IGMP version 3 adds support for “source filtering”. IGMP version 1 and version 2 allow hosts to join multicast groups but they don’t check the source of the traffic. Any source is able to receive traffic to the multicast group(s) that they joined.
With source filtering, we can join multicast groups but only from specified source addresses. IGMP version 3 is a requirement for SSM (Source Specific Multicast).
Why is this useful? Let me give you an example:
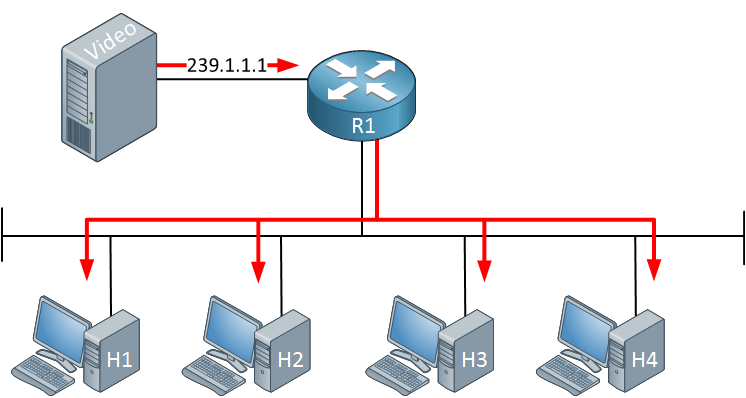
Above, we have a video server streaming multicast traffic on the network using destination address 239.1.1.1. Four hosts are listening to this traffic. Life is good. Suddenly, something happens:
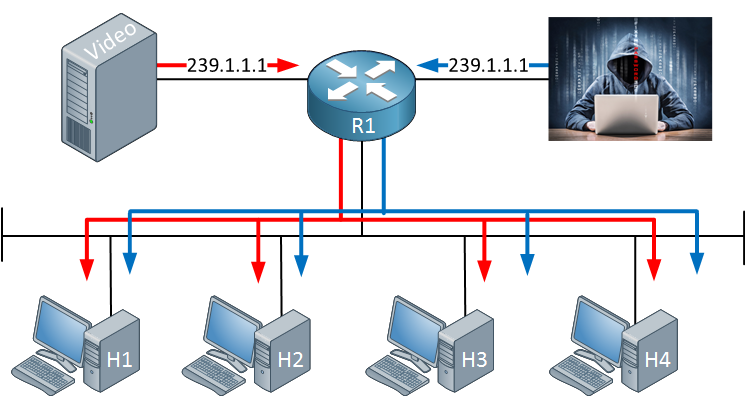
An attacker didn’t like the video stream and decided to stream his favorite video to destination address 239.1.1.1.1. Since we don’t check the source address, everyone will receive the traffic from our attacker. It’s also possible to send bogus traffic and create a DoS attack like this.
IGMP versions 1 and 2 don’t have any protection against this.
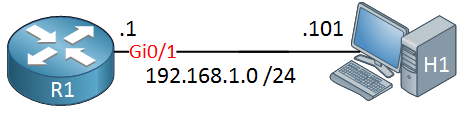
With IGMP version 3, our hosts can be configured to receive multicast traffic only from specified source addresses. Let’s see how this works. I’ll use the following topology for this:
We will only use two devices: one multicast-enabled router and a host device. I’m using a Cisco router as the host device as well.
Let’s start with R1:
R1(config)#ip multicast-routing
R1(config)#interface GigabitEthernet 0/1
R1(config-if)#ip pim sparse-mode
R1(config-if)#ip igmp version 3Our router requires multicast routing, and PIM should be enabled on the interface. The default version of IGMP is 2, so we’ll change it to version 3. Before we let H1 join a multicast group, let’s enable debugging on both devices:
R1 & H1#debug ip igmp
IGMP debugging is onR1 will start sending membership general queries like the one below:
Frame 1: 60 bytes on wire (480 bits), 60 bytes captured (480 bits) on interface 0
Ethernet II, Src: fa:16:3e:e4:d3:de (fa:16:3e:e4:d3:de), Dst: IPv4mcast_01 (01:00:5e:00:00:01)
Internet Protocol Version 4, Src: 192.168.1.1 (192.168.1.1), Dst: 224.0.0.1 (224.0.0.1)
Internet Group Management Protocol
[IGMP version: 3]
Type: Membership Query (0x11)
Max Resp Time: 10,0 sec (0x64)
Header checksum: 0xec5f [correct]
Multicast Address: 0.0.0.0 (0.0.0.0)
QRV=2 S=Do not suppress router side processing
.... 0... = S: Do not suppress router side processing
.... .010 = QRV: 2
QQIC: 60
Num Src: 0Let’s configure H1 to join a multicast group:
H1(config)#interface GigabitEthernet 0/1
H1(config-if)#ip igmp join-group 239.1.1.1 ?
source Include SSM source
<cr>Besides configuring a group, I can configure the host to include a source address. Let’s pick something:
H1(config-if)#ip igmp join-group 239.1.1.1 source 1.1.1.1H1 will now include the source address in its membership report messages. Here’s what you will see on the console:
H1#
IGMP(0): WAVL Insert group: 239.1.1.1 interface: GigabitEthernet0/1Successful
IGMP(0): Create source 1.1.1.1
IGMP(0): Building v3 Report on GigabitEthernet0/1
IGMP(0): Add Group Record for 239.1.1.1, type 5
IGMP(0): Add Source Record 1.1.1.1
IGMP(0): Add Group Record for 239.1.1.1, type 6
IGMP(0): No sources to add, group record removed from report
IGMP(0): Send unsolicited v3 Report with 1 group records on GigabitEthernet0/1
IGMP(0): Building v3 Report on GigabitEthernet0/1
IGMP(0): Add Group Record for 239.1.1.1, type 5
IGMP(0): Add Source Record 1.1.1.1
IGMP(0): Add Group Record for 239.1.1.1, type 6
IGMP(0): No sources to add, group record removed from report
IGMP(0): Send unsolicited v3 Report with 1 group records on GigabitEthernet0/1H1 sends two membership report messages. The first message includes the multicast group and source addresses we want to receive. The second message includes the “mode”. There are two modes:
- Include: this is a list of source addresses that we accept multicast traffic from. Everything else should not be forwarded.
- Exclude: this is a list of source addresses that we refuse to accept multicast traffic from. Everything else should be forwarded.
Here’s what it looks like in wireshark:
Frame 1: 58 bytes on wire (464 bits), 58 bytes captured (464 bits) on interface 0
Ethernet II, Src: fa:16:3e:35:d1:43 (fa:16:3e:35:d1:43), Dst: IPv4mcast_16 (01:00:5e:00:00:16)
Internet Protocol Version 4, Src: 192.168.1.101 (192.168.1.101), Dst: 224.0.0.22 (224.0.0.22)
Internet Group Management Protocol
[IGMP version: 3]
Type: Membership Report (0x22)
Header checksum: 0xe6f8 [correct]
Num Group Records: 1
Group Record : 239.1.1.1 Allow New Sources
Record Type: Allow New Sources (5)
Aux Data Len: 0
Num Src: 1
Multicast Address: 239.1.1.1 (239.1.1.1)
Source Address: 1.1.1.1 (1.1.1.1)Above, you can see that H1 wants to receive traffic from 239.1.1.1 from source 1.1.1.1. The destination for these membership reports is 224.0.0.22, the IGMP version 3 “all routers” group address. IGMP versions 1 and 2 use the multicast group address as the destination.
The next membership report from H1 tells the router to use include mode:
Frame 2: 58 bytes on wire (464 bits), 58 bytes captured (464 bits) on interface 0
Ethernet II, Src: fa:16:3e:35:d1:43 (fa:16:3e:35:d1:43), Dst: IPv4mcast_16 (01:00:5e:00:00:16)
Internet Protocol Version 4, Src: 192.168.1.101 (192.168.1.101), Dst: 224.0.0.22 (224.0.0.22)
Internet Group Management Protocol
[IGMP version: 3]
Type: Membership Report (0x22)
Header checksum: 0xeaf8 [correct]
Num Group Records: 1
Group Record : 239.1.1.1 Mode Is Include
Record Type: Mode Is Include (1)
Aux Data Len: 0
Num Src: 1
Multicast Address: 239.1.1.1 (239.1.1.1)
Source Address: 1.1.1.1 (1.1.1.1)Here’s what the debug looks like on R1:
R1#
IGMP(0): Received v3 Report for 1 group on GigabitEthernet0/1 from 192.168.1.101
IGMP(0): Received Group record for group 239.1.1.1, mode 5 from 192.168.1.101 for 1 sources
IGMP(0): WAVL Insert group: 239.1.1.1 interface: GigabitEthernet0/1Successful
IGMP(0): Create source 1.1.1.1
IGMP(0): Updating expiration time on (1.1.1.1,239.1.1.1) to 180 secs
IGMP(0): Setting source flags 4 on (1.1.1.1,239.1.1.1)
IGMP(0): MRT Add/Update GigabitEthernet0/1 for (*,239.1.1.1) by 0
IGMP(0): Received v3 Report for 1 group on GigabitEthernet0/1 from 192.168.1.101
IGMP(0): Received Group record for group 239.1.1.1, mode 5 from 192.168.1.101 for 1 sources
IGMP(0): Updating expiration time on (1.1.1.1,239.1.1.1) to 180 secs
IGMP(0): MRT Add/Update GigabitEthernet0/1 for (*,239.1.1.1) by 0R1 receives the membership reports from H1 and adds an entry in the multicast routing table. We can also verify this with the following command:
R1#show ip igmp groups 239.1.1.1 detail
Flags: L - Local, U - User, SG - Static Group, VG - Virtual Group,
SS - Static Source, VS - Virtual Source,
Ac - Group accounted towards access control limit
Interface: GigabitEthernet0/1
Group: 239.1.1.1
Flags:
Uptime: 00:12:27
Group mode: INCLUDE
Last reporter: 192.168.1.101
Group source list: (C - Cisco Src Report, U - URD, R - Remote, S - Static,
V - Virtual, M - SSM Mapping, L - Local,
Ac - Channel accounted towards access control limit)
Source Address Uptime v3 Exp CSR Exp Fwd Flags
1.1.1.1 00:12:27 00:02:27 stopped Yes RAbove, you can see that R1 keeps track of which multicast traffic it should forward and from which source addresses. The group mode is “include,” which is what H1 requested.
What happens when H1 leaves a group? Let’s find out:
H1(config)#interface Gigabit 0/1
H1(config-if)#no ip igmp join-group 239.1.1.1 source 1.1.1.1H1 will send a membership report to indicate that it doesn’t want to receive the multicast traffic from this source anymore:
Frame 1: 60 bytes on wire (480 bits), 60 bytes captured (480 bits) on interface 0
Ethernet II, Src: fa:16:3e:35:d1:43 (fa:16:3e:35:d1:43), Dst: IPv4mcast_16 (01:00:5e:00:00:16)
Internet Protocol Version 4, Src: 192.168.1.101 (192.168.1.101), Dst: 224.0.0.22 (224.0.0.22)
Version: 4
Header Length: 24 bytes
Differentiated Services Field: 0xc0 (DSCP 0x30: Class Selector 6; ECN: 0x00: Not-ECT (Not ECN-Capable Transport))
Total Length: 44
Identification: 0x0aaa (2730)
Flags: 0x00
Fragment offset: 0
Time to live: 1
Protocol: IGMP (2)
Header checksum: 0x773e [validation disabled]
Source: 192.168.1.101 (192.168.1.101)
Destination: 224.0.0.22 (224.0.0.22)
[Source GeoIP: Unknown]
[Destination GeoIP: Unknown]
Options: (4 bytes), Router Alert
Internet Group Management Protocol
[IGMP version: 3]
Type: Membership Report (0x22)
Header checksum: 0xe5f8 [correct]
Num Group Records: 1
Group Record : 239.1.1.1 Block Old Sources
Record Type: Block Old Sources (6)
Aux Data Len: 0
Num Src: 1
Multicast Address: 239.1.1.1 (239.1.1.1)
Source Address: 1.1.1.1 (1.1.1.1)Above, you can see that the membership report has been sent to destination 224.0.0.22. The record type is “block old sources” and includes the multicast group address and source address we no longer want to receive.
When R1 receives this packet, it will send a membership query for this specific multicast address and source address:
Frame 2: 54 bytes on wire (432 bits), 54 bytes captured (432 bits) on interface 0
Ethernet II, Src: fa:16:3e:e4:d3:de (fa:16:3e:e4:d3:de), Dst: IPv4mcast_01:01:01 (01:00:5e:01:01:01)
Internet Protocol Version 4, Src: 192.168.1.1 (192.168.1.1), Dst: 239.1.1.1 (239.1.1.1)
Version: 4
Header Length: 24 bytes
Differentiated Services Field: 0xc0 (DSCP 0x30: Class Selector 6; ECN: 0x00: Not-ECT (Not ECN-Capable Transport))
Total Length: 40
Identification: 0x2bc7 (11207)
Flags: 0x00
Fragment offset: 0
Time to live: 1
Protocol: IGMP (2)
Header checksum: 0x469d [validation disabled]
Source: 192.168.1.1 (192.168.1.1)
Destination: 239.1.1.1 (239.1.1.1)
[Source GeoIP: Unknown]
[Destination GeoIP: Unknown]
Options: (4 bytes), Router Alert
Internet Group Management Protocol
[IGMP version: 3]
Type: Membership Query (0x11)
Max Resp Time: 1,0 sec (0x0a)
Header checksum: 0xfab3 [correct]
Multicast Address: 239.1.1.1 (239.1.1.1)
QRV=2 S=Do not suppress router side processing
.... 0... = S: Do not suppress router side processing
.... .010 = QRV: 2
QQIC: 60
Num Src: 1
Source Address: 1.1.1.1 (1.1.1.1)Above, you can see the membership query from R1, which is specific for multicast group address 239.1.1.1 using source 1.1.1.1.
Want to take a look at these packet captures yourself?


Hi Hyun,
Thanks for letting me know, just fixed it.
Rene
liked the fav video
a. so this 1.1.1.1 is the IP address of video server ?
b. in today’s scenerio which igmp version is mostly used now ? is it v3 ?
c. is it correct that here HOST will be actully a router behind which we have PCs ?
d. wont it cause more over-head on client side as now they will have to configure specific IP of video server? is it feasible from scale point of view ?
thanks
Hi Abhishek,
Yes, 1.1.1.1 is the IP address of the multicast source, that could be a video server. IGMP Version 2 is probably still the most common version.
The location of your sources / hosts really depends on your network design. In a small network, it’s possible that you only see switches where the source/hosts are in the same L2 design. In larger networks, your hosts are on the access layer and the source(s) might be somewhere else, behind some router(s).
The client has to keep track of the multicast groups that it wants to receive, each client only joins
... Continue reading in our forumHello Rene,
A few questions and confusions.
- When a multicast address is being used as a group address(for example 239.1.1.1), this address is assigned to the multicast server and this address has to have route in the network design because whenever a host will encapsulate an IP packet, it will use its own address as the source and 239.1.1.1 address as the destination address. Is this correct?
- Would you also please give me a real life scenarion where multicast is used?
- In your IGMP version 3 example, 1.1.1.1 is being used as the source address. What is this add
... Continue reading in our forum