Lesson Contents
In the Python installation lesson, I explained how to install Python on Windows, and we tried IDLE, the Python Integrated Development Environment (IDE) that comes with the installer.
Integrated Development and Learning Environment (IDLE) is the default editor that comes with the Python installer. It’s a simple IDE, but a great tool to get started with Python without being overwhelmed by features you don’t need or understand yet.
What exactly is an IDE? An IDE is a development environment that provides features that help you write code. Features like:
- Syntax highlighting: Highlight your code using different colors, making it easier to read.
- Auto-completion: Shows possible options when you type code, similar to how you use a keyboard on most mobile phones.
- Run Python code: Make it easier to run your code while you write it.
- Debugger: A debugger makes it easy to find errors in your code.
- Version Control System (VCS) support: Integrated client(s) to store your code in a VCS like Git.
There are many other features. For example, advanced Python IDEs let you run Python code through SSH, on Docker containers, etc.
Searching for the right IDE can be difficult. If you search on Google for “Best Python IDE,” you’ll find dozens of opinions and discussions about whether something is an IDE or an advanced text editor. The IDE of choice also depends on your work. For example, a data scientist might select an IDE with features that make machine learning or data analysis easier. Network or DevOps engineers might prefer a more lightweight IDE.
Technically, you could write all your Python code in Notepad and run it from the CLI. This works, but an IDE can make your life so much easier. As a beginner, it’s good to start with IDLE to learn the Python syntax. Once you understand the basics, it’s best to move on to something more advanced.
In this lesson, I’ll give you an overview of IDEs and IDE features that help to create Python code.
Visual Studio Code
Visual Studio Code is an open-source text editor / IDE, released by Microsoft. You can use Visual Studio Code for Windows, Linux, and Mac OS. Since its release in 2015, it has been a popular choice for many developers. It sits somewhere in between a lightweight IDE and a text editor on steroids.
There are many extensions you can use. This makes it an excellent choice for network or DevOps engineers. I use Visual Studio Code daily, and besides Python development, here are some of the extensions I use:
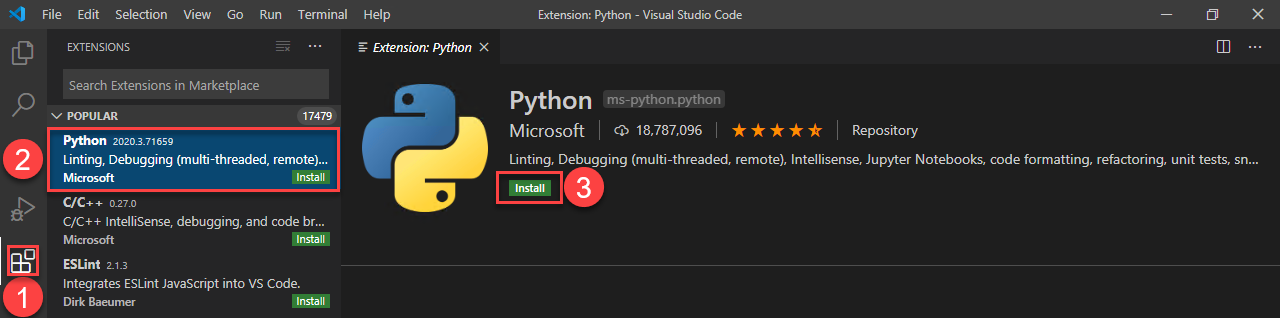
Let’s take a closer look at how we can use this IDE for Python code. Once you have installed Visual Studio code, we need to install the Python extension:
Click on the “Extensions” button on the left side, select Python, and click on the Install button. That’s all you need to do.
Features
Now let me show you some useful features we can use for Python code.
Code Linting
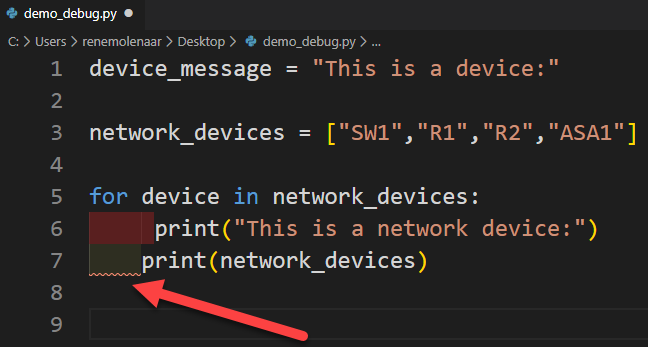
A linter analyzes your code for syntax and styling errors. If it finds any, it marks or flags the errors. A quick example is indentation. When you type code that has to be indented, Visual Studio Code automatically indents for you. When there are any indent errors, they show up:
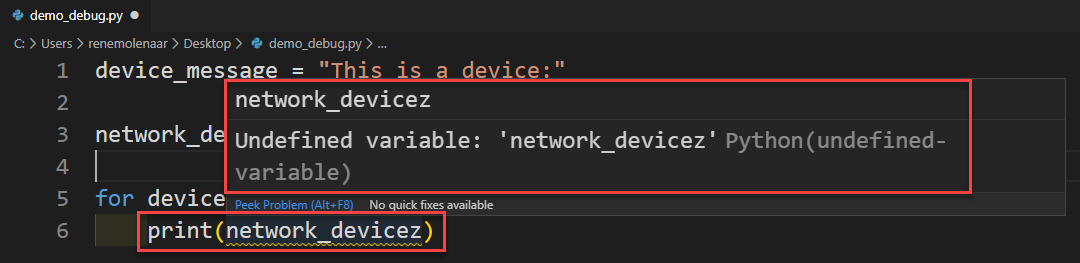
When you want to use a variable that you haven’t assigned yet, it shows up:
Code Completion
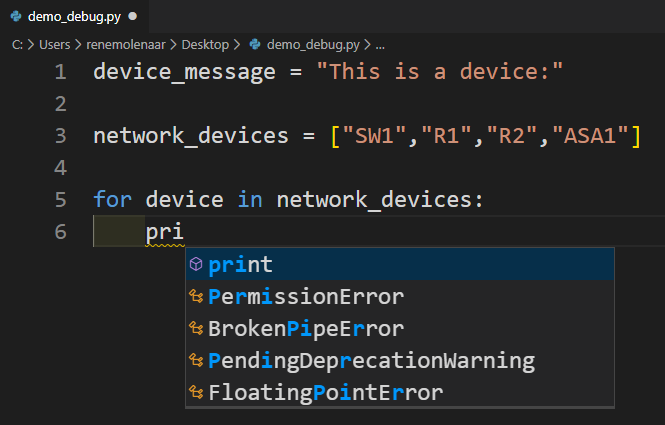
When you type code, Visual Studio Code autocompletes it for you:
This can reduce the amount you type but also helps with examples and snippets.
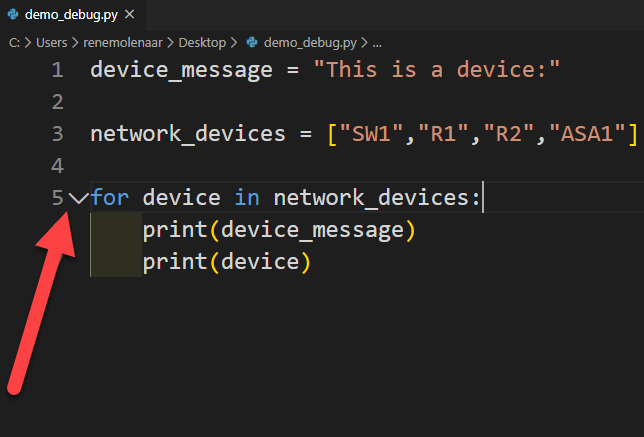
Collapse Code
Do you have a large loop somewhere in your code and want to get it out of the way for a second, so your code is easier to read? You can collapse your loops. Just click on the small arrow:
And it will look like this:
Debug
A decent debugger makes your life so much easier. Until now, you might have added some extra print commands in your code to see the output of a variable, list, or dictionary. With a debugger, you can “pause” and jump into your code at any moment and see the state of all variables.
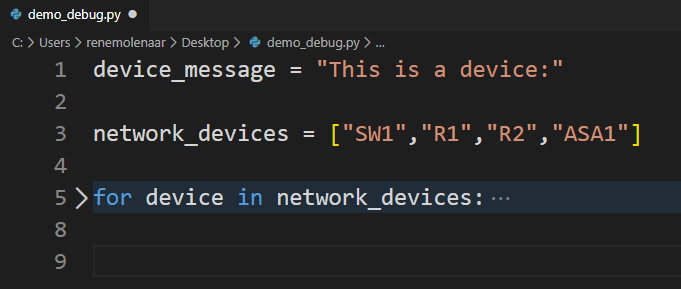
If you want to try this yourself, you can copy and paste the following code in a .py file and open it in Visual Studio Code:
device_message = "This is a device:"
network_devices = ["SW1","R1","R2","ASA1"]
for device in network_devices:
print(device_message)
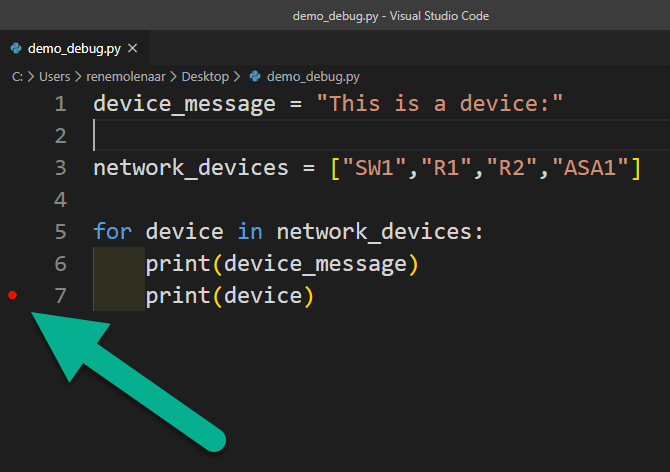
print(device)We debug code by adding a breakpoint. You need to click on the line where you want to pause your code:
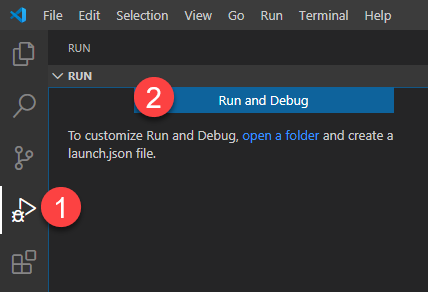
Click on the “Run” button in the left sidebar, then click on the “Run and Debug” button:
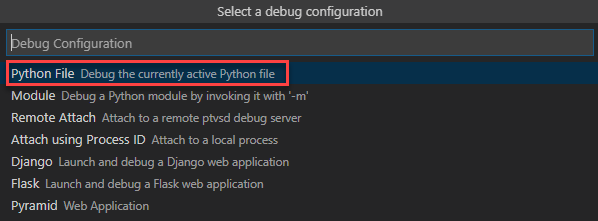
Visual Studio Code asks what you want to debug. Go for the first option (Python File) and hit enter:
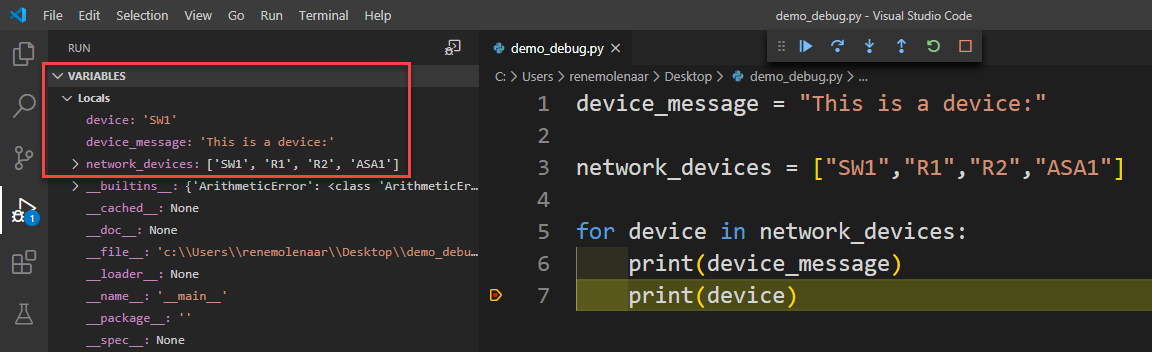
Our code now pauses at the breakpoint, which happens to be inside our for loop. On the left side, you can see the state of all variables:
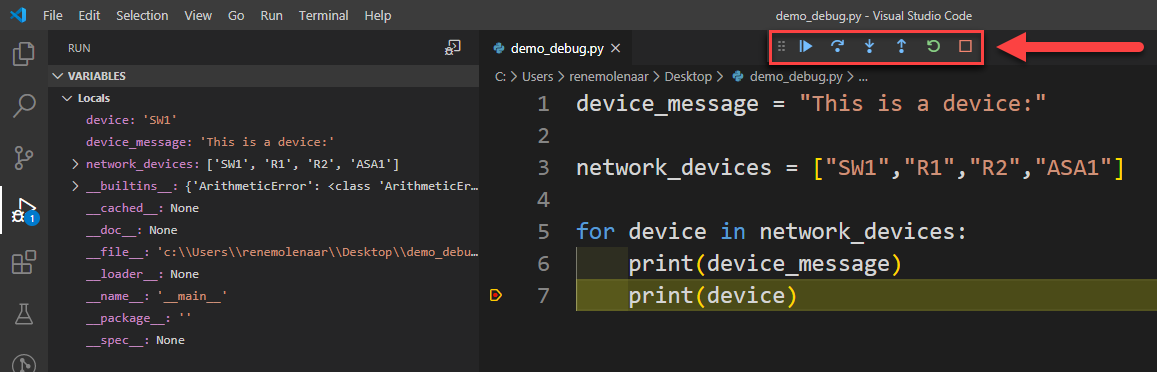
In the top middle of the editor, the “debug bar” appears. You can use this to take action. For example, the first button is for “continue,” which continues execution of your code until it hits the next breakpoint or when the program exits.
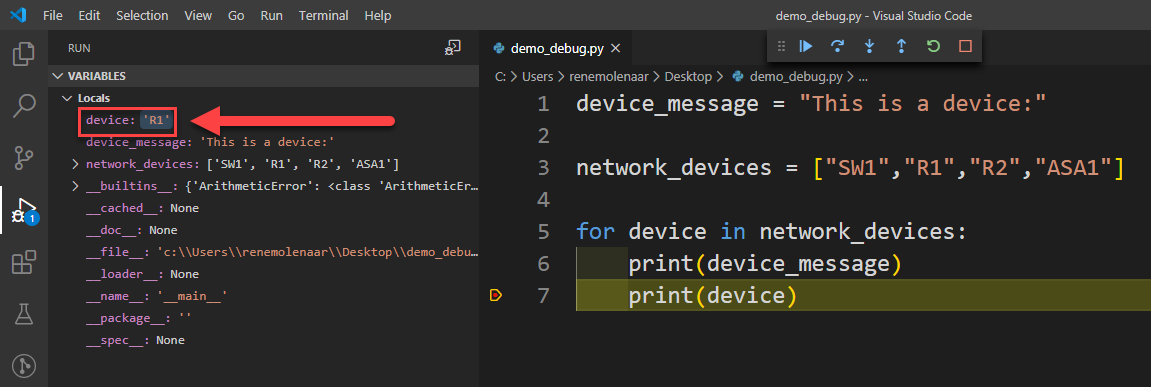
When I click on the first button (continue), the code continues until the next iteration of the for loop. On the left side, you can see that variable “device” is now R1 (the next item in the list we iterate):
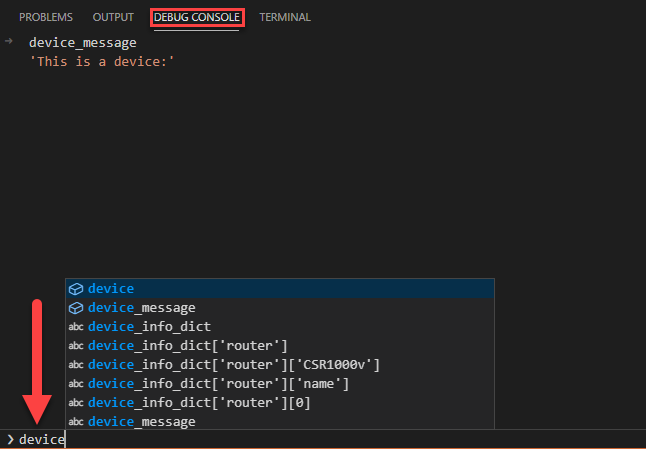
You can also open the debug console and type some Python code:
The debug console allows you to play with your code at the current state. Very useful to do some quick testing. Debugging your code like this makes it easier to see exactly what is going on within your program at any given moment.
Online IDE
You can also use an online IDE to code from your browser. In the Python installation lesson, An online IDE is an excellent way to run Python code without installing anything on your computer. You can also use it on any device you want.
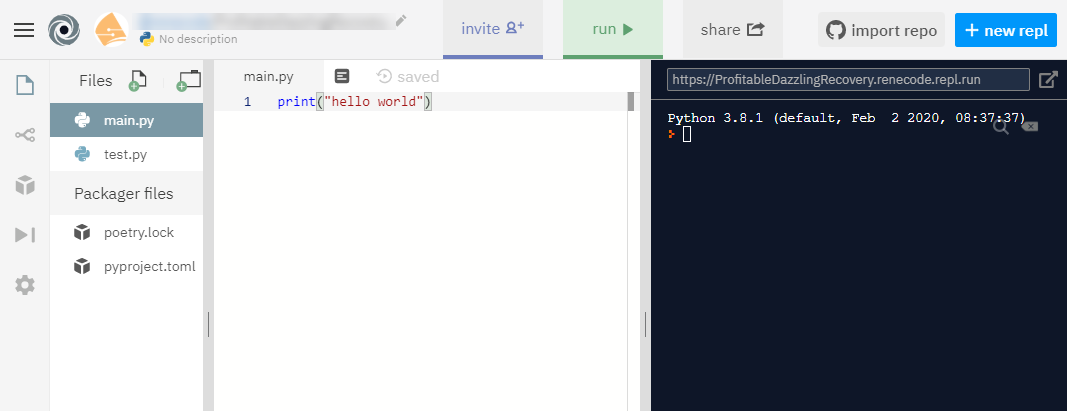
When you search on Google for online Python IDEs, you’ll find plenty. Another online IDE I like is repl.it. Here is a screenshot:
Here are some of the things you can do with repl.it:
- Create multiple files and folders, just like you would on a local device.
- Share your code with a link.
- Work together simultaneously on your code.
- Install Python packages.
- Debug your code.
Mobile
How about writing some code on your phone or tablet? You might not use these IDEs for hours of coding, but for some quick on-the-go testing or learning, it can be useful. You can try Pydroid for Android or Pythonista for Apple devices.
Conclusion
You have now learned what an IDE is and why we use them: