Cisco IOS routers and layer 3 switches can be configured as DHCP servers. It’s quite easy to do this and in this short lesson, I want to explain to you how to do this and how to verify your configuration. If you are a little fuzzy about how DHCP works, take a look at my introduction to DHCP first.
Let’s use the following topology:
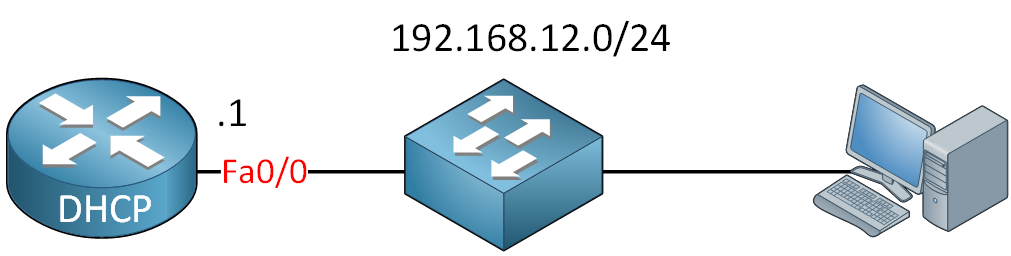
Above, we have a router that I will call ‘DHCP’. The router and computer are connected to each other using a simple switch and in the same VLAN. We will use the 192.168.12.0 /24 subnet for this demonstration. Let’s prepare the interface first:
DHCP(config)#interface fastEthernet 0/0
DHCP(config-if)#no shutdown
DHCP(config-if)#ip address 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.0Now let’s configure the DHCP server:
DHCP(config)#ip dhcp pool MYPOOL
DHCP(dhcp-config)#network 192.168.12.0 255.255.255.0Use the ip dhcp pool command to create a DHCP pool and give it a name. This DHCP pool will use network 192.168.12.0 /24. Basically, this is all you have to do to get the DHCP server going, there is no need to start a service or something. We can verify that we have DHCP clients using the following command:
DHCP#show ip dhcp binding
Bindings from all pools not associated with VRF:
IP address Client-ID/ Lease expiration Type
Hardware address/
User name
192.168.12.2 0063.6973.636f.2d63. Mar 02 2002 12:24 AM Automatic
6330.372e.3132.3265.
2e30.3030.302d.4661.
302f.30Above, you can see that we have a DHCP client that received IP address 192.168.12.2. In production networks, we will also use DHCP to hand out some other useful things like a default gateway, DNS server, and more. Let’s see how we can do this:
DHCP(config)#ip dhcp pool MYPOOL
DHCP(dhcp-config)#default-router 192.168.12.1
DHCP(dhcp-config)#dns-server 208.67.222.222Above, I configured the IP address 192.168.12.1 as the default gateway for the DHCP clients with the default-router command. The dns-server commands let us specify a DNS server.
Something else you might want to do is exclude some IP addresses. With the configuration so far, our DHCP server will hand out IP addresses .2,3,4,5,6, etc. Here’s how to do it:



Before you create the dhcp pool, you should configure the ip dhcp excluded-address command.
That’s always a good idea.
How i can configure a fast-Ethernet interface to act as a DHCP client? and, is there any configuration we need to do apart from the configuration you have shown in DHCP server for that?
Hi Rohan,
You can configure a FastEthernet interface to use DHCP client by using the “ip address dhcp” command under the interface.
That’s it…
Rene
thank you very good but i wanna to know Are the messages (discover,offer,request and ack ) still broadcast or change ?