Lesson Contents
Out of the box spanning tree does a fine job creating a loop-free topology. There are a number of things that could go wrong, maybe you expect a certain output but your switches are telling you something different. Also because of misconfiguration some funky things can happen…let’s take a look at some scenarios. Here’s the topology we will use:
Incorrect Root Port
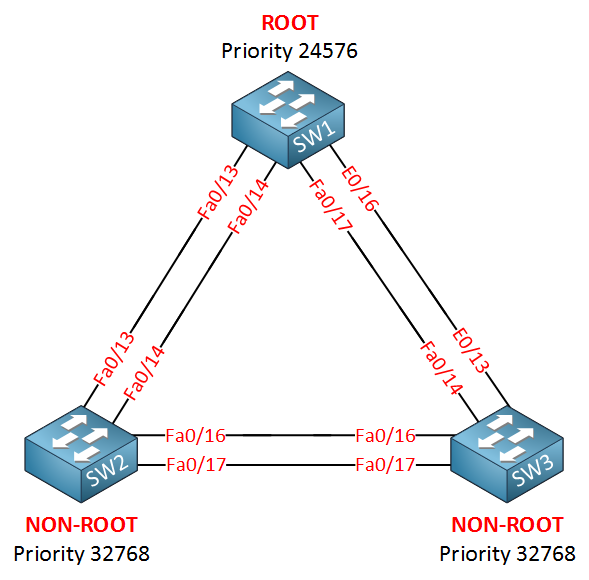
Three switches and between the switches we have two links for redundancy. SW1 has been elected as the root bridge for VLAN 1. When you are dealing with spanning tree it’s best to draw a small picture of the network and write down the interface roles for each switch (designated, non-designated/alternate or blocked). Note that one of the links between SW1 and SW3 is an Ethernet interface (10Mbit). All the other links are FastEthernet. Let’s take a closer loop at the spanning tree topology:
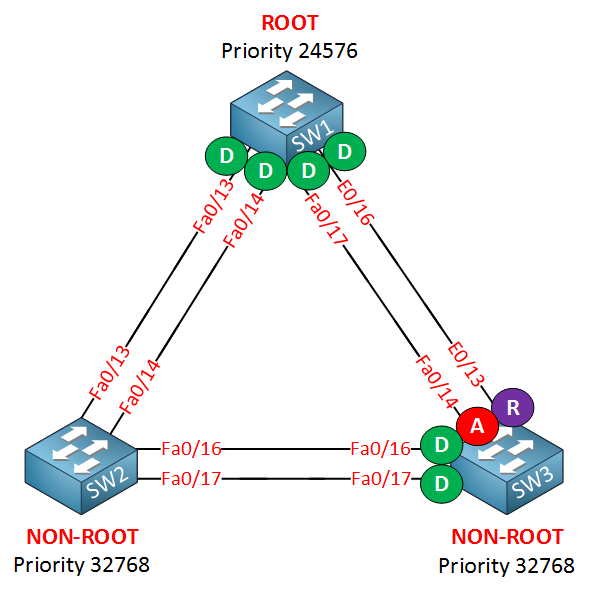
I used the show spanning-tree command to verify the interface roles for SW1 and SW3. As you can see SW3 has elected its Ethernet 0/13 interface as its root port and the FastEthernet 0/14 interface is elected as an alternate port. This is not a very good idea. It means we’ll send all traffic down the 10Mbit link while the 100Mbit is not used at all. When a switch has to elect a root port it will select one like this:
- Choose the interface that has the lowest cost to the root bridge.
- If the cost is equal, select the interface with the lowest port priority.
Normally the cost of an Ethernet interface is higher than FastEthernet so it should select the FastEthernet interface. Why did SW3 pick the Ethernet 0/13 interface?
SW3#show spanning-tree vlan 1
VLAN0001
Spanning tree enabled protocol ieee
Root ID Priority 24577
Address 0011.bb0b.3600
Cost 19
Port 13 (FastEthernet0/13)
Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Bridge ID Priority 32769 (priority 32768 sys-id-ext 1)
Address 000f.34ca.1000
Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Aging Time 15
Interface Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type
------------------- ---- --- --------- -------- --------------------------------
E0/13 Root FWD 19 128.13 P2p
Fa0/14 Altn BLK 19 128.14 P2p
Fa0/16 Desg FWD 19 128.16 P2p
Fa0/17 Desg FWD 19 128.17 P2pWe can see that the Ethernet 0/13 and FastEthernet 0/14 interface have the same cost. SW3 will then select the interface with the lowest port-priority which is interface Ethernet 0/13. Let’s check the interface:
SW3#show run interface fa0/13
Building configuration...
Current configuration : 102 bytes
!
Interface Ethernet0/13
switchport mode dynamic desirable
spanning-tree cost 19We’ll check the interface configuration and you can see that someone has changed the cost of the interface to 19 (the default for FastEthernet interfaces). Let’s get rid of this:
SW3(config)#interface Ethernet 0/13
SW3(config-if)#no spanning-tree cost 19Let’s get rid of the cost command and check the result:
SW3#show spanning-tree vlan 1
VLAN0001
Spanning tree enabled protocol ieee
Root ID Priority 24577
Address 0011.bb0b.3600
Cost 19
Port 14 (FastEthernet0/14)
Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Bridge ID Priority 32769 (priority 32768 sys-id-ext 1)
Address 000f.34ca.1000
Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Aging Time 15
Interface Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type
------------------- ---- --- --------- -------- --------------------------------
E0/13 Altn BLK 100 128.13 P2p
Fa0/14 Root FWD 19 128.14 P2p
Fa0/16 Desg FWD 19 128.16 P2p
Fa0/17 Desg FWD 19 128.17 P2pAfter we removed the cost command you can see that the port state has changed. FastEthernet 0/14 is now the root port and the cost of the Ethernet 0/13 interface is 100 (which is the default for Ethernet interfaces). Problem solved!
Lesson learned: Make sure the interface you want to be the root port has the lowest cost path to the root bridge!
Spanning Tree Disabled
Let’s look at a different scenario. We use the same topology:
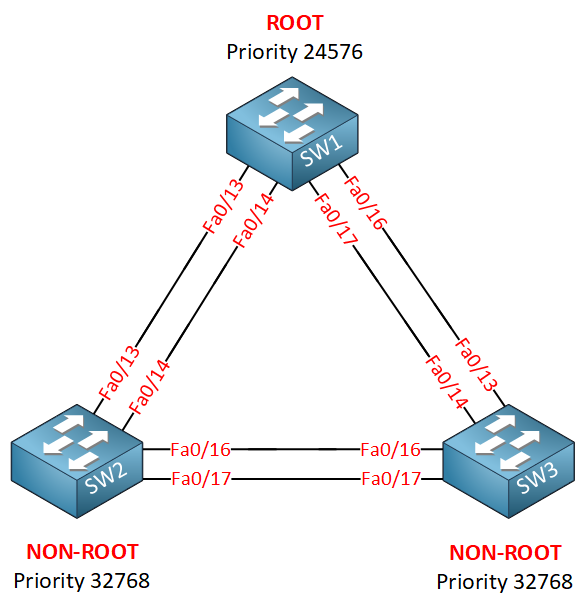
All the interfaces are equal (FastEthernet). SW1 is the root bridge for VLAN 10 and after checking the interface roles this is what we find:
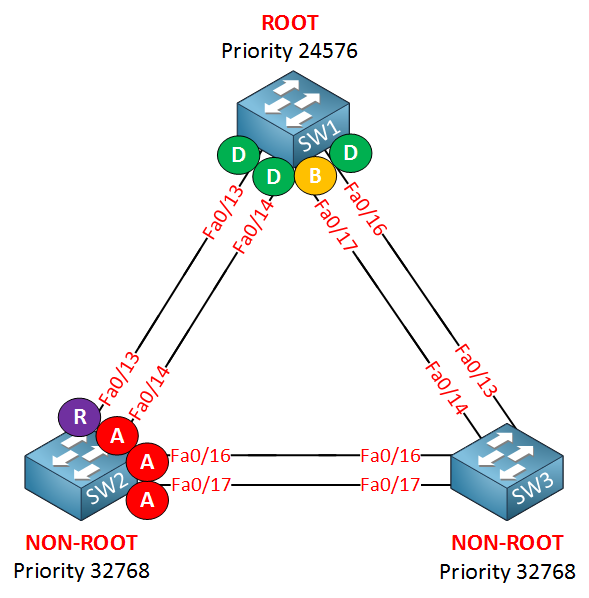
Hmm interesting…SW1 is the root bridge and FastEthernet 0/17 has been elected as a backup port. Now that’s something you don’t see every day. SW2 has elected a root port and all the other interfaces are alternate ports. I don’t see anything on SW3. Let’s take a look at the spanning tree of VLAN 10:
SW1#show spanning-tree vlan 10
VLAN0010
Spanning tree enabled protocol ieeeSW2#show spanning-tree vlan 10
VLAN0010
Spanning tree enabled protocol ieeeSW3#show spanning-tree vlan 10
Spanning tree instance(s) for vlan 10 does not exist.We can see that SW1 and SW2 are running spanning tree for VLAN 10. SW3 however is not running spanning tree for VLAN 10. What could be the issue? Just in case, let’s check the interfaces of SW3:
SW3#show interfaces fa0/13 | include line protocol
FastEthernet0/13 is up, line protocol is up (connected)SW3#show interfaces fa0/14 | include line protocol
FastEthernet0/14 is up, line protocol is up (connected)SW3#show interfaces fa0/16 | include line protocol
FastEthernet0/16 is up, line protocol is up (connected)SW3#show interfaces fa0/17 | include line protocol
FastEthernet0/16 is up, line protocol is up (connected)All interfaces are up and running, what about the trunk configuration?
SW3#show interfaces trunk
Port Mode Encapsulation Status Native vlan
Fa0/13 desirable n-isl trunking 1
Fa0/14 desirable n-isl trunking 1
Fa0/16 desirable n-isl trunking 1
Fa0/17 desirable n-isl trunking 1
Port Vlans allowed on trunk
Fa0/13 1-4094
Fa0/14 1-4094
Fa0/16 1-4094
Fa0/17 1-4094
Port Vlans allowed and active in management domain
Fa0/13 1,10
Fa0/14 1,10
Fa0/16 1,10
Fa0/17 1,10The interfaces are looking good, we have trunks and VLAN 10 is active on all interfaces of SW3. This means that spanning-tree should be active for VLAN 10.
SW3#show spanning-tree vlan 10
Spanning tree instance(s) for vlan 10 does not exist.Let’s take another look at this message. It says that spanning tree for VLAN 10 does not exist. There are two reasons why could see this message:
- There are no interfaces active for VLAN 10.
- Spanning tree has been disabled for VLAN 10.
We confirmed that VLAN 10 is active on all interfaces of SW3 so maybe spanning tree has been disabled globally? Let’s give it a try:
SW3(config)#spanning-tree vlan 10Let’s give it a shot by typing in spanning tree vlan 10 and verify our work:
SW3#show spanning-tree vlan 10
VLAN0010
Spanning tree enabled protocol ieee
Root ID Priority 24586
Address 0011.bb0b.3600
Cost 19
Port 13 (FastEthernet0/13)
Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Bridge ID Priority 32778 (priority 32768 sys-id-ext 10)
Address 000f.34ca.1000
Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Aging Time 300
Interface Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type
------------------- ---- --- --------- -------- --------------------------------
Fa0/13 Root FWD 19 128.13 P2p
Fa0/14 Altn BLK 19 128.14 P2p
Fa0/16 Desg FWD 19 128.16 P2p
Fa0/17 Desg FWD 19 128.17 P2pThere we go…that’s looking better! Spanning-tree is now enabled for VLAN 10 and is working…problem solved! This issue might sound a bit lame but I do see it every now and then in the real world. A scenario I encountered before is a customer that was told by their wireless vendor to disable spanning-tree for the interfaces that connect to the wireless access point. This is what the customer typed in on the switch:
SW3(config)#interface fa0/1
SW3(config-if)#no spanning-tree vlan 10On the interface they typed no spanning tree vlan 10 but you can see you end up in the global configuration mode. There is no command to disable spanning tree on the interface like this so the switch thinks you typed in the global command to disable spanning tree. The switch accepts the command, disabled spanning tree for VLAN 10 and kicks you back to global configuration mode…problem solved!
Lesson learned: Check if spanning-tree is enabled or disabled.
BPDUs Blocked
Onto the next exercise, same topology:

This time the customer is complaining about bad performance. Let’s start by verifying the spanning tree topology:
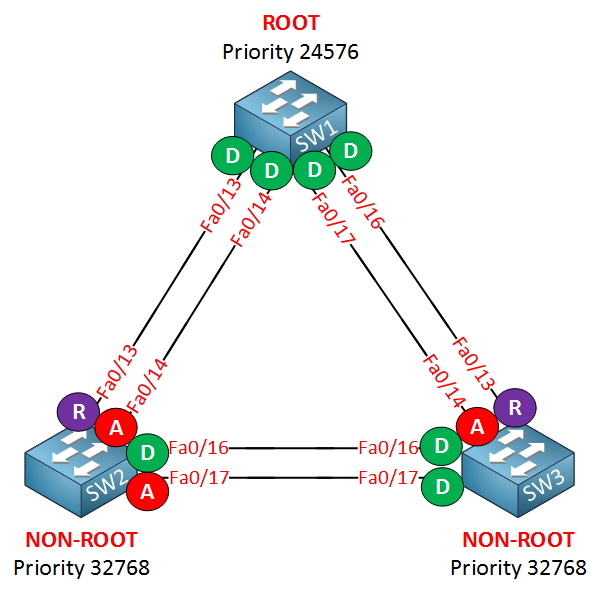
Take a look at the picture above. Do you see that Interface FastEthernet 0/16 on SW2 and SW3 are designated? On SW1 all interfaces are designated. What do you think happens once one of our switches forwards a broadcast or has to flood a frame? Bingo! We’ll have a loop…
Normally in this topology the FastEthernet 0/16 and 0/17 interfaces on SW3 should both be alternate ports because SW3 has the worst bridge ID. Since they are both designated we can assume that SW3 is not receiving BPDUs on these interfaces.
So why did spanning tree fail here? An important detail to remember here is that spanning tree requires BPDUs sent between the switches in order to create a loop-free topology. BPDUs can be filtered because of MAC access-lists, VLAN access-maps or maybe something from the spanning tree toolkit?
Let’s check all of these:
SW1#show vlan access-mapSW2#show vlan access-mapSW3#show vlan access-mapThere are no VLAN access maps on any of the switches. Any access-lists perhaps?
SW1#show access-listsSW2#show access-listsSW3#show access-listsThere are no access-lists…port-security maybe?
SW1#show port-security
Secure Port MaxSecureAddr CurrentAddr SecurityViolation Security Action
(Count) (Count) (Count)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Total Addresses in System (excluding one mac per port) : 0
Max Addresses limit in System (excluding one mac per port) : 6144SW2#show port-security
Secure Port MaxSecureAddr CurrentAddr SecurityViolation Security Action
(Count) (Count) (Count)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Total Addresses in System (excluding one mac per port) : 0
Max Addresses limit in System (excluding one mac per port) : 6144SW3#show port-security
Secure Port MaxSecureAddr CurrentAddr SecurityViolation Security Action
(Count) (Count) (Count)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Total Addresses in System (excluding one mac per port) : 0
Max Addresses limit in System (excluding one mac per port) : 6144There’s no port security…what about spanning tree related commands?
SW2#show spanning-tree interface fa0/16 detail | include filter
Bpdu filter is enabledSW2#show spanning-tree interface fa0/17 detail | include filter
Bpdu filter is enabledWe found something! BPDU filter has been enabled on the FastEthernet 0/16 and 0/17 interfaces of SW2. Because of this SW3 doesn’t receive BPDUs from SW2. Let’s get rid of this:
SW2(config)#interface fa0/16
SW2(config-if)#no spanning-tree bpdufilter enable
SW2(config-if)#interface fa0/17
SW2(config-if)#no spanning-tree bpdufilter enableAnd now we can check the spanning tree topology again:
SW3#show spanning-tree vlan 10 | begin Interface
Interface Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type
------------------- ---- --- --------- -------- --------------------------------
Fa0/13 Root FWD 19 128.13 P2p
Fa0/14 Altn BLK 19 128.14 P2p
Fa0/16 Altn BLK 19 128.16 P2p
Fa0/17 Altn BLK 19 128.17 P2pNow you can see that FastEthernet 0/16 and 0/17 are both alternate ports and blocking traffic. Our topology is now loop-free…problem solved!
Lesson learned: make sure BPDUs are not blocked or filtered between switches.
VLAN Inactive on Interface
I have one more spannng-tree issue for you, we use the same topology:

SW1 has been elected as the root bridge for VLAN 1. All the interfaces are FastEthernet links. Here’s what the port states look like:
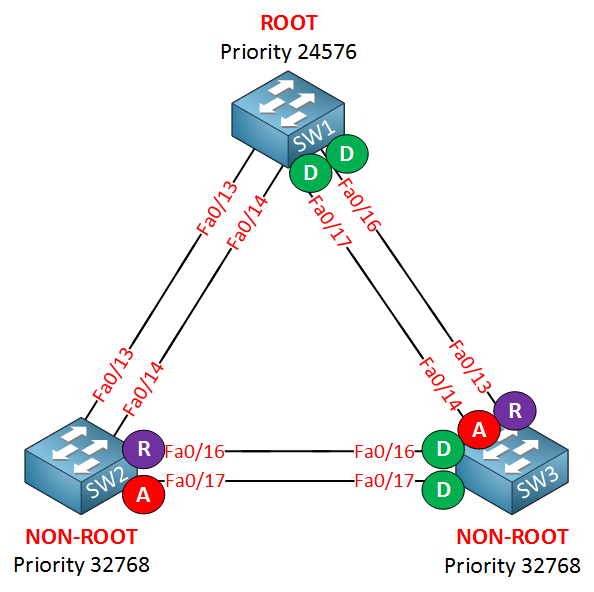
After using the show spanning tree vlan 10 command this is what we see. All interfaces are equal but for some reason SW2 decided to select FastEthernet 0/16 as its root port. Don’t you agree that FastEthernet 0/13 should be the root port? It has a lower cost to reach the root bridge than FastEthernet 0/16. Let’s take a closer look at SW2:
SW2#show spanning-tree interface fa0/13
Vlan Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type
------------------- ---- --- --------- -------- --------------------------------
VLAN0001 Root FWD 19 128.15 P2pSW2#show spanning-tree interface fa0/14
Vlan Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type
------------------- ---- --- --------- -------- --------------------------------
VLAN0001 Altn BLK 19 128.16 P2pWe can use the show spanning tree interface command to check the spanning tree information per interface. As you can see there’s only a spanning tree for VLAN 1 active on interface FastEthernet 0/13 and 0/14.
There are a number of things we could check to see what is going on:
SW2#show spanning-tree vlan 10
VLAN0010
Spanning tree enabled protocol ieee
Root ID Priority 24586
Address 0011.bb0b.3600
Cost 38
Port 18 (FastEthernet0/16)
Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Bridge ID Priority 32778 (priority 32768 sys-id-ext 10)
Address 0019.569d.5700
Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Aging Time 300
Interface Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type
------------------- ---- --- --------- -------- --------------------------------
Fa0/16 Root FWD 19 128.18 P2p
Fa0/17 Altn BLK 19 128.19 P2pFirst it’s always a good idea to check if spanning tree is active for a certain VLAN. It’s possible to disable spanning tree by using the no spanning tree vlan X command. In this scenario spanning tree is active for VLAN 10 because we can see FastEthernet 0/16 and 0/17. What other reason could there be that spanning tree doesn’t run on an interface? Let’s find out:
SW2#show interfaces fa0/13 switchport
Name: Fa0/13
Switchport: Enabled
Administrative Mode: dynamic auto
Operational Mode: static access
Administrative Trunking Encapsulation: negotiate
Operational Trunking Encapsulation: native
Negotiation of Trunking: On
Access Mode VLAN: 1 (default)SW2#show interfaces fa0/14 switchport
Name: Fa0/14
Switchport: Enabled
Administrative Mode: dynamic auto
Operational Mode: static access
Administrative Trunking Encapsulation: negotiate
Operational Trunking Encapsulation: native
Negotiation of Trunking: On
Access Mode VLAN: 1 (default)We know that spanning tree is active globally for VLAN 10 but that doesn’t mean it’s active on all interfaces. I can use the show interfaces switchport command to check if VLAN 10 is running on interface FastEthernet 0/13 and 0/14. This reveals us some interesting information. You can see that these interfaces ended up in access mode and they are in VLAN 1. Let’s turn these interfaces into trunks:
SW2(config)#interface fa0/13
SW2(config-if)#switchport mode trunk
SW2(config-if)#interface fa0/14
SW2(config-if)#switchport mode trunkLet’s change the interfaces to trunks so VLAN 10 traffic can flow through these interfaces. Now take a look at the spanning tree topology for VLAN 10:
SW2#show spanning-tree vlan 10
VLAN0010
Spanning tree enabled protocol ieee
Root ID Priority 24586
Address 0011.bb0b.3600
Cost 19
Port 15 (FastEthernet0/13)
Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Bridge ID Priority 32778 (priority 32768 sys-id-ext 10)
Address 0019.569d.5700
Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Aging Time 300
Interface Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type
------------------- ---- --- --------- -------- --------------------------------
Fa0/13 Root FWD 19 128.15 P2p
Fa0/14 Altn BLK 19 128.16 P2p
Fa0/16 Altn BLK 19 128.18 P2p
Fa0/17 Altn BLK 19 128.19 P2pThis is looking better. VLAN 10 traffic now runs on interface FastEthernet 0/13 and 0/14 and you can see that interface FastEthernet 0/13 is now elected as the root port. Problem solved!
Lesson learned: make sure the VLAN is active on the interface before looking at spanning tree related issues.
These are all the spanning tree issues I wanted to show you. Before you start looking at spanning tree commands you should verify that all your interfaces are operational and that the VLANs are active on your interface(s). Spanning tree relies on BPDUs that are exchanged between the switches so make sure these are not filtered. If you are still facing issues you should check the spanning tree configuration itself.
If you have any questions, feel free to leave a comment!


in the firs case…obviously you chanded the cost…because is more right…but to get the same thing I can change the priority of the por E0/13…or the priority of the port in switch A Fa0/17??
Hi Francesco,
You could achieve the same by changing the priority. Make sure you do this on the upstream switch though (Switch A and interface Fa0/17).
Rene
I had a question in the interview actually.
I have 3 Switches configured in the circle.
Switch 1 — 2 ----3
All Switches have 100 and 200 VLANs.
Switch 1 is root bridge for VLAN 100
After some time Switch 3 became root bridge for VLAN 100. Priority doesn’t change and no config changed.
SO what could be the other reasons can cause this?
Thank you in Advance.
Hi Ronak,
It’s the bridge ID that determines which switch will become the root bridge. The bridge ID consists of a priority and MAC address.
If the configuration didn’t change then probably the only thing that could have occurred is that one of the links went down. When SW3 doesn’t receiver superior BPDUs anymore, it can become the new root bridge.
Rene
SWITCHA ============ SWITCHB
We have 2 links, 1 link for ISP1 and 1 link for ISP 2
link of ISP2 is bundled on a port channel mode active, the link on ISP is just on a trunk port.
Question:
Will we experience a loop on that setup? one link in a portchannel bundle and 1 link that is not on port channel but on trunk port only.
Thank you.