2(config-if)#ipv6 address 2001::2/128Don’t forget to enable IPv6 unicast routing otherwise no routing protocol will work for IPv6.
R1#show ipv6 interface brief
FastEthernet0/0 [up/up]
Loopback0 [up/up]
FE80::CE09:18FF:FE0E:0
2001::1R2#show ipv6 interface brief
FastEthernet0/0 [up/up]
Loopback0 [up/up]
FE80::CE0A:18FF:FE0E:0
2001::2After configuring the IPv6 addresses on the loopback interface you can see the global unicast and the link-local IPv6 addresses. There is no link-local address on the FastEthernet interfaces however.
R1(config)#interface fastEthernet 0/0
R1(config-if)#ipv6 enableR2(config)#interface fastEthernet 0/0
R2(config-if)#ipv6 enableR1#show ipv6 interface brief
FastEthernet0/0 [up/up]
FE80::CE09:18FF:FE0E:0
Loopback0 [up/up]
FE80::CE09:18FF:FE0E:0
2001::1R2#show ipv6 interface brief
FastEthernet0/0 [up/up]
FE80::CE0A:18FF:FE0E:0
Loopback0 [up/up]
FE80::CE0A:18FF:FE0E:0
2001::2Use the IPv6 enable command to generate a link-local address for the FastEthernet interfaces.
R1(config)#ipv6 router rip RIPNGTEST
R1(config-rtr)#exit
R1(config)#interface fastEthernet 0/0
R1(config-if)#ipv6 rip RIPNGTEST enable
R1(config-if)#exit
R1(config)#interface loopback 0
R1(config-if)#ipv6 rip RIPNGTEST enableR2(config)#ipv6 router rip RIPNGTEST
R2(config-rtr)#exit
R2(config)#interface fastEthernet 0/0
R2(config-if)#ipv6 rip RIPNGTEST enable
R2(config-if)#exit
R2(config)#interface loopback 0
R2(config-if)#ipv6 rip RIPNGTEST enableTo enable RIPNG you first have to start the process with the IPV6 router rip command. You have to give it a tag name and I called mine “RIPNGTEST”.
It doesn’t matter what tag name you choose and it doesn’t have to be the same on both routers. Second step is to activate RIPNG on the interfaces you want by using the IPv6 rip enable command. That’s not too bad right? No stinky network commands! Just enable it on the interface and you are ready to go. The ipv6 rip enable command does two things:



awesome lesson. just a question rene, when we activate the RIP under the interface it does 2 things
Activate the prefix on the interface in RIPNG.
Send RIPNG updates out of this interface.
do we have a passive interface on this? is this the same as RIP or any routing protocol in IPv4 that if the interface is going to your LAN network, it is much better not to Send Routing updates to that interface. We suppressed it by using Passive Interface so that we will only advertise the network on that interface. This is for security purposes right?
Thank you!
Hi John,
Good question, the behavior of RIPng is the same as RIP for IPv4. The funny part though is that there is no “passive interface” command for RIPng.
To simulate the same behavior of the passive interface command you can use one of the following two methods:
Don’t enable RIPng on the interface that should be made passive but use “redistribute connect” instead.
Use a prefix-list to filter RIPng advertisements on the interface that should be passive.
It’s a bit lame and I don’t know why passive interface isn’t supported, but this gets you the same result
Rene
Hi Rene
Just a question, more of a general IPV6 question, why does a loopback interface generate the same link-local address as the physical interface. Yes I understand that the loopback don’t have it’s own mac address and will use the physical interface, but why doesn’t it cause a conflict on the local device, I was under the impression the link-local address must be unique on the llocal device:
... Continue reading in our forumHi Casper,
These link-local addresses are only valid on the link and unroutable so that’s why it is no problem to have the same address on multiple interfaces.
Rene
Is it possible to work with summarized routes in the dynamic routing protocol, as well as in static routing?